Abstract
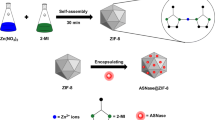
In this study, nitrilase (Nit) was immobilized in zeolite imidazole framework-90 (ZIF-90) by one-pot biomimetic mineralization strategy. The structure, morphology and functional groups of ZIF-90 and immobilized enzyme Nit@ZIF-90 were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM)/energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Circular dichroism (CD) proved that the immobilized method of encapsulation in ZIF-90 could effectively maintain the intrinsic conformation of Nit. Meanwhile, the stability and reusability of Nit@ZIF-90 were systematically evaluated. Compared with the free enzyme, the thermal, pH and organic solvents stability of Nit@ZIF-90 were significantly increased. Further, Nit@ZIF-90 exhibited better reusability during the hydrolysis of acrylonitrile and retained 48.34% of the initial activity after 10 cycles. Besides, the Ni@ZIF-90 had preferable storage stability, which showed a high degree of residual activity (more than 64 %) after storage at 4 °C for 7 d. The improved stability and reusability of the Nit@ZIF-90 implied that it could be used as a potential effective biocatalyst for hydrolysis of nitrile compounds in industrial application.









Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability Statements
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Gupta, N., Balomajumder, C., & Agarwal, V. K. (2010). Enzymatic mechanism and biochemistry for cyanide degradation: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176, 1–13.
Bhalla, T. C., Kumar, V., Kumar, V., Thakur, N., & Savitri. (2018). Nitrile Metabolizing Enzymes in Biocatalysis and Biotransformation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 185, 925–946.
Rucka, L., Chmatal, M., Kulik, N., Petraskova, L., Pelantova, H., Novotny, P., Prihodova, R., Patek, M., & Martinkova, L. (2019). Genetic and Functional Diversity of Nitrilases in Agaricomycotina. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, 5990.
Gong, J. S., Lu, Z. M., Li, H., Shi, J. S., Zhou, Z. M., & Xu, Z. H. (2012). Nitrilases in nitrile biocatalysis: recent progress and forthcoming research. Microbial Cell Factories, 11, 1–18.
Nigam, V. K., Arfi, T., Kumar, V., & Shukla, P. (2017). Bioengineering of Nitrilases Towards Its Use as Green Catalyst: Applications and Perspectives. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 57, 131–138.
Vesela, A. B., Franc, M., Pelantova, H., Kubac, D., Vejvoda, V., Sulc, M., Bhalla, T. C., Mackova, M., Lovecka, P., Janu, P., Demnerova, K., & Martinkova, L. (2010). Hydrolysis of benzonitrile herbicides by soil actinobacteria and metabolite toxicity. Biodegradation, 21, 761–770.
Roszak, M., Jablonska, J., Stachurska, X., Dubrowska, K., Kajdanowicz, J., Golebiewska, M., Kiepas-Kokot, A., Osinska, B., Augustyniak, A., & Karakulska, J. (2021). Development of an Autochthonous Microbial Consortium for Enhanced Bioremediation of PAH-Contaminated Soil. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 162–177.
Cui, J. D., Cui, L. L., Jia, S. R., Su, Z. G., & Zhang, S. P. (2016). Hybrid Cross-Linked Lipase Aggregates with Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Robust and Recyclable Biocatalysis for the Epoxidation of Oleic Acid. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64, 7179–7187.
Cui, J. D., Zhao, Y. M., Liu, R. L., Zhong, C., & Jia, S. R. (2016). Surfactant-activated lipase hybrid nanoflowers with enhanced enzymatic performance. Scientific Reports, 6, 27928.
Cui, J. D., Ren, S. Z., Lin, T., Feng, Y. X., & Jia, S. R. (2018). Shielding effects of Fe3+-tannic acid nanocoatings for immobilized enzyme on magnetic Fe3O4@silica core shell nanosphere. Chemical Engineering Journal, 343, 629–637.
Huang, S. M., Kou, X. X., Shen, J., Chen, G. S., & Ouyang, G. F. (2020). "Armor-Plating" Enzymes with Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 59, 8786–8798.
Liang, K., Ricco, R., Doherty, C. M., Styles, M. J., Bell, S., Kirby, N., Mudie, S., Haylock, D., Hill, A. J., Doonan, C. J., & Falcaro, P. (2015). Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules. Nature Communications, 6, 1–8.
Wang, Q., & Astruc, D. (2020). State of the Art and Prospects in Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based and MOF-Derived Nanocatalysis. Chemical Reviews, 120, 1438–1511.
Lu, G., Li, S. Z., Guo, Z., Farha, O. K., Hauser, B. G., Qi, X. Y., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Han, S. Y., Liu, X. G., DuChene, J. S., Zhang, H., Zhang, Q. C., Chen, X. D., Ma, J., Loo, S. C., Wei, W. D., Yang, Y. H., Hupp, J. T., & Huo, F. W. (2012). Imparting functionality to a metal-organic framework material by controlled nanoparticle encapsulation. Nature Chemistry, 4, 310–316.
