Abstract
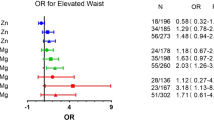
Growing evidence indicates that metal exposure is associated with metabolic syndrome (MetS); however, mixed results have been reported. The aim of this study was to clarify associations of exposure to essential and non-essential metals with body composition and risks of obesity and MetS. Anthropometry and blood biochemistry of metabolic parameters were obtained from 150 middle-aged Taiwanese adults. Plasma metals were assessed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, and body compositions were measured by a bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). The essential metals of copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), and chromium (Cr) were positively correlated with the body fat mass but inversely correlated with the skeletal muscle mass (all p < 0.05). An adjusted logistic regression showed that Mn [odds ratio (OR) = 1.624 (95% confidence interval 1.072, 2.462), p = 0.02] and, to a lesser extent, Cu [OR = 1.501 (0.985, 2.292), p = 0.059] predicted abdominal obesity, while plasma Cu [OR = 2.211 (1.146, 4.266), p = 0.02] and zinc (Zn) [OR = 2.228 (1.048, 4.736) p = 0.04] predicted MetS. Significant correlations between dyslipidemia and lithium [OR = 1.716 (1.080, 2.726)], Cu [OR = 2.210 (1.415, 3.454)], Mn [OR = 2.200 (1.320, 3.666)], molybdenum [OR = 1.853 (1.160, 2.958)], and Zn [OR = 1.993 (1.186, 3.349)], and between boron [OR = 2.583 (1.137, 5.868)] and hyperglycemia were observed (all p < 0.05). Exposure to essential metals may affect the body composition and metabolic profiles, exacerbating the risk of MetS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collaborators GBDO, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, Lee A, Marczak L, Mokdad AH, Moradi-Lakeh M, Naghavi M, Salama JS, Vos T, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Ahmed MB, Al-Aly Z, Alkerwi A, Al-Raddadi R, Amare AT, Amberbir A, Amegah AK, Amini E, Amrock SM, Anjana RM, Arnlov J, Asayesh H, Banerjee A, Barac A, Baye E, Bennett DA, Beyene AS, Biadgilign S, Biryukov S, Bjertness E, Boneya DJ, Campos-Nonato I, Carrero JJ, Cecilio P, Cercy K, Ciobanu LG, Cornaby L, Damtew SA, Dandona L, Dandona R, Dharmaratne SD, Duncan BB, Eshrati B, Esteghamati A, Feigin VL, Fernandes JC, Furst T, Gebrehiwot TT, Gold A, Gona PN, Goto A, Habtewold TD, Hadush KT, Hafezi-Nejad N, Hay SI, Horino M, Islami F, Kamal R, Kasaeian A, Katikireddi SV, Kengne AP, Kesavachandran CN, Khader YS, Khang YH, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Kim YJ, Kinfu Y, Kosen S, Ku T, Defo BK, Kumar GA, Larson HJ, Leinsalu M, Liang X, Lim SS, Liu P, Lopez AD, Lozano R, Majeed A, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Mazidi M, McAlinden C, McGarvey ST, Mengistu DT, Mensah GA, Mensink GBM, Mezgebe HB, Mirrakhimov EM, Mueller UO, Noubiap JJ, Obermeyer CM, Ogbo FA, Owolabi MO, Patton GC, Pourmalek F, Qorbani M, Rafay A, Rai RK, Ranabhat CL, Reinig N, Safiri S, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Santos IS, Sartorius B, Sawhney M, Schmidhuber J, Schutte AE, Schmidt MI, Sepanlou SG, Shamsizadeh M, Sheikhbahaei S, Shin MJ, Shiri R, Shiue I, Roba HS, Silva DAS, Silverberg JI, Singh JA, Stranges S, Swaminathan S, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tegegne BS, Terkawi AS, Thakur JS, Tonelli M, Topor-Madry R, Tyrovolas S, Ukwaja KN, Uthman OA, Vaezghasemi M, Vasankari T, Vlassov VV, Vollset SE, Weiderpass E, Werdecker A, Wesana J, Westerman R, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Yonga G, Zaidi Z, Zenebe ZM, Zipkin B, Murray CJL (2017) Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 377(1):13–27
Mehri A (2020) Trace elements in human nutrition (II)—an update. Int J Prev Med 11:2
Sheehan MC, Burke TA, Navas-Acien A, Breysse PN, McGready J, Fox MA (2014) Global methylmercury exposure from seafood consumption and risk of developmental neurotoxicity: a systematic review. Bull World Health Organ 92(4):254-269F
Chowdhury R, Ramond A, O’Keeffe LM, Shahzad S, Kunutsor SK, Muka T, Gregson J, Willeit P, Warnakula S, Khan H, Chowdhury S, Gobin R, Franco OH, Di Angelantonio E (2018) Environmental toxic metal contaminants and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 362 k3310
