Abstract
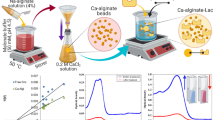
The aim of this work was to remove the dyes Reactive Blue 221 (RB 221) and Reactive Blue 198 (RB 198) of synthetic effluent using the immobilized enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in Ca-alginate beads. Experimental parameters affecting the dye removal process such as the effect of pH, temperature, hydrogen peroxide concentration, mass capsules, and reuse were evaluated, and a numerical model of mass transfer was developed. A maximum removal of 93 and 75%, respectively, for the dyes RB 221 and RB 198, at pH 5.5 and temperature of 30 °C, concentration of hydrogen peroxide of 43.75 μM for dye RB 221 and 37.5 μM for the dye of RB 198 was obtained. A removal reaction of 180 min for RB 221 and 240 min for RB 198 was observed. Three reuse cycles of use of immobilized enzyme were achieved for both dyes. The numerical model proposed led to a good fit compared to experimental data. The HRP enzyme immobilized in Ca-alginate capsules showed a great potential for biotechnological applications, especially for the removal of reactive dyes.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Absfinal :
-
Final absorbance (Ad)
- Absinitial :
-
Initial absorbance (Ad)
- \( {C}_m^{\exp } \) :
-
Experimental concentration from literature at point m
- \( {C}_m^{num} \) :
-
Numerical concentration at point m
- D :
-
Removal of dyes (%)
- D eP :
-
Effective diffusivity by product (m2 s−1)
- D eS :
-
Effective diffusivity by substrate (m2 s−1)
- E :
-
Enzyme (mg L−1)
- ε P :
-
Particle porosity (Ad)
- ε r :
-
Reactor porosity (Ad)
- ES:
-
Enzyme-substrate complex (mg L−1)
- K mS :
-
Constant for substrate (mg L−1)
- k 2 :
-
Rate constant (L mg−1 min−1)
- K eq :
-
Constant of equilibrium (Ad)
- k LS :
-
Mass transfer coefficient by substrate (m s−1)
- k LP :
-
Mass transfer coefficient by product (m s−1)
- K mP :
-
Michaelis-Menten constant for product (mg L−1)
- m :
-
The sampling point
- n :
-
Number of experimental points
- μ max :
-
Maximum reaction rate (min−1)
- P :
-
Product (mg L−1)
- P P :
-
Concentration of product in the solid liquid phase (mg L−1)
- P b :
-
Concentration of product in the bulk liquid phase (mg L−1)
- r :
-
Radial coordinate (m2 s−1)
- R :
-
Radius of particle (m)
- S :
-
Substrate (mg L−1)
- S b , o :
-
Initial concentration of substrate in the bulk phase (mg L−1)
- S b :
-
Concentration of substrate in the liquid bulk phase (mg L−1)
- ρ P :
-
Apparent density of the particles (kg m−3)
- S P :
-
Concentration of substrate in the liquid solid phase (mg L−1)
- t :
-
Time (min)
- v :
-
Reaction rate (min−1)
References
Burkinshaw, S. M., Howroyd, J., Kumar, N., & Kabambe, O. (2011). The wash-off of dyeings using interstitial water part 2: Bis(aminochlorotriazine) reactive dyes on cotton. Dyes and Pigments, 91, 134–144.
Kunz, A., Peralta-Zamora, P., Moraes, S. G. D., & Durán, N. (2002). Novas tendências no tratamento de efluentes têxteis. Química Nova, 25, 78–82.
Nguyen, T. A., & Juang, R.-S. (2013). Treatment of waters and wastewaters containing sulfur dyes: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 219, 109–117.
Deveci, E. Ü., Dizge, N., Yatmaz, H. C., & Tansel, B. (2016). Degradation of recalcitrant textile dyes by coupling fungal and photocatalytic membrane reactors. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 44, 1345–1351.
Si, J., & Cui, B.-K. (2013). A new fungal peroxidase with alkaline-tolerant, chloride-enhancing activity and dye decolorization capacity. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 89, 6–14.
Abdel-Aty, A. M., Hamed, M. B., Fahmy, A. S., & Mohamed, S. A. (2013). Comparison of the potential of Ficus sycomorus latex and horseradish peroxidases in the decolorization of synthetic and natural dyes. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 11, 95–102.
