Abstract
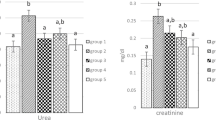
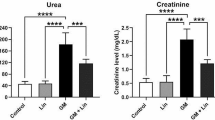
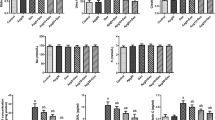
The present study was considered to assess the protective effects of boron (B) on gentamicin-induced oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines, and histopathological changes in rat kidneys. Rats were split into eight equal groups which were as follows: control (fed with low-boron diet); gentamicin group (100 mg/kg, i.p.); B5, B10, and B20 (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg B, i.p.) groups; gentamicin (100 mg/kg, i.p.) plus B5, B10, and B20 (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg B, i.p.) groups. B was given to rats 4 days before the gentamicin treatment and B administration was completed on the 14th day. Gentamicin administration was started on the 4th day and finished on the 12th day. Gentamicin increased malondialdehyde levels, while reduced glutathione levels in the blood and kidney. Furthermore, superoxide dismutase and catalase activities of erythrocyte were decreased. Besides, serum and kidney nitric oxide and 8-dihydroxyguanidine levels were increased by gentamicin. Additionally, serum levels and kidney mRNA expressions of TNF-α, NFκB, IL-1β, and IFN-γ were found to be the highest in the gentamicin group. Histopathologically, interstitial hemorrhage and tubular necrosis were detected in the kidneys of the gentamicin group. Nonetheless, B administration reversed gentamicin-induced lipid peroxidation, antioxidant status, and inflammation. In conclusion, B has a preventive effect against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and ameliorates kidney tissues of the rat.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lode H, Kemmerich B, Koeppe P (2012) Comparative clinical pharmacology of gentamicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 8:396–401
Martin J, Barras M, Ah Yui N, Kirkpatrick C, Kubler P, Norris R (2012) Gentamicin monitoring practices in teaching hospitals–time to undertake the necessary randomised controlled trial. J Clin Toxicol 2(8):1–5
Karahan I, Ateşşahin A, Yilmaz S, Ceribaşi AO, Sakin F (2005) Protective effect of lycopene on gentamicin-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicology 215:198–204
Khan SA, Priyamvada S, Farooq N, Khan S, Khan MW, Yusufi AN (2009) Protective effect of green tea extract on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative damage in rat kidney. Pharmacol Res 59:254–262
Lee IC, Kim SH, Lee SM, Baek HS, Moon C, Kim SH, Park SC, Kim HC, Kim JC (2012) Melatonin attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Arch Toxicol 86:1527–1536
Randjelovic P, Veljkovic S, Stojiljkovic N, Jankovic-Velickovic L, Sokolovic D, Stoiljkovic M, Ilic I (2012) Salicylic acid attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Sci World J 2012:1–6
Park JW, Bae EH, Kim IJ, Ma SK, Choi C, Lee J, Kim SW (2010) Renoprotective effects of paricalcitol on gentamicin-induced kidney injury in rats. Am J Physiol Physiol 298:301–313
Bae EH, Kim IJ, Joo SY, Kim EY, Choi JS, Kim CS, Ma SK, Lee J, Kim SW (2014) Renoprotective effects of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst 15:348–361
Nielsen FH (2018) Boron in aging and longevity. In: Trace elements and minerals in health and longevity. Springer, Cham, pp 163–177
Ince S, Erdogan M, Demirel HH, Agca Y, Dal G, Uguz C (2018) Boron enhances early embryonic gene expressions and improves fetal development of rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 50:34–46
Kucukkurt I, Akbel E, Karabag F, Ince S (2015) The effects of dietary boron compounds in supplemented diet on hormonal activity and some biochemical parameters in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 31:255–260
Türkez H, Geyikoğlu F, Tatar A, Keleş S, Özkan A (2007) Effects of some boron compounds on peripheral human blood. Zeitschrift fur Naturforsch - Sect C J Biosci 62:889–896
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Cigerci IH, Fidan AF, Eryavuz A (2010) The effects of dietary boric acid and borax supplementation on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant activity, and DNA damage in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 24:161–164
