Abstract
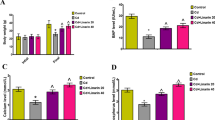
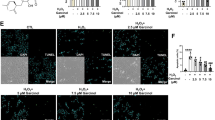
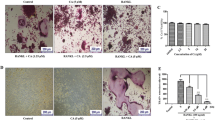
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of allicin on lead-induced bone loss in mice. Male C57BL/6 J mice (3-weeks-old) were randomly divided into four groups: control group, lead group, allicin+lead group, and allicin group. Micro-CT, histology, oxidative stress, and osteoclastogenesis-related gene expression were analyzed. The results showed that allicin significantly ameliorated lead-induced bone loss, reduced oxidative stress, and inhibited osteoclastogenesis in mice. Moreover, we found that allicin upregulated the expression of SIRT1 and deacetylation of FoxO1. In conclusion, our study demonstrated that allicin exerts protective effects on lead-induced bone loss via antioxidant activity, preventing osteoclastogenesis, and activating SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway in mice, implying a potential therapy for lead-induced bone loss.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Burbure C, Buchet JP, Leroyer A, Nisse C, Haguenoer JM, Mutti A, Smerhovsky Z, Cikrt M, Trzcinka-Ochocka M, Razniewska G, Jakubowski M, Bernard A (2006) Renal and neurologic effects of cadmium, lead, mercury, and arsenic in children: evidence of early effects and multiple interactions at environmental exposure levels. Environ Health Perspect 114(4):584–590. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8202
Zhou CC, Gao ZY, He YQ, Wu MQ, Chen F, Wang J, Liu JX, Yan CH (2019) Effects of lead, mercury, aluminium and manganese co-exposure on the serum BDNF concentration of pre-school children in Taizhou, China. Chemosphere 217:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.028
Zhou CC, Gao ZY, Wang J, Wu MQ, Hu S, Chen F, Liu JX, Pan H, Yan CH (2018) Lead exposure induces Alzheimers’s disease (AD)-like pathology and disturbes cholesterol metabolism in the young rat brain. Toxicol Lett 296:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.06.1065
Theppeang K, Glass TA, Bandeen-Roche K, Todd AC, Rohde CA, Links JM, Schwartz BS (2008) Associations of bone mineral density and lead levels in blood, tibia, and patella in urban-dwelling women. Environ Health Perspect 116(6):784–790. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10977
Beier EE, Holz JD, Sheu TJ, Puzas JE (2016) Elevated lifetime lead exposure impedes osteoclast activity and produces an increase in bone mass in adolescent mice. Toxicol Sci 149(2):277–288. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv234
Beier EE, Maher JR, Sheu TJ, Cory-Slechta DA, Berger AJ, Zuscik MJ, Puzas JE (2013) Heavy metal lead exposure, osteoporotic-like phenotype in an animal model, and depression of Wnt signaling. Environ Health Perspect 121(1):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1205374
Chen X, Wang K, Wang Z, Gan C, He P, Liang Y, Jin T, Zhu G (2014) Effects of lead and cadmium co-exposure on bone mineral density in a Chinese population. Bone 63:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2014.02.017
Abdelhamid FM, Mahgoub HA, Ateya AI (2020) Ameliorative effect of curcumin against lead acetate-induced hemato-biochemical alterations, hepatotoxicity, and testicular oxidative damage in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07718-3
Berglund M, Akesson A, Bjellerup P, Vahter M (2000) Metal-bone interactions. Toxicol Lett 112-113:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(99)00272-6
Monir AU, Gundberg CM, Yagerman SE, van der Meulen MC, Budell WC, Boskey AL, Dowd TL (2010) The effect of lead on bone mineral properties from female adult C57/BL6 mice. Bone 47(5):888–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2010.07.013
Stancic V (1984) Some subjective and objective prerequisites to educational integration of handicapped children. Int J Rehabil Res 7(3):273–282
Edwards JR, Perrien DS, Fleming N, Nyman JS, Ono K, Connelly L, Moore MM, Lwin ST, Yull FE, Mundy GR, Elefteriou F (2013) Silent information regulator (Sir)T1 inhibits NF-kappaB signaling to maintain normal skeletal remodeling. J Bone Miner Res 28(4):960–969. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1824
Yan S, Miao L, Lu Y, Wang L (2019) Sirtuin 1 inhibits TNF-alpha-mediated osteoclastogenesis of bone marrow-derived macrophages through both ROS generation and TRPV1 activation. Mol Cell Biochem 455(1–2):135–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3477-7
Kim HN, Han L, Iyer S, de Cabo R, Zhao H, O'Brien CA, Manolagas SC, Almeida M (2015) Sirtuin1 suppresses osteoclastogenesis by deacetylating FoxOs. Mol Endocrinol 29(10):1498–1509. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2015-1133
Ponugoti B, Dong G, Graves DT (2012) Role of forkhead transcription factors in diabetes-induced oxidative stress. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:939751. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/939751
Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Zhou J, Xin N, Zhu Z, Wu Y (2018) FoxO1 expression in osteoblasts modulates bone formation through resistance to oxidative stress in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(3):1401–1408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.055
Chen F, Zhou CC, Yang Y, Liu JW, Yan CH (2019) GM1 ameliorates lead-induced cognitive deficits and brain damage through activating the SIRT1/CREB/BDNF pathway in the developing male rat hippocampus. Biol Trace Elem Res 190(2):425–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1569-6