Lyu, F., Zhang, Y., Zare, R. N., Ge, J., & Liu, Z. (2014). One-pot synthesis of protein-embedded metal-organic frameworks with enhanced biological activities. Nano Letters, 14, 5761–5765.
Cui, J. D., Feng, Y. X., Lin, T., Tan, Z. L., Zhong, C., & Jia, S. (2017). Mesoporous Metal-Organic Framework with Well-Defined Cruciate Flower-Like Morphology for Enzyme Immobilization. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 10587–10594.
Du, Y. J., Jia, X. T., Zhong, L., Jiao, Y., Zhang, Z. J., Wang, Z. Y., Feng, Y. X., Bilal, M., Cui, J. D., & Jia, S. R. (2022). Metal-organic frameworks with different dimensionalities: An ideal host platform for enzyme@MOF composites. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 454, 214327.
Zhou, J., Li, M. H., Hou, Y. H., Luo, Z., Chen, Q. F., Cao, H. X., Huo, R. L., Xue, C. C., Sutrisno, L., Hao, L., Cao, Y., Ran, H. T., Lu, L., Li, K., & Cai, K. Y. (2018). Engineering of a Nanosized Biocatalyst for Combined Tumor Starvation and Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano, 12, 2858–2872.
Lin, H., Chen, Y., & Shi, J. L. (2018). Nanoparticle-triggered in situ catalytic chemical reactions for tumour-specific therapy. Chemical Society Reviews, 47, 1938–1958.
Gao, X., Ding, Y., Sheng, Y. D., Hu, M. C., Zhai, Q. G., Li, S. N., Jiang, Y. C., & Chen, Y. (2019). Enzyme Immobilization in MOF-derived Porous NiO with Hierarchical Structure: An Efficient and Stable Enzymatic Reactor. ChemCatChem, 11, 2828–2836.
Gkaniatsou, E., Sicard, C., Ricoux, R., Benahmed, L., Bourdreux, F., Zhang, Q., Serre, C., Mahy, J. P., & Steunou, N. (2018). Enzyme Encapsulation in Mesoporous Metal-Organic Frameworks for Selective Biodegradation of Harmful Dye Molecules. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, 57, 16141–16146.
Chen, G. S., Kou, X. X., Huang, S. M., Tong, L. J., Shen, Y. J., Zhu, W. S., Zhu, F., & Ouyang, G. F. (2020). Modulating the Biofunctionality of Metal-Organic-Framework-Encapsulated Enzymes through Controllable Embedding Patterns. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 59, 2867–2874.
Chen, G. S., Huang, S. M., Kou, X. X., Wei, S. B., Huang, S. Y., Jiang, S. Q., Shen, J., Zhu, F., & Ouyang, G. F. (2019). A Convenient and Versatile Amino-Acid-Boosted Biomimetic Strategy for the Nondestructive Encapsulation of Biomacromolecules within Metal-Organic Frameworks. Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, 58, 1463–1467.
Lian, X. Z., & Zhou, H. C. (2018). High efficiency and long-term intracellular activity of an enzymatic nanofactory based on metal-organic frameworks. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, 8, 2075.
Feng, Y. X., Zhong, L., Bilal, M., Tan, Z. L., Hou, Y., Jia, S. R., & Cui, J. D. (2018). Enzymes@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Protection Nanocoating: Stability and Acid-Resistant Evaluation. Polymers (Basel), 11, 27.
Nadar, S. S., Vaidya, L., & Rathod, V. K. (2020). Enzyme embedded metal organic framework (enzyme-MOF): De novo approaches for immobilization. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 149, 861–876.
Liang, S., Wu, X. L., Xiong, J., Zong, M. H., & Lou, W. Y. (2020). Metal-organic frameworks as novel matrices for efficient enzyme immobilization: An update review. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 406, 213149.
Liang, X., Li, Q., Shi, Z. Y., Bai, S. W., & Li, Q. S. (2020). Immobilization of urease in metal–organic frameworks via biomimetic mineralization and its application in urea degradation. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 28, 2173–2180.
Wang, Y. X., Zhang, N. N., Tan, D. M., Qi, Z. H., & Wu, C. Z. (2020). Facile Synthesis of Enzyme-Embedded Metal-Organic Frameworks for Size-Selective Biocatalysis in Organic Solvent. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8, 714.
Li, P., Moon, S. Y., Guelta, M. A., Lin, L., Gomez Gualdron, D. A., Snurr, R. Q., Harvey, S. P., Hupp, J. T., & Farha, O. K. (2016). Nanosizing a Metal-Organic Framework Enzyme Carrier for Accelerating Nerve Agent Hydrolysis. ACS Nano, 10, 9174–9182.
