Abstract
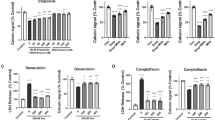
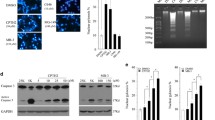
The nonselective inhibitors of class I/II histone deacetylases (HDACs) including trichostatin A and the clinically used suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA, vorinostat) are neuroprotective in several models of neuronal injury. Here, we report that in cultured cortical neurons from newborn rats and in the cerebral cortex of whole neonate rats, these HDAC inhibitors exacerbated cytotoxicity of the DNA double-strand break (DSB)-inducing anticancer drug etoposide by enhancing apoptosis. Similar neurotoxic interactions were also observed in neurons that were treated with other DNA damaging drugs including cisplatin and camptothecin. In addition, in rat neonates, SAHA increased cortical neuron apoptosis that was induced by a single injection of the NMDA receptor antagonist dizocilpine (MK801). In etoposide-treated neurons, the nonselective HDAC inhibition resulted in more DSBs. It also potentiated etoposide-induced accumulation and phosphorylation of the pro-apoptotic transcription factor p53. Moreover, nonselective HDAC inhibition exacerbated neuronal apoptosis that was induced by the overexpressed p53. Importantly, such effects cannot be fully explained by inhibition of HDAC1, which is known to play a role in DSB repair and regulation of p53. The specific HDAC1 inhibitor MS275 only moderately enhanced etoposide-induced neuronal death. Although in etoposide-treated neurons MS275 increased DSBs, it did not affect activation of p53. Our findings suggest that besides HDAC1, there are other class I/II HDACs that participate in neuronal DNA damage response attenuating neurotoxic consequences of genotoxic insults to the developing brain.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- β-gal:
-
β-Galactosidase
- BH3:
-
Bcl-2 homology domain-3
- BME:
-
Basal medium Eagle
- DIV:
-
Day in vitro
- DSB:
-
Double-strand break
- E2F1:
-
E2 promoter binding factor-1
- HAT:
-
Histone acetyltransferase
- HDACi:
-
HDAC inhibitor
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- SAHA:
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid
- SBHA:
-
Suberoyl bis-hydroxamic acid
- SSB:
-
Single-strand break
- TSA:
-
Trichostatin A
- γH2Ax:
-
Histone H2Ax variant containing the phosphorylated serine-139 residue
References
Ahles, T. A., & Saykin, A. J. (2007). Candidate mechanisms for chemotherapy-induced cognitive changes. Nature Reviews Cancer, 7(3), 192–201.
Boutillier, A. L., Trinh, E., & Loeffler, J. P. (2003). Selective E2F-dependent gene transcription is controlled by histone deacetylase activity during neuronal apoptosis. Journal of Neurochemistry, 84(4), 814–828.
Brasnjevic, I., Hof, P. R., Steinbusch, H. W., & Schmitz, C. (2008). Accumulation of nuclear DNA damage or neuron loss: Molecular basis for a new approach to understanding selective neuronal vulnerability in neurodegenerative diseases. DNA Repair (Amst), 7(7), 1087–1097.
Brochier, C., Dennis, G., Rivieccio, M. A., McLaughlin, K., Coppola, G., Ratan, R. R., et al. (2013). Specific acetylation of p53 by HDAC inhibition prevents DNA damage-induced apoptosis in neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(20), 8621–8632.
Brooks, P. J. (2008). The 8,5′-cyclospurine-2′-deoxynucleosides: Candidate neurodegenerative DNA lesions in xeroderma pigmentosum, and unique probes of transcription and nucleotide excision repair. DNA Repair (Amst), 7(7), 1168–1179.
Caldecott, K. W. (2008). Single-strand break repair and genetic disease. Nature Reviews Genetics, 9(8), 619–631.
Chen, C. S., Wang, Y. C., Yang, H. C., Huang, P. H., Kulp, S. K., Yang, C. C., et al. (2007). Histone deacetylase inhibitors sensitize prostate cancer cells to agents that produce DNA double-strand breaks by targeting Ku70 acetylation. Cancer Research, 67(11), 5318–5327.
Cherrington, J. M., & Mocarski, E. S. (1989). Human cytomegalovirus IEL transactivates the a promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. Journal of Virology, 63, 1435–1440.
Chuang, D. M., Leng, Y., Marinova, Z., Kim, H. J., & Chiu, C. T. (2009). Multiple roles of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative conditions. Trends in Neurosciences, 32(11), 591–601.
Enokido, Y., Araki, T., Tanaka, K., Aizawa, S., & Hatanaka, H. (1996). Involvement of p53 in DNA strand break-induced apoptosis in postmitotic CNS neurons. European Journal of Neuroscience, 8(9), 1812–1821.
