Abstract
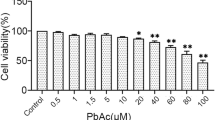
Nano-sized copper particles are widely used in various chemical, physical, and biological fields. However, earlier studies have shown that nano copper particles (40–100 μg/mL) can induce cell toxicity and apoptosis. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the role of nano copper in mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis in PK-15 cells. The cells were treated with different doses of nano copper (20, 40, 60, and 80 μg/mL) to determine the effects of apoptosis using acridine orange/ethidium bromide (AO/EB) fluorescence staining and a flow cytometry assay. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the PK-15 cells were examined using commercially available kits. Moreover, the mRNA levels of the Bax, Bid, Caspase-3, and CYCS genes were assessed by real-time PCR. The results revealed that nano copper exposure induced apoptosis and changed the mitochondrial membrane potential. In addition, nano copper significantly altered the levels of the Bax, Bid, Caspase-3, and CYCS genes at a concentration of 40 μg/mL. To summarize, nano copper significantly (P < 0.05) decreased the level of SOD and increased the level of MDA in PK-15 cells. Altogether, these results suggest that nano copper can play an important role in inducing the apoptotic pathway in PK-15 cells, which may be the mechanism by which nano copper induces nephrotoxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu P, Xu J, Liu S, Yang Z (2012) Nano copper induced apoptosis in podocytes via increasing oxidative stress. J Hazard Mater 241:279–286
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Xu J, Li Z, Xu P, Xiao L, Yang Z (2013) Nanosized copper oxide induces apoptosis through oxidative stress in podocytes. Arch Toxicol 87:1067–1073
Xia LI, Liu YM, Zhi-Ming QI, Dong SW, Liu SX et al (2010) Progress on nano-copper toxicity. Prog Vet Med 31:74–78 (in Chinese)
Gonzaleseguia A, Fu CM, Lu FY, Tufa L (2009) Effects of nanocopper on copper availability and nutrients digestibility, growth performance and serum traits of piglets. Livest Sci 126:122–129
Park JK, Kim JW, Yoo YB, Lee JY, Ohh SJ et al (2008) Effects of different sources of dietary chromium and copper on growth performances, nutrients digestibility, fecal Cr, Cu and Zn excretion in growing pigs. J Anim Sci Technol 50:355–362
Ognik K, Stępniowska A, Cholewińska E, Kozłowski K (2016) The effect of administration of copper nanoparticles to chickens in drinking water on estimated intestinal absorption of iron, zinc, and calcium. Poultry Sci 95:2045–2051
Zhao CY, Tan SX, Xiao XY, Qiu XS, Pan JQ, Tang ZX (2014) Effects of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth performance and antioxidative status in broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 160:361–367
Gonzales-Eguia A, Fu CM, Lu FY, Lien F (2010) Effects of nanocopper on copper availability and nutrients digestibility, growth performance and serum traits of piglets. Anaporc. http://agris.fao.org/aos/records/ES2010000374
Bala S, Lunney JK, Failla ML (1992) Effects of copper deficiency on t-cell mitogenic responsiveness and phenotypic profile of blood mononuclear cells from swine. Am J Vet Res 53:1231–1235
Prohaska JR, Failla ML (1993) Copper and immunity. Nutr Immunol, 309–332
Meng H, Zhen C, Xing G, Hui Y, Chen C et al (2007) Ultrahigh reactivity provokes nanotoxicity: explanation of oral toxicity of nano-copper particles. Toxicol Lett 175:102–110
Gomes SI, Novais SC, Gravato C, Guilhermino L, Scott-Fordsmand JJ et al (2012) Effect of Cu-nanoparticles versus one Cu-salt: analysis of stress biomarkers response in Enchytraeus albidus (Oligochaeta). Nanotoxicology 6:134–143
Turnlund JR, Scott KC, Peiffer GL, Jang AM, Keyes WR, Keen CL et al (1997) Copper status of young men consuming a low-copper diet. Am J Clin Nutr 65(1):72–78
Lei R, Wu C, Yang B, Ma H, Shi C et al (2008) Integrated metabolomics analysis of the nano-sized copper particle-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats: a rapid in vivo, screening method fornanotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharm 232:292–301
Lei R, Yang B, Wu C, Liao M, Ding R, Wang Q (2014) Dysfunction and oxidative damage in the liver and kidney of rats following exposure to copper nanoparticles for five consecutive days. Toxicol Res 4:351–364
Sarkar A, Das J, Manna P, Si PC (2011) Nano-copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in kidney via both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Toxicology 290:208–217
Hertel C, Terzi E, Hauser N, Jakob-Rotne R, Seelig J, Kemp JA (1997) Inhibition of the electrostatic interaction between beta-amyloid peptide and membranes prevents beta-amyloid-induced toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(17):9412–9416
Kolla N, Wei Z, Richardson JS, Li XM (2005) Amitriptyline and fluoxetine protect PC12 cells from cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. J Psychiatry Neurosci 30(3):196–201
Xu P, Xu J, Liu S, Ren G, Yang Z (2012) In vitro toxicity of nanosized copper particles in PC12 cells induced by oxidative stress. J Nanopart Res 14:906
Khan AZ, Kumbhar S, Hamid M, Afzal S, Parveen F, Liu Y, Shu H, Mengistu BM, Huang K (2016) Effects of selenium-enriched robiotics on heart lesions by influencing the mRNA expressions of selenoproteins and heat shock proteins in heat stressed broiler chickens. Pak Vet J 36(4):460–464
