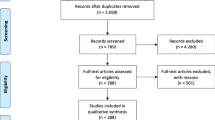
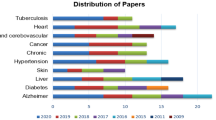
Abstract
Biomedical research has long relied on animal models to unravel the intricacies of human physiology and pathology. However, concerns surrounding ethics, expenses, and inherent species differences have catalyzed the exploration of alternative avenues. The contemporary alternatives to traditional animal models in biomedical research delve into three main categories of alternative approaches: in vitro models, in vertebrate models, and in silico models. This unique approach to artificial intelligence and machine learning has been a keen interest to be used in different biomedical research. The main goal of this review is to serve as a guide to researchers seeking novel avenues for their investigations and underscores the importance of considering alternative models in the pursuit of scientific knowledge and medical breakthroughs, including showcasing the broad spectrum of modern approaches that are revolutionizing biomedical research and leading the way toward a more ethical, efficient, and innovative future. Models can insight into cellular processes, developmental biology, drug interaction, assessing toxicology, and understanding molecular mechanisms.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available upon request from reviewers or editors.
Code Availability
Not Applicable.
References
Abdullah, K. A. L., Atazhanova, T., Chavez-Badiola, A., & Shivhare, S. B. (2023). Automation in ART: Paving the way for the future of infertility treatment. Reproductive Sciences, 30, 1006–1016.
Acarli, D., Semih, K., & Ali, K. (2019). New alternative fishing gear suggestions for trap fisheries from the waste recycle materials: Case study for Muricidae (Mollusca: Gastropoda). Marine Science and Technology Bulletin, 8, 92–97.
Afshar, L., Aghayan, H. R., Sadighi, J., Arjmand, B., Hashemi, S. M., Basiri, M., Samani, R. O., Ashtiani, M. K., Azin, S. A., Hajizadeh-Saffar, E., et al. (2020). Ethics of research on stem cells and regenerative medicine: Ethical guidelines in the Islamic Republic of Iran. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 11, 396. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01916-z
Agarrayua, D. A., Funguetto-Ribeiro, A. C., Trevisan, P., Haas, S. E., & Ávila, D. S. (2023). Safety assessment of different unloaded polymeric nanocapsules in Caenorhabditis elegans. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 263, 109477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109477
Andersen, M. L., & Winter, L. M. (2017). Animal models in biological and biomedical research-experimental and ethical concerns. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 91, e20170238.
Ansorge, M., & Pompe, T. (2018). Systems for localized release to mimic paracrine cell communication in vitro. Journal of Controlled Release, 278, 24–36.
Ashammakhi, N., GhavamiNejad, A., Tutar, R., Fricker, A., Roy, I., Chatzistavrou, X., HoqueApu, E., Nguyen, K.-L., Ahsan, T., & Pountos, I. (2022). Highlights on advancing frontiers in tissue engineering. Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews, 28, 633–664.
Athanasopoulou, K., Daneva, G. N., Adamopoulos, P. G., & Scorilas, A. (2022). Artificial Intelligence: The Milestone in Modern Biomedical Research. BioMedInformatics, 2, 727–744.
Azeloglu, E. U., & Iyengar, R. (2015). Signaling networks: Information flow, computation, and decision making. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 7, a005934.
Bailone, R. L., Fukushima, H. C. S., Ventura Fernandes, B. H., De Aguiar, L. K., Corrêa, T., Janke, H., GrejoSetti, P., Roça, R. D. O., & Borra, R. C. (2020). Zebrafish as an alternative animal model in human and animal vaccination research. Laboratory Animal Research, 36, 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42826-020-00042-4
Banach, M., & Robert, J. (2017). Tumor immunology viewed from alternative animal models—the xenopus story. Current Pathobiology Reports, 5, 49–56.
Bédard, P., Gauvin, S., Ferland, K., Caneparo, C., Pellerin, È., Chabaud, S., & Bolduc, S. (2020). Innovative human three-dimensional tissue-engineered models as an alternative to animal testing. Bioengineering (Basel), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030115
Benam, K. H., Gilchrist, S., Kleensang, A., Satz, A. B., Willett, C., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Exploring new technologies in biomedical research. Drug Discovery Today, 24, 1242–1247.