Çelikezen FÇ, Toğar B, Özgeriş FB, Izgi MS, Türkez H (2016) Cytogenetic and oxidative alterations after exposure of cultured human whole blood cells to lithium metaborate dehydrate. Cytotechnology 68(4):821–827
Coban FK, Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH, Hazman O (2015) Boron attenuates malathion-induced oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 38:391–399
Acaroz U, Ince S, Arslan-Acaroz D, Gurler Z, Demirel HH, Kucukkurt I, Eryavuz A, Kara R, Varol N, Zhu K (2019) Bisphenol-A induced oxidative stress, inflammatory gene expression, and metabolic and histopathological changes in male Wistar albino rats: Protective role of boron. Toxicol Res 8:262–269
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Acaroz U, Arslan-Acaroz D, Varol N (2019) Boron ameliorates arsenic-induced DNA damage, proinflammatory cytokine gene expressions, oxidant/antioxidant status, and biochemical parameters in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 33:1–7
Yildirim S, Celikezen FC, Oto G, Sengul E, Bulduk M, Tasdemir M, Cinar DA (2018) An investigation of protective effects of litium borate on blood and histopathological parameters in acute cadmium-induced rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 182(2):287–294
Acaroz U, Ince S, Arslan-Acaroz D, Gurler Z, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH, Arslan HO, Varol N, Zhu K (2018) The ameliorative effects of boron against acrylamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and metabolic changes in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 118:745–752
Hunt CD (1996) In: Watson RR (ed) Dietary boron deficiency and supplementation. CRC Press, Inc, New York, pp 229–254
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH, Acaroz DA, Akbel E, Cigerci IH (2014) Protective effects of boron on cyclophosphamide induced lipid peroxidation and genotoxicity in rats. Chemosphere 108:197–204
Ateşşahin A, Karahan I, Yilmaz S, Çeribaşi AO, Princci I (2003) The effect of manganese chloride on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res 48:637–642
Winterbourn CC, Hawkins RE, Brain M, Carrell RW (1975) The estimation of red cell superoxide activity. J Lab Clin Med 55:337–341
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Draper HH, Hardley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxidase dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Luck H (1955) Methods in analysis. In: Methods in analysis. Academy Press, London
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, pp 673–677
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA (2001) A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 5:62–71
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr A, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Drabkin DL, Austin JH (1935) Spectrophotometric studies. II. Preparations from washed 112, blood cells; nitric oxide hemoglobin and sulfhemoglobin. J Biol Chem:51–65
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Salem EA, Salem NA, Kamel M, Maarouf AM, Bissada NK, Hellstrom WJ, El-Adl M (2010) Amelioration of gentamicin nephrotoxicity by green tea extract in uninephrectomized rats as a model of progressive renal failure. Ren Fail 32:1210–1215
Abdelsameea AA, Mohamed AM, Amer MG, Attia SM (2016) Cilostazol attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 68:247–253
Kuhad A, Tirkey N, Pilkhwal S, Chopra K (2006) Effect of Spirulina, a blue green algae, on gentamicin-induced oxidative stres and renal dysfunction in rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 20:121–128
Dungca NT (2016) Protective effect of the methanolic leaf extract of Eclipta alba (L.) Hassk. (Asteraceae) against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Sprague Dawley rats. J Ethnopharmacol 184:18–21
Kasztan M, Jankowski M (2016) Involvement of P2 receptors in regulation of glomerular permeability to albumin by extracellular nucleotides of intra-/extra-glomerular origins. J Physiol Pharmacol 67:177–183
Moreira MA, Nascimento MA, Bozzo TA, Cintra A, da Silva SM, Dalboni MA, Mouro MG, Higa EM (2014) Ascorbic acid reduces gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats through the control of reactive oxygen species. Clin Nutr 33:296–301
