Abstract
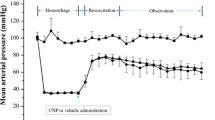
The objective of this study was to evaluate the protective effect of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide (rhBNP) on endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) in canine model of septic shock and its potential mechanisms. Dogs with endotoxin-induced septic shock were subjected to intravenous infusion of saline solution or rhBNP at the concentrations of 5 μg/kg (low-dose intervention group) or 10 μg/kg (high-dose intervention group). At 0, 2, 4, 8, and 12 h, the systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI) as well as serum levels of high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB-1) and creatinine were measured, and kidney tissue samples were taken for histological examination. We have found that low and high doses of rhBNP could significantly reduce kidney tissue damage, such as tubular epithelial swelling and atrophy, and interstitial cell swelling in response to LPS injection in the dog sepsis models. rhBNP administration significantly reduced SVRI and serum levels of creatinine in dogs with LPS-induced sepsis in a dose-dependent manner, and attenuated the rise in the circulating HMGB-1. In conclusion, these findings suggest that rhBNP may exert dose-dependent protective effect on kidney tissue with endotoxin-induced injury, and this effect may be associated with the changes in blood levels of HMGB-1. rhBNP may be considered as therapeutic agents for treating sepsis-induced AKI.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dombrovskiy, V. Y., Martin, A. A., Sunderram, J., & Paz, H. L. (2007). Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: a trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Critical Care Medicine, 35, 1244–1250.
Koçkara, A., & Kayataş, M. (2013). Renal cell apoptosis and new treatment options in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Renal Failure, 35, 291–294.
Peng, T., Shen, E., Fan, J., Zhang, Y., Arnold, J. M., & Feng, Q. (2008). Disruption of phospholipase C gamma1 signalling attenuates cardiac tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression and improves myocardial function during endotoxemia. Cardiovascular Research, 78, 90–97.
Yang, H., Song, Z., Jin, H., Cui, Y., Hou, M., & Gao, Y. (2014). Protective effect of rhBNP on intestinal injury in the canine models of sepsis. International Immunopharmacology, 19, 262–266.
Song, Z., Cui, Y., Ding, M. Z., Jin, H. X., & Gao, Y. (2013). Protective effects of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide against LPS-Induced acute lung injury in dogs. International Immunopharmacology, 17, 508–512.
Cheng, B., Xie, G., Yao, S., Wu, X., Guo, Q., Gu, M., et al. (2007). Epidemiology of severe sepsis in critically ill surgical patients in ten university hospitals in China. Critical Care Medicine, 35, 2538–2546.
Kumaraswamy, S. B., Linder, A., Åkesson, P., & Dahlbäck, B. (2011). Decreased Plasma Concentrations of Apolipoprotein M in Sepsis and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndromes. Critical Care, 16, 60–62.
Russell, J. A. (2006). Management of sepsis. The New England Journal of Medicine, 355, 1699–1713.
Rangel-Frausto, M. S., Pittet, D., Costigan, M., et al. (1995). The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): A prospective study. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 273, 117–123.
Aksoy, Y., Yapanoglu, T., Aksou, H., & Yildirim, A. K. (2004). The effect of dehydroepiandrosterone on renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rabbits. Urological Research, 32, 93–96.
Van Amersfoort, E. S., Van Berkel, T. J. C., & Kuiper, J. (2003). Receptors, mediators, and mechanisms involved in bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 16(3), 379–414.
Doi, K., Leelahavanichkul, A., Yuen, P. S. T., & Star, R. A. J. (2009). Animal models of sepsis and sepsis-induced kidney injury. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 119(10), 2868–2878.
Bone, R. C. (1991). Gram-negative sepsis. Background, clinical features, and intervention. Chest, 100, 802–808.
Yuong, J. D. (2004). The heart and circulation in severe sepsis. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 93, 114–120.
Maekawa, K., Sudoh, T., Furusawa, M., Minamino, N., Kangawa, K., Ohkubo, H., et al. (1988). Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding a precursor for porcine brain natriuretic peptide. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 157, 410–416.
Li, N., Zhang, Y., Fan, S., Xing, J., & Liu, H. (2013). BNP and NT-proBNP levels in patients with sepsis. Frontiers in Bioscience, 18, 1237–1243.
Wang, F., Wu, Y., Tang, L., Zhu, W., Chen, F., Xu, T., et al. (2012). Brain natriuretic peptide for prediction of mortality in patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Critical Care, 16, R74.
McLean, A. S., Huang, S. J., Hyams, S., Poh, G., Nalos, M., Pandit, R., et al. (2007). Prognostic values of B-type natriuretic peptide in severe sepsis and septic shock. Critical Care Medicine, 35, 1019–1026.
Potter, L. R., et al. (2009). Natriuretic peptides: their structures, receptors, physiologic functions and therapeutic applications. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 191, 341–366.
Wang, W., Zolty, E., Falk, S., Summer, S., Stearman, R., Geraci, M., et al. (2007). Prostacyclin in endotoxemia-induced acute kidney injury: cyclooxygenase inhibition and renal prostacyclin synthase transgenic mice. American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology, 293, F1131–F1136.
Chertow, G. M., Burdick, E., Honour, M., Bonventre, J. V., & Bates, D. W. (1999). Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and mice. Science, 285, 248–251.
Li, W., Li, J., Ashok, M., Wu, R., Chen, D., Yang, L., et al. (2000). Tracey KJ, Wang P, Sama AE, Wang H High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cy-tokine synthesis in human monocytes. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 192, 565–570.
Ulloa, L., Brunner, M., Ramos, L., & Deitch, E. A. (2009). Selentific and clinical challenges in sepsis. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 15, 1918–1935.
Hou, L. C., Qin, M. Z., Zheng, L. N., Lu, Y., Wang, Q., Peng, D. R., et al. (2009). Severity of sepsis is correlated with the elevation of serum high-mobility group box 1 in rats. Chinese Medical Journal, 122, 449–454.
Mori, M., Yamanashi, Y., Kobayashi, K., & Sakamoto, A. (2010). Atrial natriuretic peptide alleviates cardiovascular and metabolic disorders in a rat endotoxemia model: A possible role for its anti-inflammatory properties. Journal of Nippon Medical School, 77, 296–305.
Schmetterer, L., & Polak, K. (2001). Role of nitric oxide in the control of ocular blood. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 20, 823–847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Jin, HX., Song, Z. et al. Protective Effect of Recombinant Human Brain Natriuretic Peptide on Acute Renal Injury Induced by Endotoxin in Canines. Cell Biochem Biophys 70, 1317–1324 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0057-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0057-7