Zhuang Y, Liu P, Zhang CY, Ye S, Hu G, Cao HB (2016) Effect of cadmium on the concentration of ceruloplasmin and its mrna expression in goats under molybdenum stress. Pak Vet J 36(2):209–213
Christopher R, Gregor G (2003) Escherichia coli mechanisms of copper homeostasis in a changing environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:197–213
Miranda CL, Henderson MC, Dr B (1984) Influence of tansy ragwort (Senecio jacobaea), dietary copper, and feed restriction on the subcellular distribution of minerals in rat liver. Toxicol Appl Pharm 76:62–68
Zietz BP, Dieter HH, Lakomek M, Schneider H, Kessler-Gaedtke B, Dunkelberg H (2003) Epidemiological investigation on chronic copper toxicity to children exposed via the public drinking water supply. Sci Total Environ 302:127–144
Chen Z, Meng H, Xing G, Chen C, Zhao Y, Jia G, Wang T, Yuan H, Ye C, Zhao F, Chai Z, Zhu C, Fang X, Ma B, Wan L (2006) Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Toxicol Lett 163:109–120
Huang Z (2002) The chemical biology of apoptosis: exploring protein-protein interactions and the life and death of cells with small molecules. Chem Biol 9:1059–1072
Prakesch M, Poondra RR, Reddy PT, Arya P, Foster TL et al (2008) Chemical biology of apoptosis. Biochem Cell Biol 86:203–203
Fan CF, Xu HT, Lin XY, Yu JH, Wang EH (2011) A multiple marker analysis of apoptosis-associated protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer in a Chinese population. Folia Histochem Cyto 49:231–239
Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ, Hakem A et al (1998) Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell 94:739–750
Van LG, Saelens X, Van GM, Macfarlane M, Martin SJ, Vandenabeele P (2002) The role of mitochondrial factors in apoptosis: a Russian roulette with more than one bullet. Cell Death Differ 9:1031–1042
Esche C, Shurin GV, Kirkwood JM, Wang GQ, Rabinowich H et al (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-promoted expression of bcl-2 and inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome C release mediate resistance of mature dendritic cells to melanoma-induced apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res 7:974–979
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH, Thompson CB (2003) Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 10:709–717
Xiong X, Wei F, Lirong WU, Liu X (2012) Effects of environmental factors on ischemic cardiac myocyte apoptosis and expression of bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 in rats. J Guiyang Med Coll. (in Chinese)
Liu L, Wang SB, Zhao H, Liu M, Song NY et al (2008) Expression of Bax, Caspase-3 and cell apoptosis in human cervical intervertebral disc degeneration. J Fourth Military Med Uni 29:1192–1194 (in Chinese)
Mertens-Talcott SU, Percival SS (2005) Ellagic acid and quercetin interact synergistically with resveratrol in the induction of apoptosis and cause transient cell cycle arrest in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett 218:141–151
Brasacchio D, Noori T, House C, Brennan AJ, Simpson KJ et al (2014) A functional genomics screen identifies pcaf and ada3 as regulators of human granzyme b-mediated apoptosis and bid cleavage. Cell Death Differ 21:748–760
Inoue M, Nishikawa M, Sato E, Matsuno K, Sasaki J (1999) Synthesis of superoxide dismutase derivative that specifically accumulates in renal proximal tubule cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 368:354–360
Tsutsui H (2006) Mitochondrial oxidative stress and heart failure. Intern Med 45(13):809–813
Kuwabara M, Asanuma T, Niwa K, Inanami O (2008) Regulation of cell survival and death signals induced by oxidative stress. J Clin Biochem Nutr 43(2):51–57
Powers SK, Quindry JC, Kavazis AN (2008) Exercise-induced cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Free Radic Biol Med 44(2):193–201
Deres P, Halmosi R, Toth A, Kovacs K, Palfi A, Habon T, Czopf L, Kalai T, Hideg K, Sumegi B, Toth K (2005) Prevention of doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity by an experimental antioxidant compound. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 45(1):36–43
Rothstein JD, Bristol LA, Hosler B, Brown RH Jr, Kuncl RW (1994) Chronic inhibition of superoxide dismutase produces apoptotic death of spinal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(10):4155–4159
Troy CM, Shelanski ML (1994) Down-regulation of copper/ zinc superoxide dismutase causes apoptotic death in PC12 neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(14):6384–6387
Patel M (1998) Inhibition of neuronal apoptosis by a metalloporphyrin superoxide dismutase mimic. J Neurochem 71(3):1068–1074
Termini J (2000) Hydroperoxide-induced DNA damage and mutations. Mutat Res 450:107–124
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2014CFB244) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Program No. 2011PYO78).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZY Chang, ZY Li, H Zhang, and DH Zhou conceived and designed the experiments; H Zhang, MU Rehman, M Khalid, F Nabi, XX Wu, XX Tian, and XD Yuan contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools; and H Zhang, MU Rehman, ZY Chang, and RZ Abbas wrote the manuscript and handle the manuscript revisions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Chang, Z., Mehmood, K. et al. Nano Copper Induces Apoptosis in PK-15 Cells via a Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 181, 62–70 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1024-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1024-0