Borba, J. V., Alves, V. M., Braga, R. C., Korn, D. R., Overdahl, K., Silva, A. C., Hall, S. U., Overdahl, E., Kleinstreuer, N., & Strickland, J. (2022). STopTox: An in silico alternative to animal testing for acute systemic and topical toxicity. Environmental Health Perspectives, 130, 027012.
Borba, J. V. B., Braga, R. C., Alves, V. M., Muratov, E. N., Kleinstreuer, N., Tropsha, A., & Andrade, C. H. (2021). Pred-skin: A web portal for accurate prediction of human skin sensitizers. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 34, 258–267. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00186
Bovard, D., Sandoz, A., Luettich, K., Frentzel, S., Iskandar, A., Marescotti, D., Trivedi, K., Guedj, E., Dutertre, Q., & Peitsch, M. C. (2018). A lung/liver-on-a-chip platform for acute and chronic toxicity studies. Lab on a Chip, 18, 3814–3829.
Bray, A., Webb, J. B., Enquobahrie, A., Vicory, J., Heneghan, J., Hubal, R., TerMaath, S., Asare, P., & Clipp, R. B. (2019). Pulse physiology engine: An open-source software platform for computational modeling of human medical simulation. SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine, 1, 362–377.
Chen, T., Shu, X., Zhou, H., Beckford, F. A., & Misir, M. (2023). Algorithm selection for protein–ligand docking: Strategies and analysis on ACE. Scientific Reports, 13, 8219. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35132-5
Chen, Y.-W., Huang, S. X., de Carvalho, A. L. R. T., Ho, S.-H., Islam, M. N., Volpi, S., Notarangelo, L. D., Ciancanelli, M., Casanova, J.-L., Bhattacharya, J., et al. (2017). A three-dimensional model of human lung development and disease from pluripotent stem cells. Nature Cell Biology, 19, 542–549. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3510
Cho, Y. W., Min, D. W., Kim, H. P., An, Y., Kim, S., Youk, J., Chun, J., Im, J. P., Song, S. H., & Ju, Y. S. (2022). Patient-derived organoids as a preclinical platform for precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Molecular Oncology, 16, 2396–2412.
Chou, W.-C., Chen, Q., Yuan, L., Cheng, Y.-H., He, C., Monteiro-Riviere, N. A., Riviere, J. E., & Lin, Z. (2023). An artificial intelligence-assisted physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model to predict nanoparticle delivery to tumors in mice. Journal of Controlled Release, 361, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.07.040
Choudhury, D. R., Chowdhury, S., Talukdar, P., & Talapatra, S. (2021). In-silico study of toxicity mechanisms for metabolites of phyto-compounds from musa sp. compared to synthetic medicine ranitidine. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 12, 1521–1528.
Chu, P.-Y., Koh, A.P.-F., Antony, J., & Huang, R.Y.-J. (2022). Applications of the chick chorioallantoic membrane as an alternative model for cancer studies. Cells, Tissues, Organs, 211, 222–237.
Ciallella, H. L., Russo, D. P., Aleksunes, L. M., Grimm, F. A., & Zhu, H. (2021). Revealing adverse outcome pathways from public high-throughput screening data to evaluate new toxicants by a knowledge-based deep neural network approach. Environmental Science & Technology, 55, 10875–10887.
Davison, A., & Neiman, M. (2021). Mobilizing molluscan models and genomes in biology. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 376, 20200163.
de Cristo Soares Alves, A., RosaneDallemole, D., MedeiroCiocheta, T., Ferreira Weber, A., da Silva Gündel, S., Visioli, F., Figueiró, F., StanisçuaskiGuterres, S., & Raffin Pohlmann, A. (2023). Chicken embryo model for in vivo acute toxicological and antitumor efficacy evaluation of lipid nanocarrier containing doxorubicin. International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X, 6, 100193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpx.2023.100193
de Souza, A. M., Araujo-Silva, H., Costa, A. M., Rossi, A. L., Rossi, A. M., Granjeiro, J. M., Luchiari, A. C., & Batistuzzo de Medeiros, S. R. (2023). Embryotoxicity and visual-motor response of functionalized nanostructured hydroxyapatite-based biomaterials in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere, 313, 137519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137519
Dotti, I., & Salas, A. (2018). Potential use of human stem cell–derived intestinal organoids to study inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 24, 2501–2509.
