Abstract
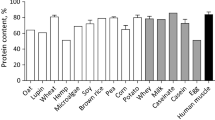
High-protein beverages are among the most consumed, but few offer nutritional or active ingredients beyond their basic nutritional content. The purpose of this study was to determine the protein quality of fermented beverages enriched with cricket protein hydrolysates (CP.H) or whole cricket proteins (CP). The protein quality was evaluated as the protein efficiency ratio (PER), net protein ratio (NPR), apparent (AD), and true (TD) digestibility realized in an animal model. The amino acid score was also calculated. Results showed that the incorporation of CP.H increased the PER and the NPR significantly compared to CP, from 1.7 to 2.0 and from 0.4 to 1.0, respectively. The AD of CP.H was 94%, which was close to the casein group (96%) and significantly higher than the CP group (85%). The analysis of amino acid content showed that cricket proteins benefit from a complete amino acid profile implicated in growth, namely methionine and cystine. Therefore, the 2 groups of cricket proteins (CP.H and CP) could be considered good quality proteins as well as a promising alternative source for human consumption.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acevedo-Pacheco, L., & Serna-Saldívar, S. O. (2016). In vivo protein quality of selected cereal-based staple foods enriched with soybean proteins. Food & Nutrition Research, 60(1), 31382. https://doi.org/10.3402/fnr.v60.31382
Afify, A.E.-M.M.R., El-Beltagi, H. S., Abd El-Salam, S. M., & Omran, A. A. (2012). Protein solubility, digestibility and fractionation after germination of Sorghum varieties. PLoS ONE, 7(2), e31154. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031154
Ali, M. A. M., El Tinay, A. H., & Abdalla, A. H. (2003). Effect of fermentation on the in vitro protein digestibility of pearl millet. Food Chemistry, 80(1), 51–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00234-0
AOAC: Official Methods of Analysis 960.48 (Volume 1). (2000). Official methods of analysis of the association of analytical chemists international (17th ed.). AOAC international.
Bauer, J., Biolo, G., Cederholm, T., Cesari, M., Cruz-Jentoft, A. J., Morley, J. E., Phillips, S., Sieber, C., Stehle, P., Teta, D., Visvanathan, R., Volpi, E., & Boirie, Y. (2013). Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 14(8), 542–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2013.05.021
Beausoleil, M., Fortier, N., Guénette, S., L’Ecuyer, A., Savoie, M., Franco, M., Lachaîne, J., & Weiss, K. (2007). Effect of a fermented milk combining Lactobacillus Acidophilus CL1285 and Lactobacillus casei in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea : A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology, 21(11), 732–736. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/720205
Belluco, S., Losasso, C., Maggioletti, M., Alonzi, C. C., Paoletti, M. G., & Ricci, A. (2013). Edible insects in a food safety and nutritional perspective : A critical review: Insects in a food perspective…. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 12(3), 296–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12014
Bovera, F., Loponte, R., Marono, S., Piccolo, G., Parisi, G., Iaconisi, V., Gasco, L., & Nizza, A. (2016). Use of Tenebrio molitor larvae meal as protein source in broiler diet: Effect on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and carcass and meat traits. Journal of Animal Science, 94(2), 639–647. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2015-9201
Boye, J., Wijesinha-Bettoni, R., & Burlingame, B. (2012). Protein quality evaluation twenty years after the introduction of the protein digestibility corrected amino acid score method. British Journal of Nutrition, 108(S2), S183–S211. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114512002309
Calbet, J. A. L., & Holst, J. J. (2004). Gastric emptying, gastric secretion and enterogastrone response after administration of milk proteins or their peptide hydrolysates in humans. European Journal of Nutrition, 43(3), 127–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0448-4
Chabot, S., Yub, H.-L., Léséleuc, L. D., Cloutier, D., Dalsteren, M.-R. V., Lessard, M., Royc, D., Lacroix, M., & Oth, D. (2001). Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus rhamnosus RW-9595M stimulate TNF, IL-6 and IL-12 in human and mouse cultured immunocompetent cells, and IFN-γ in mouse splenocytes. Le Lait, 81, 683–697.
