Abstract
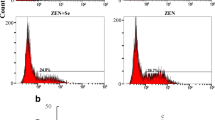
Recent studies have identified a new existence of a genetically programmed and regulated cell death characterized by necrotic cell death morphology, termed necroptosis. Lead (Pb) is a ubiquitously distributed environmental pollutant that is highly toxic to animals and human beings. However, no detailed report has been conducted on the necroptosis in lymphocytes caused by Pb. Selenium (Se), a trace element in the body, has been shown to exert cytoprotective effect in numerous pathological injury caused by heavy metals. Here, lymphocytes isolated from chicken spleen were divided into four groups, control group, Se group, Pb group, and Pb + Se co-treatment group to investigate the potential mechanism in the necroptosis triggered by Pb and in the antagonistic effect of Se on Pb toxicity. Flow cytometry analysis and AO/EB staining showed Pb caused typical necrosis characteristics in the lymphocytes. The expression of RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL was increased, whereas the level of caspase 8 was declined in Pb group, which proved the occurrence of necroptosis. Meanwhile, Pb exposure disrupted the antioxidant enzyme (SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT) balance, promoted the expression of MAPK/NF-κB pathway factors (ERK, JNK, p38, NF-κB, and TNF-α), and activated HSPs (HSP27, HSP40, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90). However, those Pb-induced changes were significantly alleviated in Se + Pb group. Our study revealed that Pb could trigger lymphocyte necroptosis through MAPK/NF-κB pathway activated by oxidative stress and that Se could antagonize Pb-induced necroptosis in chicken lymphocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams RJ, Holladay SD, Williams SM, Gogal RM Jr (2018) Environmental lead and wild birds: a review. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 245:157–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2017_9
Shacklette HT, Boerngen JG (1984) Element concentrations in soils and other surficial materials of the conterminous United States : an account of the concentrations of 50 chemical elements in samples of soils and other regoliths. In: U S geological survey professional paper, vol 1270. U.S. G.P.O., Washington
McConnell JR, Wilson AI, Stohl A, Arienzo MM, Chellman NJ, Eckhardt S, Thompson EM, Pollard AM, Steffensen JP (2018) Lead pollution recorded in Greenland ice indicates European emissions tracked plagues, wars, and imperial expansion during antiquity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(22):5726–5731. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721818115
Settle DM, Patterson CC (1980) Lead in albacore: guide to lead pollution in Americans. Science 207(4436):1167–1176. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6986654
Clark CS, Speranskaya O, Brosche S, Gonzalez H, Solis D, Kodeih N, Roda S, Lind C (2015) Total lead concentration in new decorative enamel paints in Lebanon, Paraguay and Russia. Environ Res 138:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.02.020
Berglund AM, Ingvarsson PK, Danielsson H, Nyholm NE (2010) Lead exposure and biological effects in pied flycatchers (Ficedula hypoleuca) before and after the closure of a lead mine in northern Sweden. Environ Pollut 158(5):1368–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.01.005
Gordus AG (1993) Lead concentrations in liver and kidneys of snow geese during an avian cholera epizootic in California. J Wildl Dis 29(4):582–586. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-29.4.582
Yang SM, Yoshioka M, Strovel JW, Urban DJ, Hu X, Hall MD, Jadhav A, Maloney DJ (2019) Lead optimization and efficacy evaluation of quinazoline-based BET family inhibitors for potential treatment of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29(10):1220–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.03.014
Yin K, Yang Z, Gong Y, Wang D, Lin H (2019) The antagonistic effect of Se on the Pb-weakening formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in chicken neutrophils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.033
Wang S, Zheng S, Zhang Q, Yang Z, Yin K, Xu S (2018) Atrazine hinders PMA-induced neutrophil extracellular traps in carp via the promotion of apoptosis and inhibition of ROS burst, autophagy and glycolysis. Environ Pollut 243(Pt A):282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.070
Jiao X, Yang K, An Y, Teng X, Teng X (2017) Alleviation of lead-induced oxidative stress and immune damage by selenium in chicken bursa of Fabricius. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(8):7555–7564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8329-y
Hanus J, Anderson C, Wang S (2015) RPE necroptosis in response to oxidative stress and in AMD. Ageing Res Rev 24(Pt B):286–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2015.09.002
Wang S, Li X, Wang W, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Application of transcriptome analysis: oxidative stress, inflammation and microtubule activity disorder caused by ammonia exposure may be the primary factors of intestinal microvilli deficiency in chicken. Sci Total Environ 696:134035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134035
Zhao H, Wang Y, Shao Y, Liu J, Wang S, Xing M (2018) Oxidative stress-induced skeletal muscle injury involves in NF-kappaB/p53-activated immunosuppression and apoptosis response in copper (II) or/and arsenite-exposed chicken. Chemosphere 210:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.165
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Chan FK, Kroemer G (2017) Necroptosis: mechanisms and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol 12:103–130. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-052016-100247
Li X, Chen M, Shi Q, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Hydrogen sulfide exposure induces apoptosis and necroptosis through lncRNA3037/miR-15a/BCL2-A20 signaling in broiler trachea. Sci Total Environ 699:134296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134296