Dudley, J. T., Deshpande, T., & Butte, A. J. (2011). Exploiting drug–disease relationships for computational drug repositioning. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 12, 303–311.
Elemento, O., Leslie, C., Lundin, J., & Tourassi, G. (2021). Artificial intelligence in cancer research, diagnosis and therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 21, 747–752. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00399-1
Esmaeilbeigi, M., BehzadiTayemeh, M., Johari, S. A., Ghorbani, F., Sourinejad, I., & Yu, I. J. (2022). In silico modeling of the antagonistic effect of mercuric chloride and silver nanoparticles on the mortality rate of zebrafish (Danio rerio) based on response surface methodology. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 54733–54744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19693-y
Fabre, K. M., Livingston, C., & Tagle, D. A. (2014). Organs-on-chips (microphysiological systems): Tools to expedite efficacy and toxicity testing in human tissue. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 239, 1073–1077.
Fentem, J. H. (2023). The 19th FRAME annual lecture, November 2022: Safer chemicals and sustainable innovation will be achieved by regulatory use of modern safety science, not by more animal testing. Alternatives to Laboratory Animals, 51, 90–101.
Fetah, K., Tebon, P., Goudie, M. J., Eichenbaum, J., Ren, L., Barros, N., Nasiri, R., Ahadian, S., Ashammakhi, N., & Dokmeci, M. R. (2019). The emergence of 3D bioprinting in organ-on-chip systems. Progress in Biomedical Engineering, 1, 012001.
Gan, J., Bolon, B., Van Vleet, T., & Wood, C. (2022). Alternative models in biomedical research: In silico, in vitro, ex vivo, and nontraditional in vivo approaches. In Haschek and Rousseaux's handbook of toxicologic pathology (pp. 925–966). Elsevier.
Gearty, A. J., Ignoffo, T. R., Slaughter, A. M., & Kimmerer, W. J. (2021). Growth and reproductive rates of the dominant copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi in response to environmental factors and habitat type in the northern San Francisco Estuary. Aquatic Ecology, 55, 825–848.
Germany, E. M., Zahayko, N., & Khalimonchuk, O. (2019). Isolation of specific neuron populations from roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments), e60145. https://doi.org/10.3791/60145
Gilbert-Sandoval, I., Wesseling, S., & Rietjens, I. M. (2020). Predicting the acute liver toxicity of aflatoxin B1 in rats and humans by an in vitro–in silico testing strategy. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 64, 2000063.
Gimondi, S., Ferreira, H., Reis, R. L., & Neves, N. M. (2023). Microfluidic devices: A tool for nanoparticle synthesis and performance evaluation. ACS Nano, 17, 14205–14228.
Hasan, R., Herowati, R., & Widodo, G. P. (2023). Molecular docking and pharmacokinetic prediction of potential compounds from luffa acutangula as antidiabetic candidates. PHARMACY: Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia (Pharmaceutical Journal of Indonesia), 20, 71–76.
Heikkinen, A. T., Baneyx, G., Caruso, A., & Parrott, N. (2012). Application of PBPK modeling to predict human intestinal metabolism of CYP3A substrates–an evaluation and case study using GastroPlus™. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 47, 375–386.
Herrmann, K., Pistollato, F., & Stephens, M. L. (2019). Beyond the 3Rs: Expanding the use of human-relevant replacement methods in biomedical research. ALTEX-Alternatives to Animal Experimentation, 36, 343–352.