Li, S., Dharmarwardana, M., Welch, R. P., Benjamin, C. E., Shamir, A. M., Nielsen, S. O., & Gassensmith, J. J. (2018). Investigation of Controlled Growth of Metal-Organic Frameworks on Anisotropic Virus Particles. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10, 18161–18169.
Lian, X. Z., Fang, Y., Joseph, E., Wang, Q., Li, J. L., Banerjee, S., Lollar, C., Wang, X., & Zhou, H. C. (2017). Enzyme-MOF (metal-organic framework) composites. Chemical Society Reviews, 46, 3386–3401.
Park, K. S., Ni, Z., Côté, A. P., Choi, J. Y., Huang, R. D., Uribe-Romo, F. J., Chae, H. K., O’Keeff, M., & Yaghi, O. M. (2006). Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. PNAS, 103, 10186–10191.
Liang, W., Xu, H., Carraro, F., Maddigan, N. K., Li, Q., Bell, S. G., Huang, D. M., Tarzia, A., Solomon, M. B., Amenitsch, H., Vaccari, L., Sumby, C. J., Falcaro, P., & Doonan, C. J. (2019). Enhanced Activity of Enzymes Encapsulated in Hydrophilic Metal-Organic Frameworks. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 141, 2348–2355.
Taghizadeh, T., Ameri, A., Talebian-Kiakalaieh, A., Mojtabavi, S., Ameri, A., Forootanfar, H., Tarighi, S., & Faramarzi, M. A. (2021). Lipase@zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-90: A highly stable and recyclable biocatalyst for the synthesis of fruity banana flavour. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 166, 1301–1311.
Shieh, F. K., Wang, S. C., Leo, S. Y., & Wu, K. C. (2013). Water-based synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-90 (ZIF-90) with a controllable particle size. Chemistry, 19, 11139–11142.
Zou, R. F., Gong, Q. Y., Shi, Z. Z., Zheng, J. P., Xing, J., Liu, C., Jiang, Z. Q., & Wu, A. G. (2020). A ZIF-90 nanoplatform loaded with an enzyme-responsive organic small-molecule probe for imaging the hypoxia status of tumor cells. Nanoscale, 12, 14870–14881.
Zou, Y. L., Liu, X. Y., & Zhang, H. X. (2021). A dual enzyme-containing microreactor for consecutive digestion based on hydrophilic ZIF-90 with size-selective sheltering. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 197, 111422.
Luo, H., Fan, L., Chang, Y. H., Ma, J. W., Yu, H. M., & Shen, Z. Y. (2010). Gene cloning, overexpression, and characterization of the nitrilase from Rhodococcus rhodochrous tg1-A6 in E. coli. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 393–400.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Xie, W. L., & Wan, F. (2019). Guanidine post-functionalized crystalline ZIF-90 frameworks as a promising recyclable catalyst for the production of biodiesel via soybean oil transesterification. Energy Conversion and Management, 198, 111922.
Bhattacharjee, S., Lee, Y. R., & Ahn, W. S. (2015). Post-synthesis functionalization of a zeolitic imidazolate structure ZIF-90: a study on removal of Hg(II) from water and epoxidation of alkenes. Crystengcomm, 17, 2575–2582.
Nadar, S. S., & Rathod, V. K. (2020). Immobilization of proline activated lipase within metal organic framework (MOF). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 152, 1108–1112.
Wu, X. L., Yang, C., & Ge, J. (2017). Green synthesis of enzyme/metal-organic framework composites with high stability in protein denaturing solvents. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 4, 1–8.
Shieh, F. K., Wang, S. C., Yen, C. I., Wu, C. C., Dutta, S., Chou, L. Y., Morabito, J. V., Hu, P., Hsu, M. H., Wu, K. C., & Tsung, C. K. (2015). Imparting functionality to biocatalysts via embedding enzymes into nanoporous materials by a de novo approach: size-selective sheltering of catalase in metal-organic framework microcrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137, 4276–4279.
Shi, J. F., Wang, X. L., Zhang, S. H., Tang, L., & Jiang, Z. Y. (2016). Enzyme-conjugated ZIF-8 particles as efficient and stable Pickering interfacial biocatalysts for biphasic biocatalysis. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 4, 2654–2661.
Nadar, S. S., & Rathod, V. K. (2017). Facile synthesis of glucoamylase embedded metal-organic frameworks (glucoamylase-MOF) with enhanced stability. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 95, 511–519.
Vaidya, L. B., Nadar, S. S., & Rathod, V. K. (2020). Entrapment of surfactant modified lipase within zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)-8. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 146, 678–686.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22078019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hui Peng, Yanhong Chang and Hui Luo contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Hui Peng, Wenge Dong, Qiwei Chen, Haiyan Song, Hongxu Sun and Ren Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hui Peng, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Dong, W., Chen, Q. et al. Encapsulation of Nitrilase in Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-90 to Improve Its Stability and Reusability. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 3527–3540 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03890-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03890-z