Kearney CJ, Martin SJ (2017) An inflammatory perspective on necroptosis. Mol Cell 65(6):965–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.024
Zhang S, Tang MB, Luo HY, Shi CH, Xu YM (2017) Necroptosis in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential therapeutic target. Cell Death Dis 8(6):e2905. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.286
Han CH, Guan ZB, Zhang PX, Fang HL, Li L, Zhang HM, Zhou FJ, Mao YF, Liu WW (2018) Oxidative stress induced necroptosis activation is involved in the pathogenesis of hyperoxic acute lung injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(3):2178–2183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.100
Tummers B, Green DR (2017) Caspase-8: regulating life and death. Immunol Rev 277(1):76–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12541
Mizumura K, Justice MJ, Schweitzer KS, Krishnan S, Bronova I, Berdyshev EV, Hubbard WC, Pewzner-Jung Y, Futerman AH, Choi AMK, Petrache I (2018) Sphingolipid regulation of lung epithelial cell mitophagy and necroptosis during cigarette smoke exposure. FASEB J 32(4):1880–1890. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700571R
Zhang S, Che L, He C, Huang J, Guo N, Shi J, Lin Y, Lin Z (2019) Drp1 and RB interaction to mediate mitochondria-dependent necroptosis induced by cadmium in hepatocytes. Cell Death Dis 10(7):523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1730-y
Qu KC, Wang ZY, Tang KK, Zhu YS, Fan RF (2019) Trehalose suppresses cadmium-activated Nrf2 signaling pathway to protect against spleen injury. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 181:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.007
Li X, Xing M, Chen M, Zhao J, Fan R, Zhao X, Cao C, Yang J, Zhang Z, Xu S (2017) Effects of selenium-lead interaction on the gene expression of inflammatory factors and selenoproteins in chicken neutrophils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:447–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.017
Xu T, Gao X, Liu G (2016) The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead toxicity is related to the ion profile in chicken liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 169(2):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0422-4
Jin X, Xu Z, Zhao X, Chen M, Xu S (2017) The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial dynamics pathway in the chicken kidney. Chemosphere 180:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.130
Fu J, Yang T, Wang W, Xu S (2019) Effect of selenium antagonist lead-induced damage on Th1/Th2 imbalance in the peripheral blood lymphocytes of chickens. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 175:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.036
Hu X, Chi Q, Wang D, Chi X, Teng X, Li S (2018) Hydrogen sulfide inhalation-induced immune damage is involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and the Th1/Th2 imbalance in broiler bursa of Fabricius. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.029
Comans-Bitter WM, de Groot R, van den Beemd R, Neijens HJ, Hop WC, Groeneveld K, Hooijkaas H, van Dongen JJ (1997) Immunophenotyping of blood lymphocytes in childhood. Reference values for lymphocyte subpopulations. J Pediatr 130(3):388–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(97)70200-2
Tsiridis V, Petala M, Samaras P, Hadjispyrou S, Sakellaropoulos G, Kungolos A (2006) Interactive toxic effects of heavy metals and humic acids on Vibrio fischeri. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63(1):158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.04.005
Wu YS, Huang SL, Chung HC, Nan FH (2017) Bioaccumulation of lead and non-specific immune responses in white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) to Pb exposure. Fish Shellfish Immunol 62:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.01.011
Rahman MM, Hossain KFB, Banik S, Sikder MT, Akter M, Bondad SEC, Rahaman MS, Hosokawa T, Saito T, Kurasaki M (2019) Selenium and zinc protections against metal-(loids)-induced toxicity and disease manifestations: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:146–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.054
Zhao D, Zhang X (2018) Selenium antagonizes the lead-induced apoptosis of chicken splenic lymphocytes in vitro by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 182(1):119–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1088-x
Bakker OJ, van Santvoort H, Besselink MG, Boermeester MA, van Eijck C, Dejong K, van Goor H, Hofker S, Ahmed Ali U, Gooszen HG, Bollen TL, Dutch Pancreatitis Study G (2013) Extrapancreatic necrosis without pancreatic parenchymal necrosis: a separate entity in necrotising pancreatitis? Gut 62(10):1475–1480. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302870
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM, Green DR (2017) Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(2):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.149
Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P (2015) Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 517(7534):311–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14191
He S, Huang S, Shen Z (2016) Biomarkers for the detection of necroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(11–12):2177–2181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2192-3
Marmol I, Virumbrales-Munoz M, Quero J, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Fernandez L, Ochoa I, Cerrada E, Yoldi MJR (2017) Alkynyl gold(I) complex triggers necroptosis via ROS generation in colorectal carcinoma cells. J Inorg Biochem 176:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.08.020
Yang T, Cao C, Yang J, Liu T, Lei XG, Zhang Z, Xu S (2018) miR-200a-5p regulates myocardial necroptosis induced by Se deficiency via targeting RNF11. Redox Biol 15:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.025