Chiong, T., Lau, S. Y., Lek, Z. H., Koh, B. Y., & Danquah, M. K. (2016). Enzymatic treatment of methyl orange dye in synthetic wastewater by plant-based peroxidase enzymes. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4, 2500–2509.
Marchis, T., Avetta, P., Bianco-Prevot, A., Fabbri, D., Viscardi, G., & Laurenti, E. (2011). Oxidative degradation of Remazol turquoise blue G 133 by soybean peroxidase. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 105, 321–327.
Ulson de Souza, S. M. A. G., Forgiarini, E., & Ulson de Souza, A. A. (2007). Toxicity of textile dyes and their degradation by the enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 1073–1078.
Wan, M. M., Gao, L., Chen, Z., Wang, Y. K., Wang, Y., & Zhu, J. H. (2012). Facile synthesis of new periodic mesoporous organosilica and its performance of immobilizing horseradish peroxidase. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 155, 24–33.
Gholami-Borujeni, F., Mahvi, A. H., Naseri, S., Faramarzi, M. A., Nabizadeh, R., & Alimohammadi, M. (2011). Application of immobilized horseradish peroxidase for removal and detoxification of azo dye from aqueous solution. Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment, 15, 217–222.
Akhtar, S., Khan, A. A., & Husain, Q. (2005). Potential of immobilized bitter gourd (Momordica charantia) peroxidases in the decolorization and removal of textile dyes from polluted wastewater and dyeing effluent. Chemosphere, 60, 291–301.
Bilal, M., Iqbal, H. M., Hu, H., Wang, W. and Zhang, X. (2016). Enhanced bio-catalytic performance and dye degradation potential of chitosan-encapsulated horseradish peroxidase in a packed bed reactor system. Science of the Total Environment.
Bilal, M., Asgher, M. and Iqbal, H. (2016). Polyacrylamide gel-entrapped fungal manganese peroxidase with enhanced catalytic, stability and reusability characteristics. Protein and peptide letters.
Asgher, M., Kamal, S., & Iqbal, H. M. N. (2012). Improvement of catalytic efficiency, thermo-stability and dye decolorization capability of Pleurotus ostreatus IBL-02 laccase by hydrophobic sol gel entrapment. Chemistry Central Journal, 6, 1.
Iqbal, H. M. N., & Asgher, M. (2013). Decolorization applicability of sol–gel matrix immobilized manganese peroxidase produced from an indigenous white rot fungal strain Ganoderma lucidum. BMC Biotechnology, 13, 1.
Muhammad Nasir Iqbal, H., & Asgher, M. (2013). Characterization and decolorization applicability of xerogel matrix immobilized manganese peroxidase produced from Trametes versicolor IBL-04. Protein and Peptide Letters, 20, 591–600.
Monier, M., Ayad, D. M., Wei, Y., & Sarhan, A. A. (2010). Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on modified chitosan beads. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 46, 324–330.
Jaiswal, N., Pandey, V. P., & Dwivedi, U. N. (2016). Immobilization of papaya laccase in chitosan led to improved multipronged stability and dye discoloration. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 86, 288–295.
Wu, J. C. Y., Hutchings, C. H., Lindsay, M. J., Werner, C. J., & Bundy, B. C. (2015). Enhanced enzyme stability through site-directed covalent immobilization. Journal of Biotechnology, 193, 83–90.
Preethi, S., Anumary, A., Ashokkumar, M., & Thanikaivelan, P. (2013). Probing horseradish peroxidase catalyzed degradation of azo dye from tannery wastewater. SpringerPlus, 2, 341.
Karim, Z., Adnan, R., & Husain, Q. (2012). A β-cyclodextrin–chitosan complex as the immobilization matrix for horseradish peroxidase and its application for the removal of azo dyes from textile effluent. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 72, 10–17.
Malani, R. S., Khanna, S., & Moholkar, V. S. (2013). Sonoenzymatic decolourization of an azo dye employing immobilized horse radish peroxidase (HRP): a mechanistic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 256–257, 90–97.
Kim, H. J., Suma, Y., Lee, S. H., Kim, J.-A., & Kim, H. S. (2012). Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase onto clay minerals using soil organic matter for phenol removal. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 83, 8–15.
