Abstract
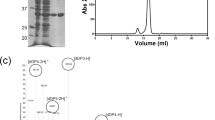
Alginate lyase can degrade alginate into oligosaccharides through β-elimination for various biological, biorefinery, and agricultural purposes. Here, we report a novel PL7 family exolytic alginate lyase VwAlg7A from marine bacteria Vibrio sp. W13 and achieve the heterologous expression in E. coli BL21 (DE3). VwAlg7A is 348aa with a calculated molecular weight of 36 kDa, containing an alginate lyase 2 domain. VwAlg7A exhibits specificity towards poly-guluronate. The optimal temperature and pH of VwAlg7A are 30 °C and 7.0, respectively. The activity of VwAlg7A can be significantly inhibited by the Ni2+, Zn2+, and NaCl. The Km and Vmax of VwAlg7A are 36.9 mg/ml and 395.6 μM/min, respectively. The ESI and HPAEC-PAD results indicate that VwAlg7A cleaves the sugar bond in an exolytic mode. Based on the molecular docking and mutagenesis results, we further confirmed that R98, H169, and Y303 are important catalytic residues.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barzkar, N., Sheng, R. L., Sohail, M., Jahromi, S. T., Babich, O., Sukhikh, S., & Nahavandi, R. (2022). Alginate lyases from marine bacteria: An enzyme ocean for sustainable future. Molecules, 27, 3375.
Lu, S., Na, K., Wei, J., Zhang, L., & Guo, X. (2022). Alginate oligosaccharides: The structure-function relationships and the directional preparation for application. Carbohydrate Polymers, 284, 119225.
Xu, F., Cha, Q. Q., Zhang, Y. Z., & Chen, X. L. (2021). Degradation and utilization of alginate by marine Pseudoalteromonas: A review. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87, 17.
Cheng, D., Jiang, C., Xu, J., Liu, Z., & Mao, X. (2020). Characteristics and applications of alginate lyases: A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 164, 1304–1320.
He, J. X., Li, R. X., Sun, X., Wang, W. X., Hu, J. E., Xie, H. G., & Yin, H. (2018). Effects of calcium alginate submicroparticles on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Polymers, 10, 1154.
Wang, M., Chen, L., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Potential applications of alginate oligosaccharides for biomedicine – A mini review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 271, 118408.
Hu, F., Cao, S., Li, Q., Zhu, B., & Yao, Z. (2021). Construction and biochemical characterization of a novel hybrid alginate lyase with high activity by module recombination to prepare alginate oligosaccharides. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 166, 1272–1279.
Inoue, A. (2018). In Marine enzymes and specialized metabolism, Pt B. In B. S. Moore (Ed.), Methods in Enzymology, 605, 499–524. Elsevier Academic Press Inc.
Garron, M.-L., & Cygler, M. (2010). Structural and mechanistic classification of uronic acid-containing polysaccharide lyases. Glycobiology, 20, 1547–1573.
Xu, F., Wang, P., Zhang, Y. Z., & Chen, X. L. (2018). Diversity of three-dimensional structures and catalytic mechanisms of alginate lyases. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 84(3), e02040–17.
Dharani, S. R., Srinivasan, R., Sarath, R., & Ramya, M. (2020). Recent progress on engineering microbial alginate lyases towards their versatile role in biotechnological applications. Folia Microbiologica, 65, 937–954.
Aarstad, O. A., Tondervik, A., Sletta, H., & Skjak-Braek, G. (2012). Alginate sequencing: An analysis of block distribution in alginates using specific alginate degrading enzymes. Biomacromolecules, 13, 106–116.
Wolfram, F., Kitova, E. N., Robinson, H., Walvoort, M. T., Codée, J. D., Klassen, J. S., & Howell, P. L. (2014). Catalytic mechanism and mode of action of the periplasmic alginate epimerase AlgG. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289, 6006–6019.
Kim, H. T., Chung, J. H., Wang, D., Lee, J., Woo, H. C., Choi, I.-G., & Kim, K. H. (2012). Depolymerization of alginate into a monomeric sugar acid using Alg17C, an exo-oligoalginate lyase cloned from Saccharophagus degradans 2-40. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 2233–2239.
Takagi, T., Yokoi, T., Shibata, T., Morisaka, H., Kuroda, K., & Ueda, M. (2016). Engineered yeast whole-cell biocatalyst for direct degradation of alginate from macroalgae and production of non-commercialized useful monosaccharide from alginate. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100, 1723–1732.
