Abstract
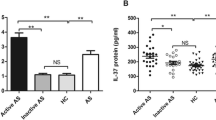
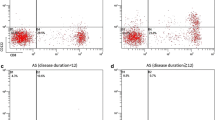
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitor-infliximab on ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients and detect the serum level of HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 before and after TNF inhibitor treatment. 138 patients at active stage of AS were treated with infliximab; serum was collected before and after TNF-α inhibitor treatment for analysis. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), flow cytometry, and enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay were applied to detect the levels of HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 at different time points, which were used for statistical analysis with clinical data including two AS indicators (erythrocyte sedimentation rate—ESR and C-reactive protein—CRP). After the treatment for 6 weeks, RT-PCR showed that the gene expressions of HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 were significantly downregulated compared with baseline before infliximab treatment (P < 0.05); flow cytometry showed that the HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 double-labeled cells were significantly downregulated (P < 0.05). After 2, 6, or 10 weeks of infliximab treatment, the levels of ESR, CRP, serum HLA-B27, and PDCD-1 of the AS patients were all significantly lower than the baseline levels (P < 0.05), and the serum HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 levels were all significantly correlated with ESR (P < 0.05). Infliximab, an anti-TNF-α inhibitor, decreases significantly not only ESR and CRP, but also the serum levels of HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 in patients with AS. HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 are involved in the pathogenesis, and disease activities of AS. HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 are potentially the useful markers of AS activity and useful parameters to evaluate the effectiveness of anti-TNF-α inhibitor in treating AS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zink, A., Braun, J., Listing, J., & Wollenhaupt, J. (2000). Disability and handicap in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis-results from the German rheumatological database. German Collaborative Arthritis Centers. The Journal of Rheumatology, 27(3), 613–622.
Rostamian, A., Mazoochy, H., Movassaghi, S., Mortazavi, S. M., Sadeghzadeh, E., Shahbazi, F., et al. (2014). Coexistence of ankylosing spondylitis and hereditary multiple exostoses: Coincidence or association. Iranian Journal of Radiology, 11(1), e4242.
Tekatas, A., & Pamuk, O. N. (2014). Increased frequency of restless leg syndrome in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases,. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12323.
Braun, J., Bollow, M., Remlinger, G., Eggens, U., Rudwaleit, M., Distler, A., et al. (1998). Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA-B27 positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 41(1), 58–67.
Zink, A., Listing, J., Klindworth, C., & Zeidler, H. (2001). The national database of the German Collaborative Arthritis Centres: I. Structure, aims, and patients. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 60(3), 199–206.
Yang, P. T., Xiao, W. G., Qin, L., Zhao, L. J., He, L. M., & Ito, M. (2010). A pilot study on changes of macrophage colony stimulating factor and transforming growth factor beta1 in male patients with ankylosing spondylitis taking thalidomide. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 69(4), 781–782.
Maksymowych, W. P. (2007). Update on the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 3(6), 1125–1133.
Feng XH, Jiang Q, Liu HX, Wang HL, He XX, Zhang HD, Tang XP, Xu FQ, Liu J, Zhou CY et al [Clinical effect analysis of ankylosing spondylitis treated by Chinese medical syndrome differentiation]. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine/Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he xue hui, Zhongguo Zhong yi yan jiu yuan zhu ban 2013, 33(10):1309–1314.
Zochling, J., & Braun, J. (2005). Management and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 17(4), 418–425.
Kiltz, U., Sieper, J., & Braun, J. (2013). ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis: Evaluation of the 2010 update in the German-speaking area. Zeitschrift fur Rheumatologie, 72(1), 71–80.
Sampaio-Barros, P. D., Keiserman, M., Meirelles Ede, S., Pinheiro Mde, M., Ximenes, A. C., Azevedo, V. F., et al. (2013). Recommendations for the management and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Revista Brasileira de Reumatologia, 53(3), 242–257.
Can, M., Aydin, S. Z., Nigdelioglu, A., Atagunduz, P., & Direskeneli, H. (2012). Conventional DMARD therapy (methotrexate–sulphasalazine) may decrease the requirement of biologics in routine practice of ankylosing spondylitis patients: A real-life experience. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, 15(6), 526–530.
Miranda-Filloy, J. A., Llorca, J., Carnero-Lopez, B., Gonzalez-Juanatey, C., Blanco, R., & Gonzalez-Gay, M. A. (2012). TNF-alpha antagonist therapy improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic ankylosing spondylitis patients. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 30(6), 850–855.
