Abstract
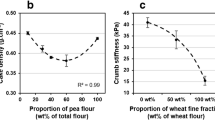
Managing the quality of pea-enriched cakes made from mixes of wheat and pea flours in various proportions (10, 35, and 60 wt% of pea, flour basis) and with various particle size distributions (0, 50, and 100 wt% of particles < 63 µm) is a challenge for the industry. A “multiobjective” model based on an I-optimal response surface design was set up in a previous study. It allows obtaining target cake structural and textural properties by adjusting several processing parameters (mixing speed and time, baking program). As the model’s ability to correct the variations in cake properties due to variations in flour properties remained to be proven, two case studies concerning the proportion and the particle size of pea flour were studied. A variation of crumb stiffness (24 to 37 kPa), lightness (85.4 to 79.6 in L*), and cell fineness (4.9 to –4.8 in PC1 score) could be observed with the increase in the proportion of pea flour from 0 to 35 wt%, and these variations were properly corrected by the model (corrected values: 28 kPa; 83.2 in L*; 3.7 in PC1 score). A change in the particle size of pea flour caused variations in cake properties inferior to those due to processing reproducibility, except for cake symmetry (7.5 to 10.1 in symmetry index; corrected value: 7.2). A selection of products representative of the diversity of cakes from the original design space was investigated by 11 trained panelists through quantitative descriptive analysis. A convergence between sensory and instrumental results was found concerning structural and textural properties. Additional sensory perceptions such as beany attributes or in-mouth drying aftertaste were pointed out.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
AACC Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th Ed. Method 10-91.01. Use of Layer Cake Measuring Template. Approved. (2010). Cereals & Grains Association, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A. http://dx.doi.org/10.1094/AACCIntMethod-10-91.01
Battaiotto, L. L., Lupano, C. E., & Bevilacqua, A. E. (2013). Optimization of basic ingredient combination for sandwich cookie filling using response surface methodology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(7), 1847–1855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0853-2
Berrazaga, I., Micard, V., Gueugneau, M., & Walrand, S. (2019). The role of the anabolic properties of plant-versus animal-based protein sources in supporting muscle mass maintenance: A critical review. Nutrients, 11(8), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081825
Bitaraf, M. S., Khodaiyan, F., Mohammadifar, M. A., & Mousavi, S. M. (2012). Application of response surface methodology to improve fermentation time and rheological properties of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus reuteri. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(4), 1394–1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0433-2
Boye, J., Zare, F., & Pletch, A. (2010). Pulse proteins: Processing, characterization, functional properties and applications in food and feed. Food Research International, 43(2), 414–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2009.09.003
Chumchuere, S., MacDougall, D. B., & Robinson, R. K. (2000). Production and properties of a semi-hard cheese made from soya milk. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 35(6), 577–581. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2000.00414.x
Costa, N. R., Lourenço, J., & Pereira, Z. L. (2011). Desirability function approach: A review and performance evaluation in adverse conditions. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 107(2), 233–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2011.04.004
Del Castillo, E. (2007). Process optimization: A statistical approach (Vol. 105). Springer Science & Business Media.
De Vries, H., Mikolajczak, M., Salmon, J.-M., Abecassis, J., Chaunier, L., Guessasma, S., Lourdin, D., Belhabib, S., Leroy, E., & Trystram, G. (2017). Small-scale food process engineering — Challenges and perspectives. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 46, 122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IFSET.2017.09.009
Dewaest, M., Villemejane, C., Berland, S., Michon, C., Verel, A., & Morel, M. H. (2017). Use of SE-HPLC to follow protein profile evolution within cake batter during process. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 79, 333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.01.036
Dewaest, M., Villemejane, C., Berland, S., Néron, S., Clément, J., Verel, A., & Michon, C. (2018). Effect of crumb cellular structure characterized by image analysis on cake softness. Journal of Texture Studies, 49(3), 328–338. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtxs.12303
Donovan, J. W. (1977). A study of the baking process by differential scanning calorimetry. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 28(6), 571–578. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740280616
Floret, C., Monnet, A.-F., Micard, V., Walrand, S., & Michon, C. (2021). Replacement of animal proteins in food: how to incorporate nutritional and gelling properties of alternative protein sources. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1956426
Goos, P., & Jones, B. (2011). Optimal design of experiments: A case study approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Goos, P., Jones, B., & Syafitri, U. (2016). I-optimal design of mixture experiments. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 111(514), 899–911. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2015.1136632
Gower, J. C. (1975). Generalized Procrustes analysis. Psychometrika, 40, 33–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291478
Hunter, E. A., & Muir, D. D. (1991). Statistical approaches to minimising experimentation. Food Quality and Preference, 3(2), 109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0950-3293(91)90030-i
Jayasena, V., & Nasar-Abbas, S. M. (2012). Development and quality evaluation of high-protein and high-dietary-fiber pasta using lupin flour. Journal of Texture Studies, 43(2), 153–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4603.2011.00326.x
Jha, S. N., Jaiswal, P., Narsaiah, K., Singh, A. K., Kaur, P. P., Sharma, R., Kumar, R., & Bhardwaj, R. (2013). Prediction of sensory profile of mango using textural attributes during ripening. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(3), 734–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0720-6
Jones, B., & Goos, P. (2012). I-optimal versus D-optimal split-plot response surface designs. Journal of Quality Technology, 44(2), 85–101.
