Abstract
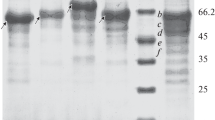
Endoinulinase production was achieved by heteroexpression of endoinulinase-encoding gene from Aspergillus ficuum which is an eukaryotic organism in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Further analysis demonstrated that the native signal peptide existed in inu2 gene lowered the enzyme expression level. To realize extracellular accumulation of target protein and improve its expression level, native signal peptide was substituted with pelB, ompC, and pelB fusing with the native signal peptides; then, the effects on endoinulinase production were investigated. As a result, E. coli A606-3, with replacement of pelB as its signal peptide, showed the highest endoinulinase enzyme activity (75.22 U/mg). Also, it suggested that eukaryotic signal peptides have an inhibition on enzyme expression in prokaryotic organism. Moreover, the condition for inulooligosaccharide (IOS) production from inulin was optimized, and an IOS yield of 94.41 % was achieved under the condition of 15 % (w/v) inulin, purified endoinulinase dosage of 5 U/g inulin, 55 °C, and pH 4.6 for 24 h. The major products of hydrolysis of inulin were identified as DP3 to DP7.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi, Z., Chi, Z., Zhang, T., Liu, G., & Yue, L. (2009). Inulinase-expressing microorganisms and applications of inulinases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 211–220.
Yun, J., Park, J., Song, C., Lee, C., Kim, J., & Song, S. (2000). Continuous production of inulo-oligosaccharides from chicory juice by immobilized endoinulinase. Bioprocess Engineering, 22, 189–194.
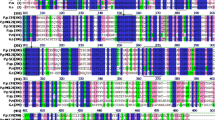
Uhm, T., Chae, K.-S., Lee, D., Kim, H., Cassart, J., & Vandenhaute, J. (1998). Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the endoinulinase-encoding gene, inu2, from Aspergillus ficuum. Biotechnology Letters, 20, 809–812.
Vandamme, A.-M., Michaux, C., Mayard, A., & Housen, I. (2013). Asparagine 42 of the conserved endo-inulinase INU2 motif WMNDPN from Aspergillus ficuum plays a role in activity specificity. FEBS Open Bio, 3, 467–472.
Kim, K.-Y., Nascimento, A. S., Golubev, A. M., Polikarpov, I., Kim, C.-S., Kang, S.-I., & Kim, S.-I. (2008). Catalytic mechanism of inulinase from Arthrobacter sp. S37. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 371, 600–605.
Nakamura, T., Kurokawa, T., Nakatsu, S., & Ueda, S. (1978). Crystallization and general properties of an extracellular inulase from aspergillus-sp-studies on microbial inulase. 4. Journal of Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 52, 159–166.
Nakamura, T., Shitara, A., Matsuda, S., Matsuo, T., Suiko, M., & Ohta, K. (1997). Production, purification and properties of an endoinulinase of Penicillium sp. TN-88 that liberates inulotriose. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 84, 313–318.
Onodera, S., & Shiomi, N. (1988). Purification and substrate specificity of endo-Typo inulinase from Penicillium purpurogenum. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 52, 2569–2576.
Xiao, R., Tanida, M., & Takao, S. (1989). Purification and some properties of endoinulinase from Chrysosporium pannorum. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 67, 244–248.
Kang, S.-I., & Kim, S.-I. (1999). Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of an endo-inulinase gene from Arthrobacter sp. Biotechnology Letters, 21, 569–574.
Jing, W., Zhengyu, J., Bo, J., & Augustine, A. (2003). Production and separation of exo-and endoinulinase from Aspergillus ficuum. Process Biochemistry, 39, 5–11.
Chen, H.-Q., Chen, X.-M., Li, Y., Wang, J., Jin, Z.-Y., Xu, X.-M., Zhao, J.-W., Chen, T.-X., & Xie, Z.-J. (2009). Purification and characterisation of exo-and endo-inulinase from Aspergillus ficuum JNSP5-06. Food Chemistry, 115, 1206–1212.
Li, Y., Liu, G.-L., Wang, K., Chi, Z.-M., & Madzak, C. (2012). Overexpression of the endo-inulinase gene from Arthrobacter sp. S37 in Yarrowia lipolytica and characterization of the recombinant endo-inulinase. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 74, 109–115.
Kim, H.-S., Lee, D. W., Ryu, E. J., Uhm, T.-B., Yang, M.-S., Kim, J. B., & Chae, K.-S. (1999). Expression of the INU2 gene for an endoinulinase of Aspergillus ficuum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology Letters, 21, 621–623.