Ganslmayer, M., Konturek, P., Herold, C., Neurath, M. F., & Zopf, S. (2012). Antitumoral efficacy of four histone deacetylase inhibitors in hepatoma in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Research, 32(12), 5263–5269.
Gaub, P., Joshi, Y., Wuttke, A., Naumann, U., Schnichels, S., Heiduschka, P., et al. (2011). The histone acetyltransferase p300 promotes intrinsic axonal regeneration. Brain, 134(Pt 7), 2134–2148.
Gozdz, A., Habas, A., Jaworski, J., Zielinska, M., Albrecht, J., Chlystun, M., et al. (2003). Role of N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptors in the neuroprotective activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 by cisplatin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(44), 43663–43671.
Graff, J., Kim, D., Dobbin, M. M., & Tsai, L. H. (2011). Epigenetic regulation of gene expression in physiological and pathological brain processes. Physiological Reviews, 91(2), 603–649.
Gu, W., & Roeder, R. G. (1997). Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal domain. Cell, 90(4), 595–606.
Habas, A., Kharebava, G., Szatmari, E., & Hetman, M. (2006). NMDA neuroprotection against a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase inhibitor, LY294002 by NR2B-mediated suppression of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta-induced apoptosis. Journal of Neurochemistry, 96(2), 335–348.
Hajji, N., Wallenborg, K., Vlachos, P., Nyman, U., Hermanson, O., & Joseph, B. (2008). Combinatorial action of the HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A and etoposide induces caspase-mediated AIF-dependent apoptotic cell death in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 27(22), 3134–3144.
Hanson, J. E., La, H., Plise, E., Chen, Y. H., Ding, X., Hanania, T., et al. (2013). SAHA enhances synaptic function and plasticity in vitro but has limited brain availability in vivo and does not impact cognition. PLoS ONE, 8(7), e69964.
Hardingham, G. E. (2006). Pro-survival signalling from the NMDA receptor. Biochemical Society Transactions, 34(Pt 5), 936–938.
Herzog, K. H., Chong, M. J., Kapsetaki, M., Morgan, J. I., & McKinnon, P. J. (1998). Requirement for Atm in ionizing radiation-induced cell death in the developing central nervous system. Science, 280(5366), 1089–1091.
Hetman, M., Kanning, K., Smith-Cavanaugh, J. E., & Xia, Z. (1999). Neuroprotection by brain-derived neurotrophic factor is mediated by extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 22569–22580.
Hetman, M., & Kharebava, G. (2006). Survival signaling pathways activated by NMDA receptors. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 6(8), 787–799.
Hetman, M., Vashishta, A., & Rempala, G. (2010). Neurotoxic mechanisms of DNA damage: focus on transcriptional inhibition. Journal of Neurochemistry, 114(6), 1537–1549.
Ikonomidou, C., Bosch, F., Miksa, M., Bittigau, P., Vockler, J., Dikranian, K., et al. (1999). Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science, 283(5398), 70–74.
Jacobs, W. B., Kaplan, D. R., & Miller, F. D. (2006). The p53 family in nervous system development and disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 97(6), 1571–1584.
Juan, L. J., Shia, W. J., Chen, M. H., Yang, W. M., Seto, E., Lin, Y. S., et al. (2000). Histone deacetylases specifically down-regulate p53-dependent gene activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(27), 20436–20443.
Kaasa, S., Olsnes, B. T., & Mastekaasa, A. (1988). Neuropsychological evaluation of patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer treated with combination chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Acta Oncologica, 27(3), 241–246.
Kalita, K., Makonchuk, D., Gomes, C., Zheng, J. J., & Hetman, M. (2008). Inhibition of nucleolar transcription as a trigger for neuronal apoptosis. Journal of Neurochemistry, 105(6), 2286–2299.
Kannarkat, G., Lasher, E. E., & Schiff, D. (2007). Neurologic complications of chemotherapy agents. Current Opinion in Neurology, 20(6), 719–725.
Katyal, S., & McKinnon, P. J. (2008). DNA strand breaks, neurodegeneration and aging in the brain. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 129(7–8), 483–491.
Kelly, W. K., O’Connor, O. A., Krug, L. M., Chiao, J. H., Heaney, M., Curley, T., et al. (2005). Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23(17), 3923–3931.
Keramaris, E., Hirao, A., Slack, R. S., Mak, T. W., & Park, D. S. (2003). Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated protein can regulate p53 and neuronal death independent of Chk2 in response to DNA damage. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(39), 37782–37789.