Chatterjea, M. N., & Shinde, R. (2008). Textbook of medical biochemistry. Jaypee Brothers.
de Carvalho, A. W., Natal, D. I. G., da Silva, C. O., Dantas, M. I. D. S., Barros, E. G. D., Ribeiro, S. M. R., Costa, N. M. B., & Martino, H. S. D. (2013). Heat-treatment reduces anti-nutritional phytochemicals and maintains protein quality in genetically improved hulled soybean flour. Food Science and Technology, 33(2), 310–315. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612013005000048
Devi, P. B., Vijayabharathi, R., Sathyabama, S., Malleshi, N. G., & Priyadarisini, V. B. (2014). Health benefits of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) polyphenols and dietary fiber : A review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 51(6), 1021–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0584-9
Dias, J., Gomes, E. F., & Kaushik, S. J. (1997). Improvement of feed intake through supplementation with an attractant mix in European seabass fed plant-protein rich diets. Aquatic Living Resources, 10(6), 385–389. https://doi.org/10.1051/alr:1997043
Douglas, S. M., Ortinau, L. C., Hoertel, H. A., & Leidy, H. J. (2013). Low, moderate, or high protein yogurt snacks on appetite control and subsequent eating in healthy women. Appetite, 60, 117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.09.012
Dridi, C., Millette, M., Aguilar, B., Manus, J., Salmieri, S., & Lacroix, M. (2021). Effect of physical and enzymatic pre-treatment on the nutritional and functional properties of fermented beverages enriched with cricket proteins. Foods, 10, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102259
Durst, P. B., & FAO (Éds.). (2010). Forest insects as food: Humans bite back ; Proceedings of a Workshop on Asia-Pacific Resources and Their Potential for Development, 19–21 February 2008, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific.
Espinosa-Páez, E., Alanis-Guzmán, Ma., Hernández-Luna, C., Báez-González, J., Amaya-Guerra, C., & Andrés-Grau, A. (2017). Increasing antioxidant activity and protein digestibility in Phaseolus vulgaris and Avena sativa by fermentation with the Pleurotus ostreatus fungus. Molecules, 22(12), 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122275
FDA - U.S. Food and Drug Administration and Department of Health and Human Services. (2020). Nutrient content claims for “good source,” “high,” “more,” and “high potency.” 21 CFR, Part 101, Subpart D, Section 101.54. Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. Retrieved June 1, 2020, from https://www.ecfr.gov/cgibin/retrieveECFR?gp=&SID=bad23c28ebd662323b3ace1e3f5ee94f&mc=true&n=pt21.2.101&r=PART&ty=HTML%23se21.2.101_154
Florence, I. O., Godwin, I. A., Abubakar, N. S., & Kudirat, O. S. (2014). Nutritional composition of Detarium microcarpum fruit. African Journal of Food Science, 8(6), 342–350. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJFS2014.1161
Friedman, M. (1996). Nutritional value of proteins from different food sources. A review. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 44(1), 6–29. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9400167
Hall, F. G., Jones, O. G., O’Haire, M. E., & Liceaga, A. M. (2017). Functional properties of tropical banded cricket (Gryllodes sigillatus) protein hydrolysates. Food Chemistry, 224, 414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.138
Hill, J. E., Hemmingsen, S. M., Goldade, B. G., Dumonceaux, T. J., Klassen, J., Zijlstra, R. T., Goh, S. H., & Van Kessel, A. G. (2005). Comparison of ileum microflora of pigs fed corn-, wheat-, or barley-based diets by chaperonin-60 sequencing and quantitative PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(2), 867–875. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.2.867-875.2005
Kechaou, E. S., Dumay, J., Donnay-Moreno, C., Jaouen, P., Gouygou, J.-P., Bergé, J.-P., & Amar, R. B. (2009). Enzymatic hydrolysis of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) and sardine (Sardina pilchardus) viscera using commercial proteases: Effects on lipid distribution and amino acid composition. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 107(2), 158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2008.10.018
Körzendörfer, A., Schäfer, J., Hinrichs, J., & Nöbel, S. (2019). Power ultrasound as a tool to improve the processability of protein-enriched fermented milk gels for Greek yogurt manufacture. Journal of Dairy Science, 102(9), 7826–7837. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-16541
Kuznetsova, L., Zabodalova, L., & Baranenko, D. (2014). On the potential of lupin protein concentrate made by enzymatic hydrolysis of carbohydrates in dairy-like applications. Agronomy Research, 12(3), 727–736, 20.