Panyod S, Wu WK, Lu KH, Liu CT, Chu YL, Ho CT, Hsiao WLW, Wu MS, Lai YS, Chen WC, Lin YE, Lin SH, Sheen LY (2020) Allicin modifies the composition and function of the gut microbiota in alcoholic hepatic steatosis mice. J Agric Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07555
Samra YA, Hamed MF, El-Sheakh AR (2020) Hepatoprotective effect of allicin against acetaminophen-induced liver injury: role of inflammasome pathway, apoptosis, and liver regeneration. J Biochem Mol Toxicol:e22470. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22470
Gao W, Wang W, Zhang J, Deng P, Hu J, Yang J, Deng Z (2019) Allicin ameliorates obesity comorbid depressive-like behaviors: involvement of the oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, autophagy, insulin resistance and NOX/Nrf2 imbalance in mice. Metab Brain Dis 34(5):1267–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00443-y
Cai SZ, Zhao LN, Liu J, Ji YT, Shi XY, Ma ZR, Lv XH, Chen K, Chen Y (2019) Allicin alleviates lead-induced hematopoietic stem cell aging by up-regulating PKM2. Biosci Rep 39(7). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190243
Cai S, Liu J, Shi X, Hu S, Zhao L (2019) Allicin alleviated learning and memory deficits caused by lead exposure at developmental stage. Life Sci 231:116532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.06.007
Aslani MR, Najarnezhad V, Mohri M (2010) Individual and combined effect of meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid and allicin on blood and tissue lead content in mice. Planta Med 76(3):241–244. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1186141
Kelainy EG, Ibrahim Laila IM, Ibrahim SR (2019) The effect of ferulic acid against lead-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in kidney and testes of rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(31):31675–31684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06099-6
Zhou L, Song H, Zhang Y, Ren Z, Li M, Fu Q (2020) Polyphyllin VII attenuated RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation via inhibiting of TRAF6/c-Src/PI3K pathway and ROS production. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 21(1):112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-3077-z
Wang S, Ren D (2016) Allicin protects traumatic spinal cord injury through regulating the HSP70/Akt/iNOS pathway in mice. Mol Med Rep 14(4):3086–3092. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5651
Wang ET, Chen DY, Liu HY, Yan HY, Yuan Y (2015) Protective effect of allicin against glycidamide-induced toxicity in male and female mice. Gen Physiol Biophys 34(2):177–187. https://doi.org/10.4149/gpb_2014038
He YQ, Yang H, Shen Y, Zhang JH, Zhang ZG, Liu LL, Song HT, Lin B, Hsu HY, Qin LP, Han T, Xin HL, Zhang QY (2018) Monotropein attenuates ovariectomy and LPS-induced bone loss in mice and decreases inflammatory impairment on osteoblast through blocking activation of NF-kappaB pathway. Chem Biol Interact 291:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.06.015
He YQ, Zhang Q, Shen Y, Han T, Zhang QL, Zhang JH, Lin B, Song HT, Hsu HY, Qin LP, Xin HL, Zhang QY (2018) Rubiadin-1-methyl ether from Morinda officinalis How. Inhibits osteoclastogenesis through blocking RANKL-induced NF-kappaB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 506(4):927–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.100
Zhan Y, Liang J, Tian K, Che Z, Wang Z, Yang X, Su Y, Lin X, Song F, Zhao J, Xu J, Liu Q, Zhou B (2019) Vindoline inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. Front Pharmacol 10:1587. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01587
Yuan G, Lu H, Yin Z, Dai S, Jia R, Xu J, Song X, Li L (2014) Effects of mixed subchronic lead acetate and cadmium chloride on bone metabolism in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 7(5):1378–1385
Qi S, Zheng H, Chen C, Jiang H (2019) Du-Zhong (Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.) cortex extract alleviates lead acetate-induced bone loss in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 187(1):172–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1362-6
Hou T, Zhang L, Yang X (2019) Ferulic acid, a natural polyphenol, protects against osteoporosis by activating SIRT1 and NF-kappaB in neonatal rats with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother 120:109205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109205
Jiang Y, Luo W, Wang B, Wang X, Gong P, Xiong Y (2020) Resveratrol promotes osteogenesis via activating SIRT1/FoxO1 pathway in osteoporosis mice. Life Sci 246:117422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117422
Ciccarone F, Di Leo L, Lazzarino G, Maulucci G, Di Giacinto F, Tavazzi B, Ciriolo MR (2020) Aconitase 2 inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 cells promoting mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and ROS/FoxO1-mediated autophagic response. Br J Cancer 122(2):182–193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0641-0
Mo X, Wang X, Ge Q, Bian F (2019) The effects of SIRT1/FoxO1 on LPS induced INS-1 cells dysfunction. Stress 22(1):70–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/10253890.2018.1501022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Liang, H., Li, Y. et al. Allicin Alleviates Lead-Induced Bone Loss by Preventing Oxidative Stress and Osteoclastogenesis Via SIRT1/FOXO1 Pathway in Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 237–243 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02136-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02136-5