Abstract
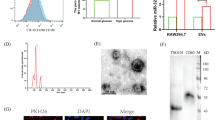
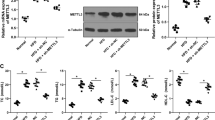
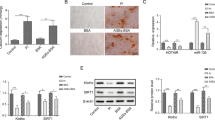
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) accumulation in the vascular wall plays a pivotal role in the development of atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. However, few studies focus on the regulatory roles of microRNAs in ox-LDL stimulated vascular calcification. The aim of the present study was to investigate how miR-33a-5p regulated vascular calcification stimulated by ox-LDL. In the present study, miR-33a-5p was downregulated during vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) calcification and upon ox-LDL treatment. ox-LDL significantly stimulated VSMCs calcification, while miR-33a-5p overexpression by its mimics transfection inhibited alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, mineralization and marker genes associated with VSMCs calcification even in the presence of ox-LDL. Methyltransferase like 3 (METTL3) was the target gene of miR-33a-5p. METTL3 was upregulated during VSMCs calcification and upon ox-LDL treatment. When VSMCs were transfected with miR-33a-5p mimics, METTL3 was downregulated. METTL3 downregulation by siRNA method decreased VSMCs calcification even in the presence of ox-LDL. Taken together, these results suggest miR-33a-5p suppresses VSMCs calcification stimulated by ox-LDL via targeting METTL3, highlighting the critical role of miR-33a-5p/METTL3 in vascular calcification.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data relevant to this article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ABCA1:
-
(ATP)-binding cassette subfamily A member 1
- ABCG1:
-
ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 1G1
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- ColI:
-
Collagen I
- GDM:
-
Gestational diabetes mellitus
- HMGA2:
-
High mobility group AT-hook 2
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- METTL3:
-
Methyltransferase like 3
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa B
- n-LDL:
-
Native LDL
- NOMO1:
-
Nodal modulator 1
- OC:
-
Osteocalcin
- ox-LDL:
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- PTH:
-
Parathyroid hormone
- PTH1r:
-
PTH 1 receptor
- Runx2:
-
Runt-related transcription factor 2
- SATB2:
-
Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2
- SIRT6:
-
Sirtuin 6
- SREBP2:
-
Sterol response binding protein 2
- TLR4:
-
Toll like receptor 4
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- VSMCs:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells
- XBP1s:
-
X-box binding protein l splicing
References
Lee, S. J., Lee, I. K., & Jeon, J. H. (2020). Vascular calcification-new insights into its mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Science, 21(8), 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082685
Lin, M. E., Chen, T., Leaf, E. M., Speer, M. Y., & Giachelli, C. M. (2015). Runx2 expression in smooth muscle cells is required for arterial medial calcification in mice. American Journal of Pathology, 185(7), 1958–1969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.020
Chistiakov, D. A., Myasoedova, V. A., Melnichenko, A. A., Grechko, A. V., & Orekhov, A. N. (2017). Calcifying matrix vesicles and atherosclerosis. Biomed Research International, 2017, 7463590. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7463590
Song, Y., Hou, M., Li, Z., Luo, C., Ou, J. S., Yu, H., et al. (2017). TLR4/NF-κB/Ceramide signaling contributes to Ox-LDL-induced calcification of human vascular smooth muscle cells. European Journal of Pharmacology, 794, 45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.11.029
Yan, J., Stringer, S. E., Hamilton, A., Charlton-Menys, V., Götting, C., Müller, B., et al. (2011). Decorin GAG synthesis and TGF-β signaling mediate Ox-LDL-induced mineralization of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, 31(3), 608–615. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.110.220749
Goettsch, C., Rauner, M., Hamann, C., Sinningen, K., Hempel, U., Bornstein, S. R., et al. (2011). Nuclear factor of activated T cells mediates oxidised LDL-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Diabetologia, 54(10), 2690–2701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2219-0
Liao, L., Zhou, Q., Song, Y., Wu, W., Yu, H., Wang, S., et al. (2013). Ceramide mediates Ox-LDL-induced human vascular smooth muscle cell calcification via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. PLoS ONE, 8(12), e82379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082379