Khan, N., Jeffers, M., Kumar, S., Hackett, C., Boldog, F., Khramtsov, N., et al. (2008). Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochemical Journal, 409(2), 581–589.
Kim, M. S., Blake, M., Baek, J. H., Kohlhagen, G., Pommier, Y., & Carrier, F. (2003). Inhibition of histone deacetylase increases cytotoxicity to anticancer drugs targeting DNA. Cancer Research, 63(21), 7291–7300.
Kim, D., Frank, C. L., Dobbin, M. M., Tsunemoto, R. K., Tu, W., Peng, P. L., et al. (2008). Deregulation of HDAC1 by p25/Cdk5 in neurotoxicity. Neuron, 60(5), 803–817.
Kinner, A., Wu, W., Staudt, C., & Iliakis, G. (2008). Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Research, 36(17), 5678–5694.
Kruman, I. I., Wersto, R. P., Cardozo-Pelaez, F., Smilenov, L., Chan, S. L., Chrest, F. J., et al. (2004). Cell cycle activation linked to neuronal cell death initiated by DNA damage. Neuron, 41(4), 549–561.
Lahue, R. S., & Frizzell, A. (2012). Histone deacetylase complexes as caretakers of genome stability. Epigenetics, 7(8), 806–810.
Langley, B., D’Annibale, M. A., Suh, K., Ayoub, I., Tolhurst, A., Bastan, B., et al. (2008). Pulse inhibition of histone deacetylases induces complete resistance to oxidative death in cortical neurons without toxicity and reveals a role for cytoplasmic p21(waf1/cip1) in cell cycle-independent neuroprotection. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(1), 163–176.
Lin, H. S., Hu, C. Y., Chan, H. Y., Liew, Y. Y., Huang, H. P., Lepescheux, L., et al. (2007). Anti-rheumatic activities of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in vivo in collagen-induced arthritis in rodents. Brit J Pharmacol, 150(7), 862–872.
Liu, D. X., Nath, N., Chellappan, S. P., & Greene, L. A. (2005). Regulation of neuron survival and death by p130 and associated chromatin modifiers. Genes & Development, 19(6), 719–732.
Lu, T., Pan, Y., Kao, S. Y., Li, C., Kohane, I., Chan, J., et al. (2004). Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature, 429(6994), 883–891.
Luo, J., Su, F., Chen, D., Shiloh, A., & Gu, W. (2000). Deacetylation of p53 modulates its effect on cell growth and apoptosis. Nature, 408(6810), 377–381.
Markesbery, W. R., & Lovell, M. A. (2006). DNA oxidation in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 8(11–12), 2039–2045.
Marks, P. A., & Xu, W. S. (2009). Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Potential in cancer therapy. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 107(4), 600–608.
Martin, L. J., Liu, Z., Pipino, J., Chestnut, B., & Landek, M. A. (2009). Molecular regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in neurons of cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 19(6), 1273–1293.
McCann, M. E., & Soriano, S. G. (2012). General anesthetics in pediatric anesthesia: Influences on the developing brain. Current Drug Targets, 13(7), 944–951.
Michalovitz, D., Halevy, O., & Oren, M. (1990). Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell, 62(4), 671–680.
Miller, K. M., Tjeertes, J. V., Coates, J., Legube, G., Polo, S. E., Britton, S., et al. (2010). Human HDAC1 and HDAC2 function in the DNA-damage response to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 17(9), 1144–1151.
Mok, T. S., Lam, K. C., Lee, C., Zhang, L., Wong, H., Chan, A. T., et al. (2005). Phase II randomized study comparing the toxicity profile of gemcitabine plus cisplatin with gemcitabine plus oral etoposide in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology., 68(4–6), 485–492.
Morris, E. J., & Geller, H. M. (1996). Induction of neuronal apoptosis by camptothecin, an inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase-I: Evidence for cell cycle-independent toxicity. Journal of Cell Biology, 134(3), 757–770.
Morrison, R. S., & Kinoshita, Y. (2000). The role of p53 in neuronal cell death. Cell Death and Differentiation, 7(10), 868–879.
Niedernhofer, L. J. (2008). Nucleotide excision repair deficient mouse models and neurological disease. DNA Repair (Amst), 7(7), 1180–1189.
Nitiss, J. L. (2009). Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 9(5), 338–350.
Oehme, I., Deubzer, H. E., Wegener, D., Pickert, D., Linke, J. P., Hero, B., et al. (2009). Histone deacetylase 8 in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. Clinical Cancer Research, 15(1), 91–99.
