Abstract
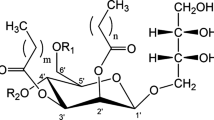
DHA-rich medium- and long-chain triacylglycerols (MLCT) were produced by lipase-catalyzed acidolysis of microbial oil from Schizochytrium sp. with medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA). Four commercial lipases, i.e., NS40086, Novozym 435, Lipozyme RM IM, and Lipozyme TL IM were screened based on their activity and fatty acid specificity. The selected conditions for MLCT synthesis were Lipozyme RM IM as catalyst, reaction time 6 h, lipase load 8 wt%, substrate molar ratio (MCFA/microbial oil) 3:1, and temperature 55 °C. Under the selected conditions, the lipase could be reused successively for 17 cycles without significant loss of lipase activity. The obtained product contained 27.53% MCFA, 95.29% at sn-1,3 positions, and 44.70% DHA, 69.77% at sn-2 position. Fifty-nine types of triacylglycerols (TAG) were identified, in which 35 types of TAG contained MCFA, the content accounting for 55.35%. This product enriched with DHA at sn-2 position and MCFA at sn-1,3 positions can improve its digestion and absorption under an infant’s digestive system, and thus has potential to be used in infant formula to increase the bioavailability of DHA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lauritzen, L., Brambilla, P., Mazzocchi, A., Harsløf, L., Ciappolino, V., & Agostoni, C. (2016). DHA effects in brain development and function. Nutrients, 8, 1–17.
Schuchardt, J. P., & Hahn, A. (2011). In D. Benton (Ed.), Lifetime nutritional influences on cognition, Behaviour and Psychiatric Illness (pp. 32–77). Philadelphia, PA: Woodhead Publishing.
Fernandes, F. S., Sardinha, F. L. C., Badia-Villanueva, M., Carulla, P., Herrera, E., & Tavares do Carmo, M. G. (2012). Dietary lipids during early pregnancy differently influence adipose tissue metabolism and fatty acid composition in pregnant rats with repercussions on pup’s development. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, 86, 167–174.
Guesnet, P., & Alessandri, J. M. (2011). Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the developing central nervous system (CNS)—implications for dietary recommendations. Biochimie, 93, 7–12.
Calder, P. C. (2012). Mechanisms of action of (n-3) fatty acids. The Journal of Nutrition, 142, 592–599.
Lauritzen, L., Hansen, H. S., Jørgensen, M. H., & Michaelsen, K. F. (2001). The essentiality of long chain n-3 fatty acids in relation to development and function of the brain and retina. Progress in Lipid Research, 40(1-2), 1–94.
Martin, C. R., DaSilva, D. A., Cluette-Brown, J. E., DiMonda, C., Hamill, A., Bhutta, A. Q., Coronel, E., Wilschanski, M., Stephens, A. J., Driscoll, D. F., Bistrian, B. R., Ware, J. H., Zaman, M. M., & Freedman, S. D. (2011). Decreased postnatal docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid blood levels in premature infants are associated with neonatal morbidities. The Journal of Pediatrics, 159, 743–749.
Heird, W. C. (2001). The role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in term and preterm infants and breastfeeding mothers. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 48, 173–188.
Brenna, J. T., Varamini, B., Jensen, R. G., Diersen-Schade, D. A., Boettcher, J. A., & Arterburn, L. M. (2007). Docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid concentrations in human breast milk worldwide. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 85, 1457–1464.
Ballard, O., & Morrow, A. L. (2013). Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 60(1), 49–74.
Zou, X. Q., Guo, Z., Huang, J. H., Jin, Q. Z., Cheong, L. Z., Wang, X. G., & Xu, X. B. (2012). Human milk fat globules from different stages of lactation: a lipid composition analysis and microstructure characterization. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(29), 7158–7167.
Soumanou, M. M., Pérignon, M., & Villeneuve, P. (2013). Lipase-catalyzed interesterification reactions for human milk fat substitutes production: a review. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 115, 270–285.