Kayacier, A., Yüksel, F., & Karaman, S. (2014). Response surface methodology study for optimization of effects of fiber level, frying temperature, and frying time on some physicochemical, textural, and sensory properties of wheat chips enriched with apple fiber. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(1), 133–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1096-6
Lassoued, N., Delarue, J., Launay, B., & Michon, C. (2008). Baked product texture: Correlations between instrumental and sensory characterization using Flash Profile. Journal of Cereal Science, 48(1), 133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2007.08.014
Lawless, H. T., & Heymann, H. (2010). Sensory evaluation of food: Principles and practices. Springer Science & Business Media.
Milde, L. B., Ramallo, L. A., & Puppo, M. C. (2012). Gluten-free bread based on tapioca starch: Texture and sensory studies. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(3), 888–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0381-x
Monnet, A. F., Eurieult, A., Berland, S., Almeida, G., Jeuffroy, M. H., & Michon, C. (2019a). Damaged starch in pea versus wheat flours: Fragmentation behavior and contribution of fine and coarse fractions. Cereal Chemistry, 96(3), 465–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10146
Monnet, A.-F., Laleg, K., Michon, C., & Micard, V. (2019b). Legume-enriched cereal products: A generic approach derived from material science to predict their structuring by the process and their final properties. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 86, 131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.02.027
Monnet, A.-F., Jeuffroy, M.-H., Michon, C., & Blumenthal, D. (2019c). Taking into account upstream variability of flours with processing variables in legume-enriched soft cakes: Conception of a multiobjective model for the monitoring of physical properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(4), 625–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2230-2
Monnet, A.-F., Jeuffroy, M.-H., Villemejane, C., & Michon, C. (2020). Effect of the order of incorporation of cake ingredients on the formation of batter and the final properties: Contribution of the addition of pea flour. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 33, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04899-0
Nemecek, T., von Richthofen, J.-S., Dubois, G., Casta, P., Charles, R., & Pahl, H. (2008). Environmental impacts of introducing grain legumes into European crop rotations. European Journal of Agronomy, 28(3), 380–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2007.11.004
Penci, M. C., Martinez, M. L., Fabani, M. P., Feresin, G. E., Tapia, A., Ighani, M., Ribotta, P. D., & Wunderlin, D. A. (2013). Matching changes in sensory evaluation with physical and chemical parameters. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(12), 3305–3316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0993-4
Roland, W. S. U., Pouvreau, L., Curran, J., Van de Velde, F., & De Kok, P. M. T. (2017). Flavor aspects of pulse ingredients. Cereal Chemistry, 94(1), 58–65. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-06-16-0161-FI
Ronda, F., Oliete, B., Gomez, M., Caballero, P. A., & Pando, V. (2011). Rheological study of layer cake batters made with soybean protein isolate and different starch sources. Journal of Food Engineering, 102(3), 272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.09.001
Saxena, A., Bawa, A. S., & Raju, P. S. (2012). Effect of minimal processing on quality of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) bulbs using response surface methodology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(1), 348–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-009-0276-x.
Tan, M. C., Chin, N. L., & Yusof, Y. A. (2012). A Box-Behnken design for determining the optimum experimental condition of cake batter mixing. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(3), 972–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0394-5
Turabi, E., Sumnu, G., & Sahin, S. (2008). Optimization of baking of rice cakes in infrared–microwave combination oven by response surface methodology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1(1), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-007-0003-4
Weissman, S. A., & Anderson, N. G. (2015). Design of experiments (DoE) and process optimization. A review of recent publications. Organic Process Research & Development, 19(11), 1605-1633. https://doi.org/10.1021/op500169m
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Marion Beugin and Clotilde Baron for their help with the sensory experiments.
Funding
This work was carried out in the framework of the FLEXIPROCESS project with financial support from the Carnot institute Qualiment. The Carnot Institute Qualiment, AgroParisTech, and the French Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation provided financial support to the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Flour variability effects were corrected by the process thanks to an I-optimal response surface design.
• The correction efficiency of the multiobjective model was proved for pea/wheat proportions variations.
• A set of instrumental cake properties was shown to be representative of sensory perceptions.
• Target instrumental cake properties were used to find adjusted processing parameters.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monnet, A.F., Saint-Eve, A., Michon, C. et al. Tailoring the Properties of Pea-Enriched Soft Cakes Using a Multiobjective Model Based on Sensory-Relevant Instrumental Characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol 15, 459–473 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02679-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02679-y