Afonso MB, Rodrigues PM, Simao AL, Ofengeim D, Carvalho T, Amaral JD, Gaspar MM, Cortez-Pinto H, Castro RE, Yuan J, Rodrigues CM (2016) Activation of necroptosis in human and experimental cholestasis. Cell Death Dis 7(9):e2390. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.280
Wang S, Zhang Q, Zheng S, Chen M, Zhao F, Xu S (2019) Atrazine exposure triggers common carp neutrophil apoptosis via the CYP450s/ROS pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:551–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.029
Gong ZG, Wang XY, Wang JH, Fan RF, Wang L (2019) Trehalose prevents cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity by blocking Nrf2 pathway, restoring autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis. J Inorg Biochem 192:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.12.008
Wang LY, Fan RF, Yang DB, Zhang D, Wang L (2019) Puerarin reverses cadmium-induced lysosomal dysfunction in primary rat proximal tubular cells via inhibiting Nrf2 pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 162:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.10.016
Li Q, Wang W, Zhu Y, Chen Y, Zhang W, Yu P, Mao G, Zhao T, Feng W, Yang L, Wu X (2017) Structural elucidation and antioxidant activity a novel Se-polysaccharide from Se-enriched Grifola frondosa. Carbohydr Polym 161:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.041
Huang YC, Tsai MS, Hsieh PC, Shih JH, Wang TS, Wang YC, Lin TH, Wang SH (2017) Galangin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death in mice through inhibition of ERK and NF-kappaB signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 329:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.034
Sun W, Wu X, Gao H, Yu J, Zhao W, Lu JJ, Wang J, Du G, Chen X (2017) Cytosolic calcium mediates RIP1/RIP3 complex-dependent necroptosis through JNK activation and mitochondrial ROS production in human colon cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med 108:433–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.04.010
Chi Q, Wang D, Hu X, Li S, Li S (2019) Hydrogen sulfide gas exposure induces necroptosis and promotes inflammation through the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway in broiler spleen. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2019:8061823. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8061823
Geng J, Ito Y, Shi L, Amin P, Chu J, Ouchida AT, Mookhtiar AK, Zhao H, Xu D, Shan B, Najafov A, Gao G, Akira S, Yuan J (2017) Regulation of RIPK1 activation by TAK1-mediated phosphorylation dictates apoptosis and necroptosis. Nat Commun 8(1):359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00406-w
Wang W, Chen M, Jin X, Li X, Yang Z, Lin H, Xu S (2018) H2S induces Th1/Th2 imbalance with triggered NF-kappaB pathway to exacerbate LPS-induce chicken pneumonia response. Chemosphere 208:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.152
Shi Q, Wang W, Chen M, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Ammonia induces Treg/Th1 imbalance with triggered NF-kappaB pathway leading to chicken respiratory inflammation response. Sci Total Environ 659:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.375
Zhang Y, Su SS, Zhao S, Yang Z, Zhong CQ, Chen X, Cai Q, Yang ZH, Huang D, Wu R, Han J (2017) RIP1 autophosphorylation is promoted by mitochondrial ROS and is essential for RIP3 recruitment into necrosome. Nat Commun 8:14329. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14329
Kudva AK, Shay AE, Prabhu KS (2015) Selenium and inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 309(2):G71–G77. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00379.2014
Rayman MP (2012) Selenium and human health. Lancet 379(9822):1256–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61452-9
Su Y, Li S, Xin H, Li J, Li X, Zhang R, Li J, Bao J (2019) Proper cold stimulation starting at an earlier age can enhance immunity and improve adaptability to cold stress in broilers. Poult Sci. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez570
Zhao Y, Zhang C, Wei X, Li P, Cui Y, Qin Y, Wei X, Jin M, Kohama K, Gao Y (2015) Heat shock protein 60 stimulates the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via toll-like receptor 4 and ERK MAPK activation. Sci Rep 5:15352–15311. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15352
Zhang A, Guo Y, Zhang S, Fan X, Wang X, Zhou X, Yang K, Zhou H (2015) Cytokine effects and cellular signaling pathways of grass carp HSP70 in head kidney leukocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 46(2):550–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.07.016
Dai X, Nie G, Cao H, Xing C, Hu G, Zhang C (2019) In vivo assessment of molybdenum and cadmium co-induced the mRNA levels of heat shock proteins, inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in Shaoxing duck (Anas platyrhyncha) testicles. Poult Sci 98(11):5424–5431. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez328
Zhao XM, Chen Z, Zhao JB, Zhang PP, Pu YF, Jiang SH, Hou JJ, Cui YM, Jia XL, Zhang SQ (2016) Hsp90 modulates the stability of MLKL and is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Cell Death Dis 7:e2089. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.390
Funding
The research was supported by funds provided by the China Agriculture Research System-41-17 and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFD0500501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shiwen Xu and Gang Sun conceived of and designed the experiments. Jiayong Zhang and Xiaofang Hao performed the experiments. Jiayong Zhang analyzed the data and wrote the paper. Shiwen Xu assisted in critically revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Hao, X. & Xu, S. Selenium Prevents Lead-Induced Necroptosis by Restoring Antioxidant Functions and Blocking MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in Chicken Lymphocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 198, 644–653 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02094-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02094-y