Alkagiet, S., & Tziomalos, K. (2017). Vascular calcification: The role of microRNAs. Biomolecular Concepts, 8(2), 119–123. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2017-0001
Costa, V., Carina, V., Raimondi, L., De Luca, A., Bellavia, D., Conigliaro, A., et al. (2019). MiR-33a controls hMSCS osteoblast commitment modulating the Yap/Taz expression through EGFR signaling regulation. Cells, 8(12), 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121495
Chen, Q., Wang, M., & Wu, S. (2020). The lncRNA MCF2L-AS1 controls osteogenic differentiation by regulating miR-33a. Cell Cycle, 19(9), 1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1747776
Hwang, J. S., Ham, S. A., Yoo, T., Lee, W. J., Paek, K. S., Lee, C. H., et al. (2016). Sirtuin 1 mediates the actions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ on the oxidized low-density lipoprotein-triggered migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Molecular Pharmacology, 90(5), 522–529. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.116.104679
Zhang, Y., Gu, X., Li, D., Cai, L., & Xu, Q. (2019). METTL3 regulates osteoblast differentiation and inflammatory response via Smad signaling and MAPK signaling. Internal Journal of Molecular Science, 21(1), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010199
Shi, X., Gao, J., Lv, Q., Cai, H., Wang, F., Ye, R., et al. (2020). Calcification in atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability: Friend or foe? Frontiers in Physiology, 11, 56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00056
Demer, L. L., & Tintut, Y. (2008). Vascular calcification: Pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation, 117(22), 2938–2948. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.107.743161
Wang, M., Wu, Y., Yu, Y., Fu, Y., Yan, H., Wang, X., et al. (2019). Rutaecarpine prevented ox-LDL-induced VSMCs dysfunction through inhibiting overexpression of connexin 43. European Journal Pharmacology, 853, 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.028
Lee, S. J., Lee, I. K., & Jeon, J. H. (2020). Vascular calcification-new insights into its mechanism. Internal Journal of Molecular Science, 21(8), 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082685
Jiang, W., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Chen, C., Yang, H., Lin, Q., et al. (2021). The cell origin and role of osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis in vascular calcification. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2021(8), 639740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.639740
Yang, P., Troncone, L., Augur, Z. M., Kim, S. S. J., McNeil, M. E., & Yu, P. B. (2020). The role of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vascular calcification. Bone, 141, 115542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2020.115542
Leopold, J. A. (2014). MicroRNAs regulate vascular medial calcification. Cells, 3(4), 963–980. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells3040963
Shen, W., Sun, B., Zhou, C., Ming, W., Zhang, S., & Wu, X. (2020). CircFOXP1/FOXP1 promotes osteogenic differentiation in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration in osteoporosis via miR-33a-5p. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(21), 12513–12524. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15792
Mi, W., Shi, Q., Chen, X., Wu, T., & Huang, H. (2016). miR-33a-5p modulates TNF-α-inhibited osteogenic differentiation by targeting SATB2 expression in hBMSCs. FEBS Letters, 590(3), 396–407. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12064
Price, N. L., Rotllan, N., Zhang, X., Canfrán-Duque, A., Nottoli, T., Suarez, Y., et al. (2019). Specific disruption of abca1 targeting largely mimics the effects of miR-33 knockout on macrophage cholesterol efflux and atherosclerotic plaque development. Circulation Research, 124(6), 874–880. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314415
Kim, S. H., Kim, G. J., Umemura, T., Lee, S. G., & Cho, K. J. (2017). Aberrant expression of plasma microRNA-33a in an atherosclerosis-risk group. Molecular Biology Reports, 44(1), 79–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4082-z
Raskurazhev, A. A., Tanashyan, M. M., Shabalina, A. A., Kuznetsova, P. I., Kornilova, A. A., & Burmak, A. G. (2020). Micro-RNA in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Human Physiology, 46, 880–885. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119720080113