Parlakpinar H, Tasdemir S, Polat A, Bay-Karabulut A, Vardi N, Ucar M, Acet A (2005) Protective role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (cape) on gentamicin-induced acute renal toxicity in rats. Toxicology 207:169–177
Yaman I, Balikci E (2010) Protective effects of nigella sativa against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:183–190
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M, Mehrad-Majd H, Mirhafez SR (2015) Thymoquinone ameliorates acute renal failure in gentamicin-treated adult male rats. Pharmacology 96:112–117
Mahmoud AM, Ahmed OM, Galaly SR (2014) Thymoquinone and curcumin attenuate gentamicininduced renal oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. EXCLI J 13:98–110
Fouad AA, Albualib WH, Zahranc A, Gomaa W (2014) Protective effect of naringenin against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 38:420–429
Yoshioka N, Nakashima H, Hosoda K, Eitaki Y, Shimada N, Omae K (2008) Urinary excretion of an oxidative stress marker, 8-hydroxyguanine (8-OH-GUA), among nickel-cadmium battery workers. J Occup Health 50:229–235
Gałazyn-Sidorczuk M, Brzóska MM, Jurczuk M, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2009) Oxidative damage to proteins and DNA in rats exposed to cadmium and/or ethanol. Chem Biol Interact 180:31–38
Iqbal M, Okazaki Y, Okada S (2009) Curcumin attenuates oxidative damage in animals treated with a renal carcinogen, ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA): Implications for cancer prevention. Mol Cell Biochem 324:157–164
Li Z, Piao F, Liu S, Wang Y, Qu S (2010) Subchronic exposure to arsenic trioxide-induced oxidative DNA damage in kidney tissue of mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:543–547
Balakumar P, Rohilla A, Thangathirupathi A (2010) Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: do we have a promising therapeutic approach to blunt it? Pharmacol Res 62:179–186
Sahu BD, Tatireddy S, Koneru M, Borkar RM, Kumar JM, Kuncha M, Srinivas R, Shyam-Sunder R, Sistla R (2014) Naringin ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and associated mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and inflammation in rats: possible mechanism of nephroprotection. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 277:8–20
Subramanian P, Anandan R, Jayapalan JJ, Hashim OH (2015) Hesperidin protects gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and inhibits inflammation mediated by NF-κB in rats. J Funct Foods 13:89–99
Veljković M, Pavlović DR, Stojiljković N, Ilić S, Petrović A, Jovanović I, Radenković M (2016) Morphological and morphometric study of protective effect of green tea in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Life Sci 147:85–91
Quirós Y, Blanco-Gozaloa V, Sanchez-Gallegoa JI, López-Hernandez FJ, Ruize J, Perez de Obanose MP, López-Novoab JM (2016) Cardiotrophin-1 therapy prevents gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicityin rats. Pharmacol Res 107:137–146
Armstrong TA, Spears JW (2003) Effect of boron supplementation of pig diets on the production of tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ. J Anim Sci 81:2552–2561
Hegazy AMS, Mosaed MM, Elshafey SH, Bayomy NA (2016) 6-Gingerol ameliorates gentamicin induced renal cortex oxidative stress and apoptosis in adult male albino rats. Tissue Cell 48:208–216
Stojiljkovic N, Stoiljkovic M, Randjelovic P, Veljkovic S, Mihailovic D (2012) Cytoprotective effect of vitamin C against gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:69–74
Sun X, Zhang B, Hong X, Zhang X, Kong X (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate, attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity by increasing prohibitin protein expression in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 707:147–154
Acknowledgment
Also, this study orally presented at 3rd International Turkic World Conference on Chemical Sciences and Technologies (ITWCCST 2017).
Funding
This study was financially supported by a grant (Project Number: 214O661) from the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ince, S., Kucukkurt, I., Demirel, H.H. et al. Boron, a Trace Mineral, Alleviates Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 195, 515–524 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01875-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01875-4