Xu, X. B. (2000). Production of specific-structured triacylglycerols by lipase-catalyzed reactions: a review. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 102, 287–303.
Zou, X., Ali, A. H., Abed, S. M., & Guo, Z. (2017). Current knowledge of lipids in human milk and recent innovations in infant formulas. Current Opinion in Food Science, 16, 28–39.
Jensen, R. G. (1996). The lipids in human milk. Progress in Lipid Research, 35(1), 53–92.
Zou, L., Pande, G., & Akoh, C. C. (2016). Infant formula fat analogs and human milk fat: new focus on infant developmental needs. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 7, 139–165.
Uauy, R., Hoffman, D. R., Mena, P., Llanos, A., & Birch, E. E. (2003). Term infant studies of DHA and ARA supplementation on neurodevelopment: results of randomized controlled trials. The Journal of Pediatrics, 143, 17–25.
Hoffman, D. R., Birch, E. E., Castañeda, Y. S., Fawcett, S. L., Wheaton, D. H., Birch, D. G., & Uauy, R. (2003). Visual function in breast-fed term infants weaned to formula with or without long-chain polyunsaturates at 4 to 6 months: a randomized clinical trial. The Journal of Pediatrics, 142, 669–677.
Innis, S. M., Adamkin, D. H., Hall, R. T., Kalhan, S. C., Lair, C., Lim, M., Stevens, D. C., Twist, P. F., Diersen-Schade, D. A., Harris, C. L., Merkel, K. L., & Hansen, J. W. (2002). Docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid enhance growth with no adverse effects in preterm infants fed formula. The Journal of Pediatrics, 140(5), 547–554.
Bourlieu, C., Ménard, O., Bouzerzour, K., Mandalari, G., Macierzanka, A., Mackie, A. R., & Dupont, D. (2014). Specificity of infant digestive conditions: some clues for developing relevant in vitro models. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 54(11), 1427–1457.
Armand, M., Hamosh, M., Mehta, N. R., Angelus, P. A., Philpott, J. R., Henderson, T. R., Dwyer, N. K., Lairon, D., & Hamosh, P. (1996). Effect of human milk or formula on gastric function and fat digestion in the premature infant. Pediatric Research, 40(3), 429–437.
Liu, Z., Cocks, B. G., & Rochfort, S. (2016). Comparison of molecular species distribution of dha-containing triacylglycerols in milk and different infant formulas by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64(10), 2134–2144.
Daniela, G., Claudio, M., Valeria, G., Riccardo, A., Federica, D. B., & Claudio, B. (2011). HPLC-APCI analysis of triacylglycerols in milk fat from different sources. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 113, 197–207.
Osborn, H. T., & Akoh, C. C. (2002). Structured lipids-novel fats with medical, nutraceutical, and food applications. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 1, 110–120.
Liu, W., Liu, W. L., Liu, C. M., Liu, J. H., Yang, S. B., Zheng, H. J., Lei, H. W., Ruan, R., Li, T., Tu, Z. C., & Song, X. Y. (2011). Medium-chain fatty acid nanoliposomes for easy energy supply. Nutrition, 27(6), 700–706.
Metges, C. C., & Wolfram, G. (1991). Medium and long chain triglycerides labeled with 13C: a comparison of oxidation after oral or parenteral administration in humans. The Journal of Nutrition, 121(1), 31–36.
Zhou, S. M., Wang, Y. Q., Jacoby, J. J., Jiang, Y. R., Zhang, Y. Q., & Yu, L. L. L. (2017). Effects of medium-and long-chain triacylglycerols on lipid metabolism and gut microbiota composition in C57BL/6J mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(31), 6599–6607.
Hu, J. N., Shen, J. R., Xiong, C. Y., Zhu, X. M., & Deng, Z. Y. (2018). Investigation of lipid metabolism by a new structured lipid with medium- and long-chain triacylglycerols from cinnamomum camphora seed oil in healthy C57BL/6J mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66(8), 1990–1998.