Lee K (2018) Blood mercury concentration in relation to metabolic and weight phenotypes using the KNHANES 2011–2013 data. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 91(2):185–193
Zhu X, Fan Y, Sheng J, Gu L, Tao Q, Huang R, Liu K, Yang L, Chen G, Cao H, Li K, Tao F, Wang S (2021) Association between blood heavy metal concentrations and dyslipidemia in the elderly. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(4):1280–1290
Skalny AV, Chang JS, Bobrovnitsky IP, Kopylov PY, Skalnaya MG, Huang SY, Paoliello MMB, Ivanova ES, Wang W, Tinkov AA (2020) Relationship between elevated hair mercury levels, essential element status, and metabolic profile in overweight and obese adults. Biol Trace Elem Res
Tinkov AA, Aschner M, Ke T, Ferrer B, Zhou JC, Chang JS, Santamaria A, Chao JC, Aaseth J, Skalny AV (2021) Adipotropic effects of heavy metals and their potential role in obesity. Fac Rev 10:32
Ayoub N, Mantash H, Dhaini HR, Mourad A, Hneino M, Daher Z (2021) Serum cadmium levels and risk of metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional study. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(10):3625–3633
Xu P, Liu A, Li F, Tinkov AA, Liu L, Zhou JC (2021) Associations between metabolic syndrome and four heavy metals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 273 116480
Zhong Q, Qin QR, Yang WJ, He JL, Zhu JL, Zhu ZY, Huang F (2021) Multiple metal exposure and obesity: a prospective cohort study of adults living along the Yangtze River. China, Environ Pollut 285 117150
Lee S, Yoon JH, Won JU, Lee W, Lee JH, Seok H, Kim YK, Kim CN, Roh J (2016) The association between blood mercury levels and risk for overweight in a general adult population: results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Biol Trace Elem Res 171(2):251–261
Shin YY, Ryu IK, Park MJ, Kim SH (2018) The association of total blood mercury levels and overweight among Korean adolescents: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010–2013. Korean J Pediatr 61(4):121–128
Niehoff NM, Keil AP, O’Brien KM, Jackson BP, Karagas MR, Weinberg CR, White AJ (2020) Metals and trace elements in relation to body mass index in a prospective study of US women. Environ Res 184 109396
Rothenberg SE, Korrick SA, Fayad R (2015) The influence of obesity on blood mercury levels for U.S. non-pregnant adults and children: NHANES 2007–2010. Environ Res 138:173–80
Skalny AV, Skalnaya MG, Serebryansky EP, Zhegalova IV, Grabeklis AR, Skalnaya OA, Skalnaya AA, Huang PT, Wu CC, Bykov AT, Tinkov AA (2018) Comparative hair trace element profile in the population of Sakhalin and Taiwan Pacific Islands. Biol Trace Elem Res 184(2):308–316
Lu CW, Lee YC, Kuo CS, Chiang CH, Chang HH, Huang KC (2021) Association of serum levels of zinc, copper, and iron with risk of metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 13(2)
Fernandez-Cao JC, Warthon-Medina M, Arija HMVV, Doepking C, Serra-Majem L, Lowe NM (2019) Zinc intake and status and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients 11(5)
Cempaka AR, Tseng SH, Yuan KC, Bai CH, Tinkov AA, Skalny AV, Chang JS (2019) Dysregulated iron metabolism-associated dietary pattern predicts an altered body composition and metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 11(11)
Gaman MA, Dobrica EC, Cozma MA, Antonie NI, Stanescu AMA, Gaman AM, Diaconu CC (2021) Crosstalk of magnesium and serum lipids in dyslipidemia and associated disorders: a systematic review. Nutrients 13(5)
Lo K, Yang JL, Chen CL, Liu L, Huang YQ, Feng YQ, Yang AM (2021) Associations between blood and urinary manganese with metabolic syndrome and its components: cross-sectional analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2016. Sci Total Environ 780 146527
Lin C-F, Chang Y-H, Chien S-C, Lin Y-H, Yeh H-Y (2018) Epidemiology of dyslipidemia in the Asia Pacific Region. Int J Gerontol
Tan C-E, Ma S, Wai D, Chew S-K, Tai E-S (2004) Can we apply the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel definition of the metabolic syndrome to Asians? Diabetes Care 27(5):1182–1186