Xu, F., Chen, X.-L., Sun, X.-H., Dong, F., Li, C.-Y., Li, P.-Y., Ding, H., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y.-Z., & Wang, P. (2020). Structural and molecular basis for the substrate positioning mechanism of a new PL7 subfamily alginate lyase from the arctic. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 295, 16380–16392.
Lyu, Q., Zhang, K., Zhu, Q., Li, Z., Liu, Y., Fitzek, E., Yohe, T., Zhao, L., Li, W., Liu, T., Yin, Y., & Liu, W. (2018). Structural and biochemical characterization of a multidomain alginate lyase reveals a novel role of CBM32 in CAZymes. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj, 1862, 1862–1869.
Kawai, S., & Hashimoto, W. (2022). 4-Deoxy-l-erythro-5-hexoseulose uronate (DEH) and DEH reductase: Key molecule and enzyme for the metabolism and utilization of alginate. Molecules, 27, 338.
Kawai, S., Ohashi, K., Yoshida, S., Fujii, M., Mikami, S., Sato, N., & Murata, K. (2014). Bacterial pyruvate production from alginate, a promising carbon source from marine brown macroalgae. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 117, 269–274.
Lim, H. G., Kwak, D. H., Park, S., Woo, S., Yang, J. S., Kang, C. W., Kim, B., Noh, M. H., Seo, S. W., & Jung, G. Y. (2019). Vibrio sp. dhg as a platform for the biorefinery of brown macroalgae. Nature Communications, 10, 1–9.
Wargacki, A., Leonard, E., Win, M., Regitsky, D., Santos, C., Kim, P., Cooper, S., Raisner, R., Herman, A., Sivitz, A., Lakshmanaswamy, A., Kashiyama, Y., Baker, D., & Yoshikuni, Y. (2012). An engineered microbial platform for direct biofuel production from brown macroalgae. Science, 335, 308–313.
Enquist-Newman, M., Faust, A. M., Bravo, D., Santos, C., Raisner, R., Hanel, A., Sarvabhowman, P., Le, C., Regitsky, D., Cooper, S., Peereboom, L., Clark, A., Martinez, Y., Goldsmith, J., Cho, M., Donohoue, P., Luo, L., Lamberson, B., Tamrakar, P., & Yoshikuni, Y. (2013). Efficient ethanol production from brown macroalgae sugars by a synthetic yeast platform. Nature, 505, 239–243.
Doi, H., Tokura, Y., Mori, Y., Mori, K., Asakura, Y., Usuda, Y., Fukuda, H., & Chinen, A. (2017). Identification of enzymes responsible for extracellular alginate depolymerization and alginate metabolism in Vibrio algivorus. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 101, 1581–1592.
Takagi, T., Sasaki, Y., Motone, K., Shibata, T., Tanaka, R., Miyake, H., Mori, T., Kuroda, K., & Ueda, M. (2017). Construction of bioengineered yeast platform for direct bioethanol production from alginate and mannitol. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 101, 6627–6636.
Zhang, K., Li, Z., Zhu, Q., Cao, H., He, X., Zhang, X. H., Liu, W., & Lyu, Q. (2022). Determination of oligosaccharide product distributions of PL7 alginate lyases by their structural elements. Communications Biology, 5, 1–12.
Zhu, B. W., Li, K. K., Wang, W. X., Ning, L. M., Tan, H. D., Zhao, X. M., & Yin, H. (2019). Preparation of trisaccharides from alginate by a novel alginate lyase Alg7A from marine bacterium Vibrio sp. W13. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 139, 879–885.
Clark, M., Cramer, R. D., III, & Van Opdenbosch, N. (1989). Validation of the general purpose tripos 5.2 force field. Journal of Computational Chemistry., 10, 982–1012.
Zhu, B., & Yin, H. (2015). Alginate lyase: Review of major sources and classification, properties, structure-function analysis and applications. Bioengineered, 6, 125–131.
Mizutani, H., Sugawara, H., Buckle, A. M., Sangawa, T., Miyazono, K.-i., Ohtsuka, J., Nagata, K., Shojima, T., Nosaki, S., Xu, Y., Wang, D., Hu, X., Tanokura, M., & Yura, K. (2017). REFOLDdb: A new and sustainable gateway to experimental protocols for protein refolding. BMC Structural Biology, 17, 1–8.