Lee, Y., Tang, T., & Lai, O. (2012). Health benefits, enzymatic production, and application of medium- and long-chain triacylglycerol (MLCT) in food industries: a review. Journal of Food Science, 77, 137–144.
Jennings, B. H., & Akoh, C. C. (2001). Lipase-catalyzed modification of fish oil to incorporate capric acid. Food Chemistry, 72, 273–278.
Fritsche, K. (2007). Important differences exist in the dose–response relationship between diet and immune cell fatty acids in humans and rodents. Lipids, 42(11), 961–979.
Jacobs, M. N., Covaci, A., Gheorghe, A., & Schepens, P. (2004). Time trend investigation of pcbs, pbdes, and organochlorine pesticides in selected n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid rich dietary fish oil and vegetable oil supplements; nutritional relevance for human essential n-3 fatty acid requirements. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(6), 1780–1788.
Ratledge, C. (2004). Fatty acid biosynthesis in microorganisms being used for single cell oil production. Biochimie, 86(11), 807–815.
Zou, X. Q., Huang, J. H., Jin, Q. Z., Liu, Y. F., Tao, G. J., Cheong, L. Z., & Wang, X. G. (2012). Preparation of human milk fat substitutes from palm stearin with arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid: combination of enzymatic and physical methods. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(37), 9415–9423.
Xu, X., Skands, A. R. H., Høy, C. E., Mu, H., Balchen, S., & Adler-Nissen, J. (1998). Production of specific-structured lipids by enzymatic interesterification: elucidation of acyl migration by response surface design. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 75, 1179.
Rangheard, M. S., Langrand, G., Triantaphylides, C., & Baratti, J. (1989). Multi-competitive enzymatic reactions in organic media: a simple test for the determination of lipase fatty acid specificity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Specialized Section on Enzymological Subjects, 1004, 20–28.
He, Y., Li, J., Kodali, S., Chen, B., & Guo, Z. (2016). The near-ideal catalytic property of Candida antarctica lipase A to highly concentrate n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in monoacylglycerols via one-step ethanolysis of triacylglycerols. Bioresource Technology, 219, 466–478.
Zou, X., Jin, Q., Guo, Z., Huang, J., Xu, X., & Wang, X. (2016). Preparation of 1, 3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglycerol-rich structured lipids from basa catfish oil: combination of fractionation and enzymatic acidolysis. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 118, 708–715.
Cleland, W. W. (1963). The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products: I. nomenclature and rate equations. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Specialized Section on Enzymological Subjects, 67, 104–137.
Abed, S. M., Zou, X. Q., Ali, A. H., Jin, Q. Z., & Wang, X. G. (2017). Synthesis of 1,3-dioleoyl-2-arachidonoylglycerol-rich structured lipids by lipase-catalyzed acidolysis of microbial oil from Mortierella alpina. Bioresource Technology, 243, 448–456.
Iwasaki, Y., & Yamane, T. (2000). Enzymatic synthesis of structured lipids. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 10, 129–140.
Yankah, V. V., & Akoh, C. C. (2000). Lipase-catalyzed acidolysis of tristearin with oleic or caprylic acids to produce structured lipids. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 77, 495–500.
Wang, J., Wang, X. D., Zhao, X. Y., Liu, X., Dong, T., & Wu, F. A. (2015). From microalgae oil to produce novel structured triacylglycerols enriched with unsaturated fatty acids. Bioresource Technology, 184, 405–414.
Yeh, A., Kruse, S. E., Marcinek, D. J., & Gallagher, E. P. (2015). Effect of omega-3 fatty acid oxidation products on the cellular and mitochondrial toxicity of BDE 47. Toxicology In Vitro, 29(4), 672–680.
Funding
This study was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31601433) and Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation (BK20140149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, X., Ye, L., He, X. et al. Preparation of DHA-Rich Medium- and Long-Chain Triacylglycerols by Lipase-Catalyzed Acidolysis of Microbial Oil from Schizochytrium sp.with Medium-Chain Fatty Acids. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 191, 1294–1314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03261-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03261-6