Hoffmann, P., Schnepel, N., Langeheine, M., Künnemann, K., Grassl, G. A., Brehm, R., Seeger, B., Mazzuoli-Weber, G., & Breves, G. (2021). Intestinal organoid-based 2D monolayers mimic physiological and pathophysiological properties of the pig intestine. PLoS ONE, 16, e0256143. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256143
Huang, C., Sanaei, F., Verdurmen, W. P. R., Yang, F., Ji, W., & Walboomers, X. F. (2023). The application of organs-on-a-chip in dental, oral, and craniofacial research. Journal of Dental Research, 102, 364–375. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345221145555
Huang, H.-J., Lee, Y.-H., Hsu, Y.-H., Liao, C.-T., Lin, Y.-F., & Chiu, H.-W. (2021). Current strategies in assessment of nanotoxicity: Alternatives to in vivo animal testing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 4216.
Hwang, S.-H., Lee, S., Park, J. Y., Jeon, J. S., Cho, Y.-J., & Kim, S. (2021). Potential of drug efficacy evaluation in lung and kidney cancer models using organ-on-a-chip technology. Micromachines, 12, 215.
Ingber, D. E. (2022). Human organs-on-chips for disease modelling, drug development and personalized medicine. Nature Reviews Genetics, 23, 467–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-022-00466-9
Ishwarya, R., Tamilmani, G., Jayakumar, R., Albeshr, M. F., Mahboob, S., Shahid, D., Riaz, M. N., Govindarajan, M., & Vaseeharan, B. (2023). Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Vigna mungo seed husk extract: An enhanced antibacterial, anticancer activity and eco-friendly bio-toxicity assessment on algae and zooplankton. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 79, 104002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.104002
Johnson, K. B., Wei, W. Q., Weeraratne, D., Frisse, M. E., Misulis, K., Rhee, K., Zhao, J., & Snowdon, J. L. (2021). Precision medicine, AI, and the future of personalized health care. Clinical and Translational Science, 14, 86–93.
Kammala, A. K., Richardson, L. S., Radnaa, E., Han, A., & Menon, R. (2023). Microfluidic technology and simulation models in studying pharmacokinetics during pregnancy. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 14, 1241815. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1241815
Khabib, M. N. H., Sivasanku, Y., Lee, H. B., Kumar, S., & Kue, C. S. (2022). Alternative animal models in predictive toxicology. Toxicology, 465, 153053.
Khan, P. M., & Roy, K. (2018). Current approaches for choosing feature selection and learning algorithms in quantitative structure–activity relationships (QSAR). Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 13, 1075–1089.
Koning, J. J., Rodrigues Neves, C. T., Schimek, K., Thon, M., Spiekstra, S. W., Waaijman, T., de Gruijl, T. D., & Gibbs, S. (2021). A multi-organ-on-chip approach to investigate how oral exposure to metals can cause systemic toxicity leading to langerhans cell activation in skin. Frontiers in Toxicology, 3, 824825. https://doi.org/10.3389/ftox.2021.824825
Krishna, S., Borrel, A., Huang, R., Zhao, J., Xia, M., & Kleinstreuer, N. (2022). High-throughput chemical screening and structure-based models to predict hERG inhibition. Biology, 11, 209.
Laksanasopin, T., Chin, C. D., Moore, H., Wang, J., Cheung, Y. K., & Sia, S. K. (2009). Microfluidic point-of-care diagnostics for resource-poor environments. IEEE, 1057–1059,. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5334942
Lee, H. J., Mun, S. J., Jung, C. R., Kang, H. M., Kwon, J. E., Ryu, J. S., Ahn, H. S., Kwon, O. S., Ahn, J., & Moon, K. S. (2023). In vitro modeling of liver fibrosis with 3D co-culture system using a novel human hepatic stellate cell line. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 120, 1241–1253.
Lee, J., Kim, J.-H., Hong, S.-H., & Yang, S.-R. (2021). Organoid model in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. International Journal of Stem Cells, 14, 1–8.
Lee, S. Y., Kang, J. H., Jeong, J. W., Kim, J. H., Kim, H. W., Oh, D. H., Kim, J.-M., Rhim, S.-J., Kim, G.-D., & Kim, H. S. (2022). Alternative experimental approaches to reduce animal use in biomedical studies. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 68, 103131.