Bilal, M., Asgher, M., Shahid, M., & Bhatti, H. N. (2016). Characteristic features and dye degrading capability of agar–agar gel immobilized manganese peroxidase. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 86, 728–740.
Fuenzalida, J. P., Nareddy, P. K., Moreno-Villoslada, I., Moerschbacher, B. M., Swamy, M. J., Pan, S., Ostermeier, M., & Goycoolea, F. M. (2016). On the role of alginate structure in complexing with lysozyme and application for enzyme delivery. Food Hydrocolloids, 53, 239–248.
Wang, Y., Chen, H., Wang, J., & Xing, L. (2014). Preparation of active corn peptides from zein through double enzymes immobilized with calcium alginate–chitosan beads. Process Biochemistry, 49, 1682–1690.
Langlois, G., Dusseault, J., Bilodeau, S., Tam, S. K., Magassouba, D., & Hallé, J.-P. (2009). Direct effect of alginate purification on the survival of islets immobilized in alginate-based microcapsules. Acta Biomaterialia, 5, 3433–3440.
Silva, M. C., Corrêa, A. D., Amorim, M. T. S. P., Parpot, P., Torres, J. A., & Chagas, P. M. B. (2012). Decolorization of the phthalocyanine dye Reactive Blue 21 by turnip peroxidase and assessment of its oxidation products. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 77, 9–14.
Cristóvão, R. O., Tavares, A. P. M., Ribeiro, A. S., Loureiro, J. M., Boaventura, R. A. R., & Macedo, E. A. (2008). Kinetic modelling and simulation of laccase catalyzed degradation of reactive textile dyes. Bioresource Technology, 99, 4768–4774.
Al-Muftah, A. E., & Abu-Reesh, I. M. (2005). Effects of simultaneous internal and external mass transfer and product inhibition on immobilized enzyme-catalyzed reactor. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 27, 167–178.
Mayer, D. A., de Souza, A. A. U., Fontana, E., & de Souza, S. M. A. U. (2016). Kinetic study of biodegradation of BTX compounds in mono- and multicomponent systems in reactor with immobilized biomass. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 39, 1441–1454.
Matto, M., & Husain, Q. (2009). Decolorization of direct dyes by immobilized turnip peroxidase in batch and continuous processes. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 965–971.
Dawkar, V. V., Jadhav, U. U., Telke, A. A., & Govindwar, S. P. (2009). Peroxidase from Bacillus sp. VUS and its role in the decolorization of textile dyes. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 14, 361.
Silva, M. C., Torres, J. A., Vasconcelos de Sá, L. R., Chagas, P. M. B., Ferreira-Leitão, V. S., & Corrêa, A. D. (2013). The use of soybean peroxidase in the decolourization of Remazol brilliant blue R and toxicological evaluation of its degradation products. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 89, 122–129.
Bilal, M., Iqbal, H. M. N., Hussain Shah, S. Z., Hu, H., Wang, W., & Zhang, X. (2016). Horseradish peroxidase-assisted approach to decolorize and detoxify dye pollutants in a packed bed bioreactor. Journal of Environmental Management, 183(Part 3), 836–842.
Shoabargh, S., Karimi, A., Dehghan, G., & Khataee, A. (2014). A hybrid photocatalytic and enzymatic process using glucose oxidase immobilized on TiO2/polyurethane for removal of a dye. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 3150–3156.
Jung, K.-W., Hwang, M.-J., Jeong, T.-U., Chau, D. M., Kim, K., & Ahn, K.-H. (2016). Entrapment of powdered drinking water treatment residues in calcium-alginate beads for fluoride removal from actual industrial wastewater. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 39, 101–111.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank CNPq for the financial support given by way of the scholarship, LCME and Central Analysis of EQA at the Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC) by analyses of SEM and texture, respectively. Also would like thank Malwee and Toyobo do Brasil for supplying the dyes and HRP enzyme, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farias, S., Mayer, D.A., de Oliveira, D. et al. Free and Ca-Alginate Beads Immobilized Horseradish Peroxidase for the Removal of Reactive Dyes: an Experimental and Modeling Study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 182, 1290–1306 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2399-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2399-2