Rosano, G. L., & Ceccarelli, E. A. (2014). Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 172.
Sadeghi, S., Deshpande, S., Vallerinteavide Mavelli, G., Aksoyoglu, A., Bafna, J., Winterhalter, M., Kini, R. M., Lane, D. P., & Drum, C. L. (2021). A general approach to protein folding using thermostable exoshells. Nature Communications, 12, 1–15.
Oh, E., Becker, A. H., Sandikci, A., Huber, D., Chaba, R., Gloge, F., Nichols, R. J., Typas, A., Gross, C. A., Kramer, G., Weissman, J. S., & Bukau, B. (2011). Selective ribosome profiling reveals the cotranslational chaperone action of trigger factor in vivo. Cell, 147, 1295–1308.
Tian, Y., Ban, X., Li, C., Gu, Z., & Li, Z. (2022). Modulation of Flexible loops in catalytic cavities reveals the thermal activation mechanism of a glycogen-debranching enzyme. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 70, 13358–13366.
Thomas, F., Lundqvist, L. C. E., Jam, M., Jeudy, A., Barbeyron, T., Sandstrom, C., Michel, G., & Czjzek, M. (2013). Comparative characterization of two marine alginate lyases from Zobellia galactanivorans reveals distinct modes of action and exquisite adaptation to their natural substrate. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 23021–23037.
Arntzen, M., Pedersen, B., Klau, L. J., Stokke, R., Oftebro, M., Antonsen, S. G., Fredriksen, L., Sletta, H., Aarstad, O. A., Aachmann, F. L., Horn, S. J., & Eijsink, V. G. H. (2021). Alginate degradation: Insights obtained through characterization of a thermophilic exolytic alginate lyase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87, e02399–20.
Ochiai, A., Yamasaki, M., Mikami, B., Hashimoto, W., & Murata, K. (2010). Crystal structure of exotype alginate lyase atu3025 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 24519–24528.
Park, D., Jagtap, S., & Nair, S. K. (2014). Structure of a PL17 family alginate lyase demonstrates functional similarities among exotype depolymerases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289, 8645–8655.
Qin, H.-M., Miyakawa, T., Inoue, A., Nishiyama, R., Nakamura, A., Asano, A., Ojima, T., & Tanokura, M. (2018). Structural basis for controlling the enzymatic properties of polymannuronate preferred alginate lyase FlAlyA from the PL-7 family. Chemical Communications, 54, 555–558.
Li, H., Huang, X., Yao, S., Zhang, C., Hong, X., Wu, T., Jiang, Z., Ni, H., & Zhu, Y. (2022). Characterization of a bifunctional and endolytic alginate lyase from Microbulbifer sp. ALW1 and its application in alginate oligosaccharides production from Laminaria japonica. Protein Expression and Purification, 200, 106171.
Xu, X., Zeng, D., Wu, D., & Lin, J. (2021). Single-point mutation near active center increases substrate affinity of alginate lyase AlgL-CD. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 193, 1513–1531.
Cao, S. S., Li, L., Zhu, B. W., & Yao, Z. (2022). Biochemical characterization and elucidation of the hybrid action mode of a new psychrophilic and cold-tolerant alginate lyase for efficient preparation of alginate oligosaccharides. Marine Drugs, 20, 506.
Bazeera Ferdhous, P., Aanandhalakshmi, R., Ramya, P., & Vanavil, B. (2022). Scrutiny of metal ion binding sites in different alginate lyases through in silico analysis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 194, 124–147.
Funding
This work was supported by the Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Fund-Key&Major Subject (2020JJ25CY017); Liaoning Provincial Marine Economic Development Project (2022-47); ANSO Collaborative Research Program (ANSO-CR-KP-2020-14); Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (2020-MS-025); and Outstanding Member Fund of CAS Youth Innovation Promotion Association (Y201939).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by ZBX, FXZ, and JYX. Data collection and analysis were performed by ZBX. Method development was performed by KKL, TL, MZ, and HY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ZBX and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Funding acquisition and supervision were performed by HY. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable
Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Z., Li, K., Li, T. et al. Characterization and Mechanism Study of a Novel PL7 Family Exolytic Alginate Lyase from Marine Bacteria Vibrio sp. W13. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 68–84 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04483-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04483-0