Li, W., Zhou, Z., Zhou, X., Khoo, B. L., Gunawan, R., Chin, Y. R., Zhang, L., Yi, C., Guan, X., & Yang, M. (2023). 3D biomimetic models to reconstitute tumor microenvironment in vitro: Spheroids, organoids, and tumor-on-a-chip. Advanced Healthcare Materials. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202202609
Li, Z., Xu, H., Yu, L., Wang, J., Meng, Q., Mei, H., Cai, Z., Chen, W., & Huang, W. (2022). Patient-derived renal cell carcinoma organoids for personalized cancer therapy. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 12, e970. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.970
Liang, L., Li, W., Zhang, Z., Li, D., Pu, S., Xiang, R., & Zhai, F. (2023). Develop adult extrapolation to pediatrics and pediatric dose optimization based on the physiological pharmacokinetic model of azithromycin. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition., 4, 245–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2352
Lipinski, C. F., Maltarollo, V. G., Oliveira, P. R., Da Silva, A. B., & Honorio, K. M. (2019). Advances and perspectives in applying deep learning for drug design and discovery. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 6, 108.
Liu, Z., Cai, Y., Liao, Z., Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Jiang, X., Li, Y., Lu, Y., Nie, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2019). Cloning of a gene edited macaque monkey by somatic cell nuclear transfer. National Science Review, 6, 101–108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz003
Low, L. A., Mummery, C., Berridge, B. R., Austin, C. P., & Tagle, D. A. (2021). Organs-on-chips: Into the next decade. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 20, 345–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-0079-3
Ly, K. L., Rooholghodos, S. A., Rahimi, C., Rahimi, B., Bienek, D. R., Kaufman, G., Raub, C. B., & Luo, X. (2021). An Oral-mucosa-on-a-chip sensitively evaluates cell responses to dental monomers. Biomedical Microdevices, 23, 7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00543-6
Ma, C., Peng, Y., Li, H., & Chen, W. (2021). Organ-on-a-chip: A new paradigm for drug development. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 42, 119–133.
Madden, J. C., Enoch, S. J., Paini, A., & Cronin, M. T. D. (2020). A review of in silico tools as alternatives to animal testing: Principles, resources and applications. Alternatives to Laboratory Animals, 48, 146–172. https://doi.org/10.1177/0261192920965977
Mansouri, K., Cariello, N. F., Korotcov, A., Tkachenko, V., Grulke, C. M., Sprankle, C. S., Allen, D., Casey, W. M., Kleinstreuer, N. C., & Williams, A. J. (2019). Open-source QSAR models for pKa prediction using multiple machine learning approaches. Journal of Cheminformatics, 11, 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-019-0384-1
Mansouri, K., Grulke, C. M., Judson, R. S., & Williams, A. J. (2018). OPERA models for predicting physicochemical properties and environmental fate endpoints. Journal of Cheminformatics, 10, 1–19.
Mansouri, K., Kleinstreuer, N., Abdelaziz, A. M., Alberga, D., Alves, V. M., Andersson, P. L., Andrade, C. H., Bai, F., Balabin, I., & Ballabio, D. (2020). CoMPARA: Collaborative modeling project for androgen receptor activity. Environmental Health Perspectives, 128, 027002.
Menegola, E., Battistoni, M., Metruccio, F., & Di Renzo, F. (2023). Advantages and disadvantages of the use of Xenopus laevis embryos and Zebra fish as alternative methods to assess teratogens. Current Opinion in Toxicology, 34, 100387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2023.100387
Mukherjee, P., Roy, S., Ghosh, D., & Nandi, S. (2022). Role of animal models in biomedical research: A review. Laboratory Animal Research, 38, 18.
Noben, M., Verstockt, B., de Bruyn, M., Hendriks, N., Van Assche, G., Vermeire, S., Verfaillie, C., & Ferrante, M. (2017). Epithelial organoid cultures from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease: A truly long-term model to study the molecular basis for inflammatory bowel disease? Gut, 66, 2193–2195.
Ouchi, R., Togo, S., Kimura, M., Shinozawa, T., Koido, M., Koike, H., Thompson, W., Karns, R. A., Mayhew, C. N., & McGrath, P. S. (2019). Modeling steatohepatitis in humans with pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids. Cell Metabolism, 30, 374-384. e376.