Liu T-Y, Hung Y-M, Huang W-C, Wu M-L, Lin S-L (2017) Do people from Taiwan have higher heavy metal levels than those from Western countries? Singapore Med J 58(5):267–271
Lian S, Zhang T, Yu Y, Zhang B (2021) Relationship of circulating copper level with gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis and systemic review. Biol Trace Elem Res
Chen J, Lan C, An H, Jin Y, Li Q, Ge S, Yu Y, Shen G, Pan B, Xu Y, Ye R, Li Z, Wang B (2021) Potential interference on the lipid metabolisms by serum copper in a women population: a repeated measurement study, Sci Total Environ 760 143375
Gu K, Li X, Xiang W, Jiang X (2020) The relationship between serum copper and overweight/obesity: a meta-analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 194(2):336–347
Romero A, Ramos E, de Los Rios C, Egea J, Del Pino J, Reiter RJ (2021) A review of metal-catalyzed molecular damage: protection by melatonin. J Pineal Res 56(4):343–70
Fan Y, Zhang C, Bu J (2017) Relationship between selected serum metallic elements and obesity in children and adolescent in the U.S. Nutrients 9(2)
Wang X, Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Mukherjee B, Herman WH, Park SK (2021) Urinary metals and adipokines in midlife women: the study of women’s health across the nation (SWAN). Environ Res 196 110426
Flores CR, Puga MP, Wrobel K, GaraySevilla ME, Wrobel K (2021) Trace elements status in diabetes mellitus type 2: possible role of the interaction between molybdenum and copper in the progress of typical complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 91(3):333–41
Nielsen FH, Eckhert CD (2020) Boron. Adv Nutr 11(2):461–462
Jung SR, Park SY, Koh JH, Kim JY (2021) Lithium enhances exercise-induced glycogen breakdown and insulin-induced AKT activation to facilitate glucose uptake in rodent skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch 473(4):673–682
McKnight RF, Adida M, Budge K, Stockton S, Goodwin GM, Geddes JR (2012) Lithium toxicity profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 379(9817):721–728
Aliyazicioglu R, Kural B, Colak M, Karahan SC, Ayvaz S, Deger O (2007) Treatment with lithium, alone or in combination with olanzapine, relieves oxidative stress but increases atherogenic lipids in bipolar disorder. Tohoku J Exp Med 213(1):79–87
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the technique assistances of Trace Element Research Center, Tri-Service General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, and Dr. Skalny Laboratory Asia-Pacific promotion center.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology,Taiwan (MOST 109–2923-B-038–001-MY3) and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (No. 20–515-S52003). Dr. JS Chang was also supported by the grants from the Taipei Medical University Hospital (110TMU-TMUH-109) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 109–2923-B-038–001-MY3, MOST 110–2320-B-038–046). Российский Фонд Фундаментальных Исследований (РФФИ),No. 20–515-S52003,Anatoly V. Skalny,Ministry of Science and Technology,Taiwan,MOST 110–2320-B-038–046,Jung-Su Chang,MOST109-2923-B-038–001-MY3,Jung-Su Chang,Taipei Medical University Hospital,110TMU-TMUH-109,Jung-Su Chang
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.C., A.V.S., and A.A.T.; methodology, Y.K.C., C.F.C., and C.S.T.; validation, A.V.S. and A.A.T.; formal analysis, Y.J.N.; investigation, Y.J.N.; resources, Y.K.C. and C.F.C.; data curation, C.F.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.K.C. and C.F.C.; supervision, C.S.T., A.V.S., and A.A.T.; project administration, C.S.T.; funding acquisition, J.S.C. and A.V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Taipei Medical University Hospital (201,502,018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngu, Y.J., Skalny, A.V., Tinkov, A.A. et al. Association Between Essential and Non-essential Metals, Body Composition, and Metabolic Syndrome in Adults. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 4903–4915 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03077-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-03077-3