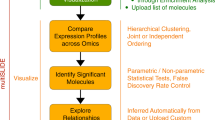
Abstract
Heatmaps are preferred visualization modes for biologists to display high-dimensional information from high-throughput omics data. Many software including website services and R packages are available to generate various types of customized heatmaps. Here, we describe oppHeatmap (omics pilot platform of heatmap), a new tool constructed to render different kinds of heatmaps through MATLAB. oppHeatmap is available for plotting ordinary heatmaps, hierarchical clustering, TreeMaps, microplates graph, sample correlation (full heatmap and upper and lower triangle parts), gene correlation (between columns or tables), and polar heatmaps. oppHeatmap can support the modification of borders, fonts, and colors to customize the final plots. oppHeatmap can not only read data from Microsoft Excel to generate specific heatmaps but also make Excel heatmaps by coloring each cell in Excel. The graphs can be stored in SVG (supported vector graph) format and modified by other SVG recognition software. oppHeatmap is designed by MATLAB AppDesigner with GUI (graphical user interface) operation. The program for oppHeatmap was available at https://github.com/HangZhouSheep/oppHeatmap.are diagramed by
Graphical Abstract
All kinds of heatmaps oppHeatmap. The main function of oppHeatmap is to enable visualization of two types of heatmaps and a total of 11 graphs. The first type is a heatmap with a polar or rectangular coordinate system, including ordinary heatmap, microplates graph, polar heatmap, and Excel heatmap. The last one involves writing the heatmap in Excel and others in MATLAB. The second type is with rearranged rows and columns, which includes hierarchical clustering, TreeMaps, and sample/gene correlation between columns or rows. All plots support row standardization for better color contrast. Eleven base functions implement heatmap plotting in the command line environment of MATLAB. GUI designed by AppDesigner supports the interactive construction of heatmaps.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The program of oppHeatmap was available at https://github.com/HangZhouSheep/oppHeatmap.
Abbreviations
- oppHeatmap:
-
Omics pilot platform of heatmap
- GUI:
-
Graphical user interface
- HCA:
-
Hierarchical cluster analysis
- HTML:
-
Hypertext markup language
- SVG:
-
Supported vector graph
References
Waugh, W., Allen, J., Wightman, J., Sims, A. J., & Beale, T. A. W. (2018). Novel signal noise reduction method through cluster analysis, applied to photoplethysmography. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2018, 6812404.
Zhuang, H., Cui, J., Liu, T., & Wang, H. (2020). A physical model inspired density peak clustering. PLoS One, 15(9), e0239406.
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Qiao, C., Liu, X., Hao, M., Shugart, Y. Y., Xiong, M., & Jin, L. (2018). Nuclear norm clustering: A promising alternative method for clustering tasks. Scientific Reports 8(1), 10873.
Sarikaya, A., Albers, D., Mitchell, J., & Gleicher, M. (2014). Visualizing validation of protein surface classifiers. Computer Graphics Forum, 33(3), 171–180.
Khomtchouk, B. B., Van Booven, D. J., & Wahlestedt, C. (2014). HeatmapGenerator: High performance RNAseq and microarray visualization software suite to examine differential gene expression levels using an R and C++ hybrid computational pipeline. Source Code for Biology and Medicine 9(1), 30.
Zhao, S., Guo, Y., Sheng, Q., & Shyr, Y. (2014). Advanced heat map and clustering analysis using heatmap3. BioMed Research International, 2014, 986048.
R, K. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps (2019-01-04). https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pheatmap/index.html.
Barter, R. L., & Yu, B. (2018). Superheat: An R package for creating beautiful and extendable heatmaps for visualizing complex data. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 27(4), 910–922.
Gu, Z., Eils, R., & Schlesner, M. (2016). Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics, 32(18), 2847–2849.
Galili, T., O’Callaghan, A., Sidi, J., & Sievert, C. (2018). heatmaply: An R package for creating interactive cluster heatmaps for online publishing. Bioinformatics, 34(9), 1600–1602.
Fernandez, N. F., Gundersen, G. W., Rahman, A., Grimes, M. L., Rikova, K., Hornbeck, P., & Ma’ayan, A. (2017). Clustergrammer, a web-based heatmap visualization and analysis tool for high-dimensional biological data. Scientific Data, 4, 170151.
de Hoon, M. J., Imoto, S., Nolan, J., & Miyano, S. (2004). Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics, 20(9), 1453–1454.
CIRCOS: http://www.circos.ca/
File Exchange: https://ww2.mathworks.cn/matlabcentral/fileexchange
Acknowledgements
We are so grateful for the selfless help from HSEN Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for oppHeatmap maintenance.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFF0703702) and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (32070605).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
1. Conception and design: Yang Zhang.
2. Administrative support: Hong Jin and Yang Zhang.
3. Data analysis and interpretation: Zening Wang.
4. Program writing: Yang Zhang and Yang Liu.
5. Manuscript writing: Jun Yao and Hang Liu.
6. Final approval of manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors consent to participate in the project.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to publish the paper.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ze-ning Wang and Jun Yao contributed equally.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 15.3 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zn., Yao, J., Liu, H. et al. oppHeatmap: Rendering Various Types of Heatmaps for Omics Data. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 2356–2366 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04652-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04652-1