Pagadala, N. S., Syed, K., & Tuszynski, J. (2017). Software for molecular docking: A review. Biophysical Reviews, 9, 91–102.
Paiola, M., Dimitrakopoulou, D., Pavelka, M. S., & Robert, J. (2023). Amphibians as a model to study the role of immune cell heterogeneity in host and mycobacterial interactions. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 139, 104594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2022.104594
Panteleev, J., Gao, H., & Jia, L. (2018). Recent applications of machine learning in medicinal chemistry. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 28, 2807–2815.
Pappalardo, F., Russo, G., Tshinanu, F. M., & Viceconti, M. (2018). In silico clinical trials: Concepts and early adoptions. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 20, 1699–1708. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bby043
Paramasivam, S., & Perumal, S. S. (2023). In silico rationalization for leads from Oldenlandia umbellata L. to inhibit multiple molecular targets regulating osteoporosis. Pharmacognosy Magazine, 09731296231196189. https://doi.org/10.1177/09731296231196189
Park, C., Took, C. C., & Seong, J.-K. (2018). Machine learning in biomedical engineering. Biomedical Engineering Letters, 8, 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-018-0058-3
Park, T.-E., Mustafaoglu, N., Herland, A., Hasselkus, R., Mannix, R., FitzGerald, E. A., Prantil-Baun, R., Watters, A., Henry, O., & Benz, M. (2019). Hypoxia-enhanced Blood-Brain Barrier Chip recapitulates human barrier function and shuttling of drugs and antibodies. Nature Communications, 10, 2621.
Pawar, G., Wu, F., Zhao, L., Fang, L., Burckart, G. J., Feng, K., Mousa, Y. M., Al Shoyaib, A., Jones, M.-C., & Batchelor, H. K. (2023). Integration of biorelevant pediatric dissolution methodology into PBPK Modeling to predict in vivo performance and bioequivalence of generic drugs in pediatric populations: A Carbamazepine case study. The AAPS Journal, 25, 67. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-023-00826-1
Priyadarshini, S., & Pati, S. (2023). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus and its antibacterial properties. Applied Nanoscience, 13, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-023-02900-8
Rai, J., & Kaushik, K. (2018). Reduction of animal sacrifice in biomedical science & research through alternative design of animal experiments. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 26, 896–902.
Raies, A. B., & Bajic, V. B. (2016). In silico toxicology: Computational methods for the prediction of chemical toxicity. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science, 6, 147–172.
Rani, N., Alam, M. M., Jamal, A., Bin Ghaffar, U., & Parvez, S. (2023). Caenorhabditis elegans: A transgenic model for studying age-associated neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Research Reviews, 91, 102036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2023.102036
Rao, M. S., Gupta, R., Liguori, M. J., Hu, M., Huang, X., Mantena, S. R., Mittelstadt, S. W., Blomme, E. A., & Van Vleet, T. R. (2019). Novel computational approach to predict off-target interactions for small molecules. Frontiers in Big Data, 2, 25.
Rikhtegar, R., Pezeshkian, M., Dolati, S., Safaie, N., Afrasiabi Rad, A., Mahdipour, M., Nouri, M., Jodati, A. R., & Yousefi, M. (2019). Stem cells as therapy for heart disease: IPSCs, ESCs, CSCs, and skeletal myoblasts. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 109, 304–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.065
Rudrapal, M., Khairnar, S. J., & Jadhav, A. G. (2020). Drug repurposing (DR): An emerging approach in drug discovery. Drug repurposing-hypothesis, molecular aspects and therapeutic applications (10). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.93193
Saavedra, L. M., Martinez, J. C. G., & Duchowicz, P. R. (2024). Advances of the QSAR approach as an alternative strategy in the environmental risk assessment. In QSAR in safety evaluation and risk assessment (pp. 117–137). Elsevier.
Saeidnia, S., Manayi, A., & Abdollahi, M. (2015). From in vitro experiments to in vivo and clinical studies; pros and cons. Current drug discovery technologies, 12, 218–224.