Mang, Y. D., Njintang, Y. N., Abdou, B. A., Scher, J., Bernard, C., & Mbofung, M. C. (2016). Dehulling reduces toxicity and improves in vivo biological value of proteins in vegetal milk derived from two mucuna (Mucuna pruriens L.) seeds varieties. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(6), 2548–2557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2211-2
Manus, J., Millette, M., Uscanga, B. R. A., Salmieri, S., Maherani, B., & Lacroix, M. (2021). In vitro protein digestibility and physico-chemical properties of lactic acid bacteria fermented beverages enriched with plant proteins. Journal of Food Science, 1750–3841, 15859. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15859
Marinangeli, C. P. F., & House, J. D. (2017). Potential impact of the digestible indispensable amino acid score as a measure of protein quality on dietary regulations and health. Nutrition Reviews, 75(8), 658–667. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nux025
Marono, S., Piccolo, G., Loponte, R., Di Meo, C., Attia, Y. A., Nizza, A., & Bovera, F. (2015). In vitro crude protein digestibility of Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia illucens insect meals and its correlation with chemical composition traits. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 14(3), 3889. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2015.3889
Mathai, J.K., Liu, Y., Stein, H.H., 2017. Values for digestible indispensable amino acid scores (DIAAS) for some dairy and plant proteins may better describe protein quality than values calculated using the concept for protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores (PDCAAS). British Journal of Nutrition 117, 490–499. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114517000125
McFarland, L. V. (2007). Meta-analysis of probiotics for the prevention of traveler’s diarrhea. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(2), 97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2005.10.003
Mokrane, H., Amoura, H., Belhaneche-Bensemra, N., Courtin, C. M., Delcour, J. A., & Nadjemi, B. (2010). Assessment of Algerian sorghum protein quality [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] using amino acid analysis and in vitro pepsin digestibility. Food Chemistry, 121(3), 719–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.01.020
Nakagaki, B. J., Sunde, M. L., & Defoliart, G. R. (1987). Protein quality of the house cricket, Acheta domesticus, when fed to broiler chicks. Poultry Science, 66(8), 1367–1371. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.0661367
Ngatchic, J. T. M., Sokeng, S. D., Njintang, N. Y., Maoundombaye, T., Oben, J., & Mbofung, C. M. F. (2013). Evaluation of some selected blood parameters and histopathology of liver and kidney of rats fed protein-substituted mucuna flour and derived protein rich product. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 57, 46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.045
Nielsen, S. S. (2017). Food analysis laboratory manual. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44127-6
Nieuwenhuizen, W. F., Weenen, H., Rigby, P., & Hetherington, M. M. (2010). Older adults and patients in need of nutritional support: Review of current treatment options and factors influencing nutritional intake. Clinical Nutrition, 29(2), 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2009.09.003
Nosworthy, M., Medina, G., Franczyk, A., Neufeld, J., Appah, P., Utioh, A., Frohlich, P., & House, J. (2018). Effect of processing on the in vitro and in vivo protein quality of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris and Vicia faba). Nutrients, 10(6), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060671
Oibiokpa, F. I., Akanya, H. O., Jigam, A. A., Saidu, A. N., & Egwim, E. C. (2018). Protein quality of four indigenous edible insect species in Nigeria. Food Science and Human Wellness, 7(2), 175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2018.05.003
Piccolo, G., Iaconisi, V., Marono, S., Gasco, L., Loponte, R., Nizza, S., Bovera, F., & Parisi, G. (2017). Effect of Tenebrio molitor larvae meal on growth performance, in vivo nutrients digestibility, somatic and marketable indexes of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Animal Feed Science and Technology, 226, 12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.02.007
Pieper, R., Jha, R., Rossnagel, B., Van Kessel, A. G., Souffrant, W. B., & Leterme, P. (2008). Effect of barley and oat cultivars with different carbohydrate compositions on the intestinal bacterial communities in weaned piglets: Barley and oat cultivars and intestinal microbiota in pigs. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 66(3), 556–566. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00605.x
Pires, C. V., Oliveira, M. G. D. A., Rosa, J. C., & Costa, N. M. B. (2006). Qualidade nutricional e escore químico de aminoácidos de diferentes fontes protéicas. Ciência e Tecnologia De Alimentos, 26(1), 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612006000100029
Plaza, M., Cifuentes, A., & Ibanez, E. (2008). In the search of new functional food ingredients from algae. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 19(1), 31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2007.07.012
Plummer, S., Weaver, M. A., Harris, J. C., Dee, P., & Hunter, J. (2004). Clostridium difficile pilot study: effects of probiotic supplementation on the incidence of C. difficile diarrhoea. International Microbiology, 7(1), 59–62.