He, M., Wu, D., Wu, J., & Chen, J. (2014). Enhanced expression of endoinulinase from Aspergillus niger by codon optimization in Pichia pastoris and its application in inulooligosaccharide production. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 41, 105–114.
Chen, M., Lei, X., Chen, C., Zhang, S., Xie, J., & Wei, D. (2015). Cloning, overexpression, and characterization of a highly active endoinulinase gene from Aspergillus fumigatus Cl1 for production of inulo-oligosaccharides. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175, 1153–1167.
Yun, J., Song, C., Choi, J., Choi, Y., & Song, S. (1999). Production of inulo-oligosaccharides from inulin by recombinant E. coli containing endoinulinase activity. Bioprocess Engineering, 21, 101–106.
Chen, X.-M., Xu, X.-M., Jin, Z.-Y., & Chen, H.-Q. (2012). Expression of an endoinulinase from Aspergillus ficuum JNSP5-06 in Escherichia coli and its characterization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 88, 748–753.
Mergulhao, F., Summers, D., & Monteiro, G. (2005). Recombinant protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology Advances, 23, 177–202.
Hegde, R. S., & Bernstein, H. D. (2006). The surprising complexity of signal sequences. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 31, 563–571.
Page, N., Kluepfel, D., Shareck, F., & Morosoli, R. (1996). Effect of signal peptide alterations and replacement on export of xylanase A in Streptomyces lividans. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 109–114.
Sjöström, M., Wold, S., Wieslander, A., & Rilfors, L. (1987). Signal peptide amino acid sequences in Escherichia coli contain information related to final protein localization. A multivariate data analysis. The EMBO Journal, 6, 823.
Choi, J., & Lee, S. (2004). Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 64, 625–635.
Sletta, H., Tøndervik, A., Hakvåg, S., Aune, T. V., Nedal, A., Aune, R., Evensen, G., Valla, S., Ellingsen, T., & Brautaset, T. (2007). The presence of N-terminal secretion signal sequences leads to strong stimulation of the total expression levels of three tested medically important proteins during high-cell-density cultivations of Escherichia coli. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 906–912.
Leonhartsberger, S. (2006). E. coli expression system efficiently secretes recombinant proteins into culture broth. BioProcess International, 4, 64–66.
Humphreys, D. P., Sehdev, M., Chapman, A. P., Ganesh, R., Smith, B. J., King, L. M., Glover, D. J., Reeks, D. G., & Stephens, P. E. (2000). High-level periplasmic expression in Escherichia coli using a eukaryotic signal peptide: importance of codon usage at the 5′ end of the coding sequence. Protein Expression and Purification, 20, 252–264.
Lu, L., Fu, F., Zhao, R., Jin, L., He, C., Xu, L., & Xiao, M. (2014). A recombinant levansucrase from Bacillus licheniformis 8-37-0-1 catalyzes versatile transfructosylation reactions. Process Biochemistry, 49, 1503–1510.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Box, G. E., & Wilson, K. (1951). On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B Methodological, 13, 1–45.
Choi, J., Jeong, K., Kim, S., & Lee, S. (2000). Efficient secretory production of alkaline phosphatase by high cell density culture of recombinant Escherichia coli using the Bacillus sp. endoxylanase signal sequence. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 53, 640–645.
Matsumoto, T., Katsura, D., Kondo, A., & Fukuda, H. (2002). Efficient secretory overexpression of Bacillus subtilis pectate lyase in Escherichia coli and single-step purification. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 12, 175–179.
Stern, B., Olsen, L. C., Tröße, C., Ravneberg, H., & Pryme, I. F. (2007). Improving mammalian cell factories: the selection of signal peptide has a major impact on recombinant protein synthesis and secretion in mammalian cells. Trends in Cell and Molecular Biology, 2, 1–17.
Kim, S. K., Park, Y. C., Lee, H. H., Jeon, S. T., Min, W. K., & Seo, J. H. (2015). Simple amino acid tags improve both expression and secretion of Candida antarctica lipase B in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 112, 346–355.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21390200), the Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation for Youths (BK20140940), a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, a project supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. 06-A-047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Peipei Wang and Jiangfeng Ma These authors equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Ma, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Efficient Secretory Overexpression of Endoinulinase in Escherichia coli and the Production of Inulooligosaccharides. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179, 880–894 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2037-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2037-4