Sakai, Y., Matsumura, M., Yamada, H., Doi, A., Saito, I., Iwao, T., & Matsunaga, T. (2023). Development of a perfusing small intestine – liver microphysiological system device. Applied Sciences, 13, 10510.
Sardanelli, F., Castiglioni, I., Colarieti, A., Schiaffino, S., & Di Leo, G. (2023). Artificial intelligence (AI) in biomedical research: Discussion on authors’ declaration of AI in their articles title. European Radiology Experimental, 7, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41747-022-00316-7
Seaman, K., Sun, Y., & You, L. (2023). Recent advances in cancer-on-a-chip tissue models to dissect the tumour microenvironment. Med-X, 1, 11.
Sharmin, S., Islam, M. B., Saha, B. K., Ahmed, F., Maitra, B., Rasel, M. Z. U., Quaisaar, N., & Rabbi, M. A. (2023). Evaluation of antibacterial activity, in-vitro cytotoxicity and catalytic activity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Leea macrophylla. Heliyon, 9, E20810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20810
Shrestha, J., Razavi Bazaz, S., AboulkheyrEs, H., Yaghobian Azari, D., Thierry, B., EbrahimiWarkiani, M., & Ghadiri, M. (2020). Lung-on-a-chip: The future of respiratory disease models and pharmacological studies. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 40, 213–230.
Singh, A. V., Ansari, M. H. D., Rosenkranz, D., Maharjan, R. S., Kriegel, F. L., Gandhi, K., Kanase, A., Singh, R., Laux, P., & Luch, A. (2020). Artificial intelligence and machine learning in computational nanotoxicology: Unlocking and empowering nanomedicine. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 9, 1901862.
Singh, A. V., Rosenkranz, D., Ansari, M. H. D., Singh, R., Kanase, A., Singh, S. P., Johnston, B., Tentschert, J., Laux, P., & Luch, A. (2020). Artificial intelligence and machine learning empower advanced biomedical material design to toxicity prediction. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2, 2000084.
Smits, L. M., Reinhardt, L., Reinhardt, P., Glatza, M., Monzel, A. S., Stanslowsky, N., Rosato-Siri, M. D., Zanon, A., Antony, P. M., Bellmann, J., et al. (2019). Modeling Parkinson’s disease in midbrain-like organoids. npj Parkinson’s Disease, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-019-0078-4
Soni, A. N., Varshney, M., & Tale, V. S. (2023). Molecular docking and pharmacodynamic study of potential inhibitors of streptococcus mutans biofilm. Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal (BBRJ), 7, 471–477. https://doi.org/10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_176_23
Stern, N., Gacs, A., Tátrai, E., Flachner, B., Hajdú, I., Dobi, K., Bágyi, I., Dormán, G., Lőrincz, Z., Cseh, S., et al. (2022). Dual inhibitors of AChE and BACE-1 for reducing Aβ in Alzheimer’s disease: From in silico to in vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 13098.
Sulimov, V. B., Kutov, D. C., & Sulimov, A. V. (2019). Advances in docking. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 26, 7555–7580.
Sundarakrishnan, A., Chen, Y., Black, L. D., Aldridge, B. B., & Kaplan, D. L. (2018). Engineered cell and tissue models of pulmonary fibrosis. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 129, 78–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.12.013
Takla, T. N., Luo, J., Sudyk, R., Huang, J., Walker, J. C., Vora, N. L., Sexton, J. Z., Parent, J. M., & Tidball, A. M. (2023). A Shared pathogenic mechanism for valproic acid and SHROOM3 knockout in a brain organoid model of neural tube defects. Cells, 12, 1697.
Testai, E., Bechaux, C., Buratti, F. M., Darney, K., Di Consiglio, E., Kasteel, E. E., Kramer, N. I., Lautz, L. S., Santori, N., & Skaperda, Z. V. (2021). Modelling human variability in toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic processes using Bayesian meta-analysis, physiologically-based modelling and in vitro systems. EFSA Supporting Publications, 18, 6504E.
Thakur, A., Mishra, A. P., Panda, B., Rodríguez, D., Gaurav, I., & Majhi, B. (2020). Application of artificial intelligence in pharmaceutical and biomedical studies. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 26, 3569–3578.