Voloshyna, I., Seshadri, S., Anwar, K., Littlefield, M. J., Belilos, E., Carsons, S. E., et al. (2014). Infliximab reverses suppression of cholesterol efflux proteins by TNF-alpha: A possible mechanism for modulation of atherogenesis. BioMed Research International, 2014, 312647.
Furst, D. E., Keystone, E. C., So, A. K., Braun, J., Breedveld, F. C., Burmester, G. R., et al. (2013). Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2012. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 72(Suppl 2), ii2–34.
Braun, J., & Sieper, J. (2004). Biological therapies in the spondyloarthritis: the current state. Rheumatology (Oxford), 43(9), 1072–1084.
Braun, J., Deodhar, A., Dijkmans, B., Geusens, P., Sieper, J., Williamson, P., et al. (2008). Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis over a two-year period. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 59(9), 1270–1278.
Evans, D. M., Spencer, C. C., Pointon, J. J., Su, Z., Harvey, D., Kochan, G., et al. (2011). Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility. Nature Genetics, 43(8), 761–767.
Li, M. Y., Yao, Z. Q., & Liu, X. Y. (2011). Advance of research on HLA-B27 and the immunological mechanism of ankylosing spondylitis. Sheng li ke xue jin zhan [Progress in Physiology], 42(1), 16–20.
Gu, X., Wu, H., & Fu, P. (2013). Allicin attenuates inflammation and suppresses HLA-B27 protein expression in ankylosing spondylitis mice. BioMed Research International, 2013, 171573.
Wu, Z., Mou, Y., Lin, Z., Huang, J., Wei, Q., & Gu, J. (2009). HLA-B27 polymorphism in Han Chinese patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A distinctive disease association for B*2715 in a multiplex family. The Journal of Rheumatology, 36(12), 2849–2850.
Brewerton, D. A., Hart, F. D., Nicholls, A., Caffrey, M., James, D. C., & Sturrock, R. D. (1973). Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet, 1(7809), 904–907.
Diyarbakir, E., Eyerci, N., Melikoglu, M., Topcu, A., & Pirim, I. (2012). HLA B27 subtype distribution among patients with ankylosing spondylitis in eastern Turkey. Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, 16(5), 456–458.
Mahmoudi, M., Amirzargar, A. A., Jamshidi, A. R., Farhadi, E., Noori, S., Avraee, M., et al. (2011). Association of IL1R polymorphism with HLA-B27 positive in Iranian patients with ankylosing spondylitis. European Cytokine Network, 22(4), 175–180.
Peng, W., Liu, C., Xu, C., Lou, Y., Chen, J., Yang, Y., et al. (2012). PD-1 blockade enhances T-cell migration to tumors by elevating IFN-gamma inducible chemokines. Cancer Research, 72(20), 5209–5218.
Tahoori, M. T., Pourfathollah, A. A., Akhlaghi, M., Daneshmandi, S., Nicknam, M. H., & Soleimanifar, N. (2011). Association of programmed cell death-1 (PDCD-1) gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Iranian patients. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 29(5), 763–767.
Hiromine, Y., Ikegami, H., Fujisawa, T., Kawabata, Y., Noso, S., Yamaji, K., et al. (2006). Molecular scanning of the gene for programmed cell death-1 (PDCD-1) as a candidate for type 1 diabetes susceptibility. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1079, 285–288.
Wei, J. C., Hung, K. S., Hsu, Y. W., Wong, R. H., Huang, C. H., Jan, M. S., et al. (2012). Genetic polymorphisms of stromal interaction molecule 1 associated with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis patients. PLoS ONE, 7(12), e49698.
de Vries, M. K., van Eijk, I. C., van der Horst-Bruinsma, I. E., Peters, M. J., Nurmohamed, M. T., Dijkmans, B. A., et al. (2009). Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein level, and serum amyloid a protein for patient selection and monitoring of anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 61(11), 1484–1490.
Poddubnyy, D. A., Rudwaleit, M., Listing, J., Braun, J., & Sieper, J. (2010). Comparison of a high sensitivity and standard C reactive protein measurement in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 69(7), 1338–1341.
Benhamou, M., Gossec, L., & Dougados, M. (2010). Clinical relevance of C-reactive protein in ankylosing spondylitis and evaluation of the NSAIDs/coxibs’ treatment effect on C-reactive protein. Rheumatology (Oxford), 49(3), 536–541.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Zhou, X., Li, X. et al. Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor on Serum Level of HLA-B27 and PDCD-1 in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Cell Biochem Biophys 70, 1453–1457 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0082-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0082-6