Abstract
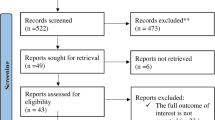
The purpose of the present study is to investigate the clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in treating breast cancer patients after mastectomy. We searched EMBASE, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Chinese Biomedical Database, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP), and PubMed to collect randomized controlled trials of TCM in treatment of breast cancer patients after mastectomy. Quality of the methodology was assessment in accordance with Cochrane 4.2.2 Handbook. All patients were divided into two groups: TCM group (TCM only or TCM plus conventional treatment) and control group (conventional treatment only). Effects of TCM on short-term clinical outcome, long-term survival rate, and incidence of adverse reaction were compared between the two groups. Twenty-nine studies were included in this meta-analysis, involving a total of 3142 breast cancer patients. Meta-analyses showed that TCM could improve short-term treatment efficacy (Z = 7.67, RR = 1.59, 95 % cl [1.41–1.80], P < 0.00001), extend 3-year (Z = 5.47, RR = 1.26, 95 % cl [1.16–1.37], P < 0.00001) and 5-year (Z = 5.53, RR = 1.17, 95 % cl [1.11–1.24], P < 0.00001) survival, reduce the incidence of adverse reactions in breast cancer patients after mastectomy. TCM provides beneficial and complementary effects in the treatment of breast cancer patients after mastectomy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., et al. (2006). Cancer statistics, 2006. A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 56, 106–130.
Zhang, Z. Q., Li, G. S., & Ye, Z. (2000). Breast cancer trends analysis. Journal of China Caner, 9, 454–455.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. (Eds.). (2006). Cochrance handbook for systematic reviews of interventions 4.2.6 (updated September 2006). In The Cochrane Library (Issue 4). Chichester, UK: Wiley.
The Cochrane collaboration. (2001). Review Manager 5.1 Tutorial. 25–40.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 21, 1539–1558.
Alderson, P., Green, S., & Higgins, J. P. T. (2004). Cochrane Reviewer’s Handbook 4.2.2 (updated March 2004). The Cochrane Library. Chichester, UK: Wiley.
Sun, Z. (2009). Bazhen particles combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced breast cancer clinical observation of 30 cases. China Modern Medicine, 16, 121–122.
Li, D. M., Jiang, X. S., Tang, L. C., et al. (2010). Added health-restoring and detoxin on new chemotherapy to treat 33 cases of breast cancer. World Chinese Medicine, 5, 394–396.
Cheng, H. (2011). Clinical observation of righting the anticancer treats breast cancer advanced combined TP regimen. Journal of Wireless Internet Technology, 12, 92–93.
Huang, C. Y., & Chen, J. Q. (2011). The research of Pingxiao capsule controls Pgp, TOPO II and GSTπof breast cancer multidrug resistance gene. Journal of Lingnan Modern Clinical Surgery, 11, 38–40.
Chi, C. (2011). 126 cases of ping xiao capsule combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy for some breast cancer clinical analysis. Journal of Chinese Community Doctors, 23, 180.
Dai, H., Zhu, C. L., & Wang, X. L. (2004). 25 cases of tune liver nourishing agent combined with NP chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced breast cancer. Jilin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 24, 33–34.
Wang, Z. Y., & Li, A. J. (2004). The clinical observation of breast cancer is treated by TCM after mastectomy. Clinical Journal of Medical Officer, 31, 22–24.
Zhao, Y. P., & Cao, L. J. (2000). 50 Cases of application of radiotherapy chemotherapy combined with Chinese medicine treatment of breast cancer. Heilongjiang Journal of Medicine, 6(4), 28.
Zhou, X. P. (2011). The Clinical observation of breast cancer is treated by TCM with chemotherapy for Breast Cancer Advanced. CMO, 3, 355.
Wang, Z. Y., & Li, A. J. (2003). Clinical observation of liver metastasis of mammary cancer treats with CAF chemotherapy plus traditional Chinese drugs. Clinical Journal of Medical Officer, 31, 22–24.
Zhao, S. F., & Wu, J. H. (2004). Traditional Chinese medicine combined with letrozole treatment for advanced breast cancer. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 22, 2089.