Unagolla, J. M., & Jayasuriya, A. C. (2022). Recent advances in organoid engineering: A comprehensive review. Applied Materials Today, 29, 101582.
Urzì, O., Gasparro, R., Costanzo, E., De Luca, A., Giavaresi, G., Fontana, S., & Alessandro, R. (2023). Three-dimensional cell cultures: The bridge between in vitro and in vivo models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24, 12046.
Van Norman, G. A. (2020). Limitations of animal studies for predicting toxicity in clinical trials: Part 2: Potential alternatives to the use of animals in preclinical trials. Basic to Translational Science, 5, 387–397.
Villenave, R., Wales, S. Q., Hamkins-Indik, T., Papafragkou, E., Weaver, J. C., Ferrante, T. C., Bahinski, A., Elkins, C. A., Kulka, M., & Ingber, D. E. (2017). Human gut-on-a-chip supports polarized infection of coxsackie B1 virus in vitro. PLoS ONE, 12, e0169412.
Wang, H., Brown, P. C., Chow, E. C., Ewart, L., Ferguson, S. S., Fitzpatrick, S., Freedman, B. S., Guo, G. L., Hedrich, W., & Heyward, S. (2021). 3D cell culture models: Drug pharmacokinetics, safety assessment, and regulatory consideration. Clinical and Translational Science, 14, 1659–1680.
Wood, C. R., Wu, W.-T., Yang, Y.-S., Yang, J.-S., Xi, Y., & Yang, W.-J. (2023). From ecology to oncology: To understand cancer stem cell dormancy, ask a Brine shrimp (Artemia). Advances in Cancer Research, 158, 199–231.
Xie, Y., Wang, S., Wu, S., Gao, S., Meng, Q., Wang, C., Lan, J., Luo, L., Zhou, X., & Xu, J. (2022). Genome of the giant panda roundworm illuminates its host shift and parasitic adaptation. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 20, 366–381.
Yadav, A. R., & Mohite, S. K. (2020). Toxicological evaluation of Psidium guajava leaf extracts using brine shrimp (Artemia salina L.) model. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Technology, 12, 258–260.
Yang, S., Kar, S., & Leszczynski, J. (2023). Tools and software for computer-aided drug design and discovery. In Cheminformatics, QSAR and machine learning applications for novel drug development (pp. 637–661). Elsevier.
Yong, U., Kang, B., & Jang, J. (2021). 3D bioprinted and integrated platforms for cardiac tissue modeling and drug testing. Essays in Biochemistry, 65, 545–554.
Zeilinger, K., Auth, S., Unger, J., Grebe, A., Mao, L., Petrik, M., Holland, G., Appel, K., Nüssler, A., Neuhaus, P., & Gerlach, J. (2000). Liver cell culture in bioreactors for in vitro drug studies as an alternative to animal testing] [Article in German. ALTEX - Alternatives to Animal Experimentation, 17, 3–10.
Zheng, F., Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Fan, Y., & Dao, M. (2021). Patient-specific organoid and organ-on-a-chip: 3D cell-culture meets 3D printing and numerical simulation. Advanced Biology, 5, e2000024.
Jusop, A. S., Thanaskody, K., Tye, G. J., Dass, S. A., Wan Kamarul Zaman, W. S., & Nordin, F. (2023). Development of brain organoid technology derived from iPSC for the neurodegenerative disease modelling: a glance through. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 16,. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2023.1173433
Funding
BDK and PP are thankful to Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, India for providing financial assistances in the form of ICMR- Adhoc Research Project. (File No.:5/13/20/2022-NCD-III; RFCNumber NCD/Ad-hoc/202/2022-23;IRIS ID:2021-10799).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Vashishat: Writing, Original draft preparation, P. Patel: Checking and evaluation, G.D. Gupta: Editing of manuscript, B.D. Kurmi: Conceptualization and Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Authors are agreeing to publish.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vashishat, A., Patel, P., Das Gupta, G. et al. Alternatives of Animal Models for Biomedical Research: a Comprehensive Review of Modern Approaches. Stem Cell Rev and Rep (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-024-10701-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-024-10701-x