Poelaert, C., Francis, F., Alabi, T., Megido, R. C., Crahay, B., Bindelle, J., & Beckers, Y. (2018). Protein value of two insects, subjected to various heat treatments, using growing rats and the protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 4(2), 77–87. https://doi.org/10.3920/JIFF2017.0003
Pranoto, Y., Anggrahini, S., & Efendi, Z. (2013). Effect of natural and Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on in-vitro protein and starch digestibilities of sorghum flour. Food Bioscience, 2, 46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2013.04.001
Rumpold, B. A., & Schlüter, O. K. (2013). Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 57(5), 802–823. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200735
Rutherfurd, S. M., Fanning, A. C., Miller, B. J., Moughan, P. J. (2015). Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Scores and Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Scores Differentially Describe Protein Quality in Growing Male Rats. The Journal of Nutrition 145, 372–379. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.114.195438
Sinha, V. R., Singh, A., Kumar, R. V., Singh, S., Kumria, R., & Bhinge, J. R. (2007). Oral colon-specific drug delivery of protein and peptide drugs. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 24(1), 63–92.
Song, X., Pérez-Cueto, F. J. A., Bølling Laugesen, S. M., van der Zanden, L. D. T., & Giacalone, D. (2019). Older consumers’ attitudes towards food carriers for protein-enrichment. Appetite, 135, 10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2018.12.033
Synowiecki, J., & Al-Khateeb, N. A. A. Q. (2000). The recovery of protein hydrolysate during enzymatic isolation of chitin from shrimp Crangon crangon processing discards. Food Chemistry, 68(2), 147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00165-X
Vercruysse, L., Smagghe, G., Beckers, T., & Camp, J. V. (2009). Antioxidative and ACE inhibitory activities in enzymatic hydrolysates of the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera Littoralis. Food Chemistry, 114(1), 38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.011
Weltgesundheitsorganisation, FAO, & Vereinte Nationen (Éds.). (2007). Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition : Report of a joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation; [Geneva, 9 - 16 April 2002]. WHO.
Xie, J., Xie, W., Yu, J., Xin, R., Shi, Z., Song, L., & Yang, X. (2021). Extraction of chitin from shrimp shell by successive two-step fermentation of Exiguobacterium profundum and Lactobacillus acidophilus. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 677126. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.677126
Yang, Q., Liu, S., Sun, J., Yu, L., Zhang, C., Bi, J., & Yang, Z. (2014). Nutritional composition and protein quality of the edible beetle Holotrichia parallela. Journal of Insect Science. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieu001
Zhao, M., Lin, Y., & Chen, H. (2020). Improving nutritional quality of rice for human health. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 133(5), 1397–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03530-x
Acknowledgements
Bio-K + is also acknowledged for providing Bio-K+ beverages and for supplying cricket powder. Chaima Dridi was a fellowship recipient of the Armand-Frappier Foundation.
Funding
This research was supported by the Quebec Ministry of Economy and Innovation (MEI) (PSR-SIIRI-984), the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada with Bio-K + , a Kerry company (NSERC no.: CRDPJ/505365–2016), and the Quebec Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (MAPAQ) PPIA12 Research Chair granted to Prof. Monique Lacroix.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chaima Dridi: methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, original draft preparation, review, and editing. Mathieu Millette: resources, validation, supervision, data curation, review and editing. Blanca R. Aguilar Uscanga: review and editing. Stephane Salmieri: software, formal analysis—supporting, validation, data curation, review, and editing. Zahra Allahdad: review and editing—equal. Monique Lacroix: conceptualization, project administration, funding acquisition, validation, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research Involving Animals
The protocol for the animal study was approved on December 20, 2018, by the National Experimental Biology Centre and the Institutional Animal Care Committee of the INRS Armand-Frappier Health Biotechnology Research Centre, in accordance with the principles of the Canadian Council on Animal Care, (Protocol CIPA no 1809–04).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dridi, C., Millette, M., Uscanga, B.R.A. et al. Evaluation of the Nutritional Quality and In Vivo Digestibility of Probiotic Beverages Enriched with Cricket Proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 1992–2000 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03043-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03043-y