Horie, T., Baba, O., Kuwabara, Y., Chujo, Y., Watanabe, S., Kinoshita, M., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-33 deficiency reduces the progression of atherosclerotic plaque in ApoE-/- mice. Journal of the American Heart Association, 1(6), e003376. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.112.003376
Price, N. L., Rotllan, N., Canfrán-Duque, A., Zhang, X., Pati, P., Arias, N., et al. (2017). Genetic dissection of the impact of miR-33a and miR-33b during the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Reports, 21(5), 1317–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.023
Rayner, K. J., Sheedy, F. J., Esau, C. C., Hussain, F. N., Temel, R. E., Parathath, S., et al. (2011). Antagonism of miR-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol transport and regression of atherosclerosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121(7), 2921–2931. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci57275
He, J., Zhang, G., Pang, Q., Yu, C., Xiong, J., Zhu, J., et al. (2017). SIRT6 reduces macrophage foam cell formation by inducing autophagy and cholesterol efflux under ox-LDL condition. The FEBS Journal, 284(9), 1324–1337. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14055
Du, M., Zhang, Y., Mao, Y., Mou, J., Zhao, J., Xue, Q., et al. (2017). MiR-33a suppresses proliferation of NSCLC cells via targeting METTL3 mRNA. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 482(4), 582–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.077
Zhang, M., Tang, M., Wu, Q., Wang, Z., Chen, Z., Ding, H., et al. (2020). LncRNA DANCR attenuates brain microvascular endothelial cell damage induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation through regulating of miR-33a-5p/XBP1s. Aging, 12(2), 1778–1791. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102712
Mao, M., Lei, H., Liu, Q., Chen, Y., Zhao, L., Li, Q., et al. (2014). Effects of miR-33a-5P on ABCA1/G1-mediated cholesterol efflux under inflammatory stress in THP-1 macrophages. PLoS ONE, 9(10), e109722. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109722
Xing, W., Li, T., Wang, Y., Qiang, Y., Ai, C., & Tang, H. (2020). MiR-33a-5p targets NOMO1 to modulate human cardiomyocyte progenitor cells proliferation and differentiation and apoptosis. Journal of Receptors and Signal Transduction, 14, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/10799893.2020.1825492
Feng, Y., Qu, X., Chen, Y., Feng, Q., Zhang, Y., Hu, J., et al. (2020). MicroRNA-33a-5p sponges to inhibit pancreatic β-cell function in gestational diabetes mellitus LncRNA DANCR. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 18(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-020-00618-8
Zheng, W., Dong, X., Zhao, Y., Wang, S., Jiang, H., Zhang, M., et al. (2019). Multiple functions and mechanisms underlying the role of METTL3 in human cancers. Frontiers in Oncology, 9, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01403
Chen, X., Hua, W., Huang, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., & Li, G. (2019). Regulatory role of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine modification in bone biology and osteoporosis. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 10, 911. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00911
Yan, G., Yuan, Y., He, M., Gong, R., Lei, H., Zhou, H., et al. (2020). m(6)A methylation of precursor-miR-320/RUNX2 controls osteogenic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids, 19, 421–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.12.001
Wu, Y., Xie, L., Wang, M., Xiong, Q., Guo, Y., Liang, Y., et al. (2018). Mettl3-mediated m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Nature Communication, 9(1), 4772–4772. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06898-4
Chen, J., Ning, Y., Zhang, H., Song, N., Gu, Y., Shi, Y., et al. (2019). METTL14-dependent m6A regulates vascular calcification induced by indoxyl sulfate. Life Sciences, 239, 117034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117034
Funding
This word was funded by Shanghai Xuhui Central Hospital and The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RH and LW conceived and designed the project. JL, LL and HZ acquired the data. RH analyzed the data. RH wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Y. James Kang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, R., Luo, J., Wang, L. et al. miR-33a-5p Suppresses ox-LDL-Stimulated Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Targeting METTL3. Cardiovasc Toxicol 21, 737–746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09663-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09663-0