Papadia, S., Soriano, F. X., Leveille, F., Martel, M. A., Dakin, K. A., Hansen, H. H., et al. (2008). Synaptic NMDA receptor activity boosts intrinsic antioxidant defenses. Nature Neuroscience, 11(4), 476–487.
Pietrzak, M., Smith, S. C., Geralds, J. T., Hagg, T., Gomes, C., & Hetman, M. (2011). Nucleolar disruption and apoptosis are distinct neuronal responses to etoposide-induced DNA damage. Journal of Neurochemistry, 117(6), 1033–1046.
Pufahl, L., Katryniok, C., Schnur, N., Sorg, B. L., Metzner, J., Grez, M., et al. (2012). Trichostatin A induces 5-lipoxygenase promoter activity and mRNA expression via inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 and 3. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 16(7), 1461–1473.
Raz, L., Zhang, Q. G., Han, D., Dong, Y., De Sevilla, L., & Brann, D. W. (2011). Acetylation of the pro-apoptotic factor, p53 in the hippocampus following cerebral ischemia and modulation by estrogen. PLoS ONE, 6(10), e27039.
Riva, D., Massimino, M., Giorgi, C., Nichelli, F., Erbetta, A., Usilla, A., et al. (2009). Cognition before and after chemotherapy alone in children with chiasmatic-hypothalamic tumors. Journal of Neuro-oncology, 92(1), 49–56.
Robaey, P., Krajinovic, M., Marcoux, S., & Moghrabi, A. (2008). Pharmacogenetics of the neurodevelopmental impact of anticancer chemotherapy. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 14(3), 211–220.
Robert, T., Vanoli, F., Chiolo, I., Shubassi, G., Bernstein, K. A., Rothstein, R., et al. (2011). HDACs link the DNA damage response, processing of double-strand breaks and autophagy. Nature, 471(7336), 74–79.
Salminen, A., Tapiola, T., Korhonen, P., & Suuronen, T. (1998). Neuronal apoptosis induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research, 61(1–2), 203–206.
Suberbielle, E., Sanchez, P. E., Kravitz, A. V., Wang, X., Ho, K., Eilertson, K., et al. (2013). Physiologic brain activity causes DNA double-strand breaks in neurons, with exacerbation by amyloid-beta. Nature Neuroscience, 16(5), 613–621.
Tang, Y., Zhao, W., Chen, Y., Zhao, Y., & Gu, W. (2008). Acetylation is indispensable for p53 activation. Cell, 133(4), 612–626.
Terui, T., Murakami, K., Takimoto, R., Takahashi, M., Takada, K., Murakami, T., et al. (2003). Induction of PIG3 and NOXA through acetylation of p53 at 320 and 373 lysine residues as a mechanism for apoptotic cell death by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Research, 63(24), 8948–8954.
Uo, T., Veenstra, T. D., & Morrison, R. S. (2009). Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent p53-dependent and p53-independent Bax-mediated neuronal apoptosis through two distinct mechanisms. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(9), 2824–2832.
Wallace, D. M., & Cotter, T. G. (2009). Histone deacetylase activity in conjunction with E2F-1 and p53 regulates Apaf-1 expression in 661 W cells and the retina. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 87(4), 887–905.
Whitney, K. A., Lysaker, P. H., Steiner, A. R., Hook, J. N., Estes, D. D., & Hanna, N. H. (2008). Is”chemobrain” a transient state? A prospective pilot study among persons with non-small cell lung cancer. The Journal of Supportive Oncology, 6(7), 313–321.
Wright, K. M., Smith, M. I., Farrag, L., & Deshmukh, M. (2007). Chromatin modification of Apaf-1 restricts the apoptotic pathway in mature neurons. Journal of Cell Biology, 179(5), 825–832.
Xiang, H., Kinoshita, Y., Knudson, C. M., Korsmeyer, S. J., Schwartzkroin, P. A., & Morrison, R. S. (1998). Bax involvement in p53-mediated neuronal cell death. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(4), 1363–1373.
Zhang, J., Kan, S., Huang, B., Hao, Z., Mak, T. W., & Zhong, Q. (2011). Mule determines the apoptotic response to HDAC inhibitors by targeted ubiquitination and destruction of HDAC2. Genes & Development, 25(24), 2610–2618.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH (NS073584 and 8P30GM103507 to MH), NSF (IOS1021860 to MH), and the Commonwealth of Kentucky Challenge for Excellence Fund. The authors wish to thank Ms. Jing-Juan Zheng for excellent technical assistance and Mr. Justin Hallgren for critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Authors do not have any conflict of interest concerning this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vashishta, A., Hetman, M. Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases Enhance Neurotoxicity of DNA Damage. Neuromol Med 16, 727–741 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8322-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8322-x