Gao, Q. Q., Wang, H., Li, X. R., et al. (2011). Influence of disease-free survival of treatment with breast cancer patients by ‘Ruai Houfang’ after mastectomy. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 45(10), 49–52.
Wang, H., Wu, X. Q., Gao, Q. Q., et al. (2009). Influence of the high risk of recurrence of treatment with breast cancer patients by ‘Ruai Houfang’ after Mastectomy. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 10, 55–61.
Xu, J., Wang, Y., & Zhang, L. (2007). 72 Cases of the clinical observation of breast cancer is treated by the self parameters mau xiaojie soup after metastasis. Sichuan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 25, 80–81.
Li, H. B., & Qiu, G. C. (2010). The overview of chinese medicine prevents the recurrence of breast cancer after metastasis. Chinese Medicine Oration, 2, 219.
Ze, W. C., Wu, X. Q., Feng, J. M., et al. (2011). Chinese herbal treat with 5-year disease-free survival and overall survival of breast cancer patients. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 10, 55–58.
Ouyang, H. Q., Huang, W. X., Liu, L. M., et al. (2006). 110 cases of the clinical observation of breast cancer is treated by ‘xaioxiafang’ after mastectomy. Journal of Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine, 40, 50–51.
Li, G. X. (2012). The clinical observation of breast cancer patients is treated by integrative medicine after mastectomy. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Guide, 10, 293.
Wang, X. Z. (2011). The clinical observation of nausea and vomiting of breast cancer patients is treated by TCM after mastectomy. Journal of Clinical Rational Drug, 4, 77.
Wang, Y. A. (2009). The clinical observation of six gentlemen decoction observed vomiting efficacy of breast cancer chemotherapy. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 10, 138–140.
Liu, J., Wei, S. X., & Lu, M. (2011). The clinical observation of attenuated efficiency of postoperative chemotherapy for breast cancer is treated by traditional chinese medicine. Journal of Western Medicine, 23, 896–899.
Wu, L. N. (2011). Clinical analysis of breast cancer is treated by ‘days chicho capsule secondary’ after chemotherapy. Journal of Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine, 7, 54–55.
Hou, W., Zhang, Z. Z., Yan, H. F., et al. (2000). 45 cases of the ‘adora’ righting lin breast cancer is treated by adora righting lin after chemotherapy leucopenia. Journal of Chinese Folk Medicine, 18, 38–39.
Gao, X. H., Liu, F. W., Zhang, Z. Y., et al. (2011). The research of ‘astragalus’ modified decoction prevents breast cancer after chemotherapy leucopenia. Journal of World Health Digest, 8, 45–46.
Xiong, K. G. (2011). The 43 cases of clinical observation of breast cancer are treated by integrative medicine after chemotherapy. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 32, 28–29.
Tang, L., & Wang, H. (2012). The application of upper limb edema of breast cancer patient is treated by ‘Huoxue Tongluo’ after mastectomy. Practical Journal of Preventive Medicine, 19, 233–251.
Huang, M. L., Jia, Y. J., & Sun, Y. Y. (2008). The clinical observation of upper limb edema of breast cancer patient is treated by ‘Jianpi Lishi and Huoxue Tongluo’ after mastectomy. Henan Traditional Chinese Medicine, 28, 55–56.
Luo, Z. Q., & Huan, Li. (2006). Clinical observation of upper limb edema of breast cancer patient is treated by ‘Wuling San’ after mastectomy. Liaoning. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 33, 1132.
Gao, S., Wang, X. M., Yang, G. W., et al. (2011). Clinical observation of upper limb edema of breast cancer patient is treated by the Soothing tongluo combined with physiotherapy after mastectomy. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 18, 63–64.
Ezzo, J., Berman, B., Vickers, A., & Linde, K. (1998). Complementary medicine and the Cochrane collaboration. JAMA, 280, 1628–1630.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Xu, L. & Shen, C. Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treatment of Breast Cancer Patients After Mastectomy: A Meta-Analysis. Cell Biochem Biophys 71, 1299–1306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0348-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0348-z