Abstract
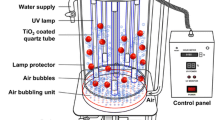
Ultraviolet (UV) light-assisted titanium dioxide (TiO2) photocatalysis is an emerging technology in food safety that utilizes TiO2 photocatalysts to accelerate the generation of reactive oxygen species during UV illumination. In this work, we studied the use of immobilized TiO2-SiO2 photocatalysts illuminated with UVA radiation (350 nm; 14.8 mW/cm2) for the inactivation of Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 in white grape juice, and compared the effectiveness of the photocatalytic disinfection with respect to the quality attributes of white grape juice against those of thermal and UVC (254 nm; 19.7 mW/cm2) treated samples. To obtain a 5-log reduction of the target microorganism, treatment durations of UVA in the absence and presence of the photocatalyst were 60 and 40 min, respectively. A 5-log reduction with UVC radiation led to the loss of health-related compounds such as vitamin C, total phenolic content, and total antioxidant capacity at 92.0 ± 1.1%, 19.4 ± 5.6%, and 54.3 ± 10.0%, respectively. However, the same level of reduction with UVA led to a loss of 74.2 ± 2.3%, 7.1 ± 3.6%, and 39.7 ± 2.5%, and with UVA-assisted photocatalytic method resulted in a loss of 75.8 ± 6.1%, 13.6 ± 5.8%, and 45.6 ± 4.4% of vitamin C, total phenolic content, and total anti-oxidant capacity, respectively. Given its efficacy in deactivating E. coli while retaining a relatively higher level of health-related constituents in the fruit juice compared to other common pasteurization techniques, the photocatalyst developed in this study provides a promising technology for food disinfection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akgun, B. A., Wren, A. W., Durucan, C., Towler, M. R., & Mellott, N. P. (2011). Sol–gel derived silver-incorporated titania thin films on glass: bactericidal and photocatalytic activity. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 59(2), 228–238.
Anderson, C., & Bard, A. J. (1995). An improved photocatalyst of TiO2/SiO2 prepared by a sol-gel synthesis. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 99(24), 9882–9885.
Anpo, M., Nakaya, H., Kodama, S., Kubokawa, Y., Domen, K., & Onishi, T. (1986). Photocatalysis over binary metal oxides. Enhancement of the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide in titanium–silicon oxides. Journal of Chemical Physics, 90, 1633–1636.
AOAC. (1990). Acidity. Method 942.15. Official methods of analysis (15th ed.). Arlington: Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
AOAC. (2007). Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Method 967.21. Official methods of analysis (18th ed.). Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
Balasubramanian, G., Dionysiou, D., Suidan, M., Baudin, I., & Laine, J. (2004). Evaluating the activities of immobilized TiO2 powder films for the photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants in water. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 47(2), 73–84.
Benzie, I. F., & Strain, J. J. (1999). [2] Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods in Enzymology, 299, 15–27.
Caminiti, I. M., Palgan, I., Muñoz, A., Noci, F., Whyte, P., Morgan, D. J., Cronin, D. A., & Lyng, J. G. (2012). The effect of ultraviolet light on microbial inactivation and quality attributes of apple juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(2), 680–686.
Chai, C., Lee, J., Lee, Y., Na, S., & Park, J. (2014). A combination of TiO2-UV photocatalysis and high hydrostatic pressure to inactivate Bacillus cereus in freshly squeezed Angelica keiskei juice. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 55(1), 104–109.
Chawengkijwanich, C., & Hayata, Y. (2008). Development of TiO2 powder-coated food packaging film and its ability to inactivate Escherichia coli in vitro and in actual tests. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 123(3), 288–292.
Chen, Y., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2006). Correlation of structural properties and film thickness to photocatalytic activity of thick TiO2 films coated on stainless steel. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 69(1-2), 24–33.
Chia, S. L., Shamsudin, R., Mohd Adzahan, N., & Wan Daud, W. R. (2012). The effect of storage on the quality attributes of ultraviolet-irradiated and thermally pasteurised pineapple juices. International Food Research Journal, 19(3), 1001–1010.
Cho, M., Choi, Y., Park, H., Kim, K., Woo, G., & Park, J. (2007). Titanium dioxide/UV photocatalytic disinfection in fresh carrots. Journal of Food Protection, 70(1), 97–101.
Choi, H., Stathatos, E., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2007). Photocatalytic TiO2 films and membranes for the development of efficient wastewater treatment and reuse systems. Desalination, 202(1), 199–206.
de Sá Borges, R., da Silva, G. A., Roberto, S. R., de Assis, A. M., & Yamamoto, L. Y. (2013). Phenolic compounds, favorable oxi-redox activity and juice color of ‘Concord’ grapevine clones. Scientia Horticulturae, 161, 188–192.
Donahue, D. W., Canitez, N., & Bushway, A. A. (2004). UV inactivation of E. coli O157:H7 in apple cider: quality, sensory and shelf-life analysis. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 28(5), 368–387.
Falguera, V., Garvín, A., Garza, S., Pagán, J., & Ibarz, A. (2013). Effect of UV–Vis photochemical processing on pear juices from six different varieties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(1), 84–92.
Feng, M., Ghafoor, K., Seo, B., Yang, K., & Park, J. (2013). Effects of ultraviolet-C treatment in Teflon®-coil on microbial populations and physico-chemical characteristics of watermelon juice. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 19, 133–139.
Gayán, E., Serrano, M. J., Monfort, S., Álvarez, I., & Condón, S. (2013). Pasteurization of apple juice contaminated with Escherichia coli by a combined UV–mild temperature treatment. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(11), 3006–3016.
Guerrero-Beltrán, J. A., & Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V. (2005). Reduction of saccharomyces cerevisiae, escherichia coli and listeria innocua in apple juice by ultraviolet light. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 28(5), 437-452.
Guneser, O., & Karagul Yuceer, Y. (2012). Effect of ultraviolet light on water- and fat-soluble vitamins in cow and goat milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 95(11), 6230–6241.
Hakguder Taze, B., Unluturk, S., Buzrul, S., & Alpas, H. (2015). The impact of UV-C irradiation on spoilage microorganisms and colour of orange juice. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(2), 1000–1007.
Hurum, D. C., Agrios, A. G., Gray, K. A., Rajh, T., & Thurnauer, M. C. (2003). Explaining the enhanced photocatalytic activity of Degussa P25 mixed-phase TiO2 using EPR. Journal of Physical Chemistry B., 107(19), 4545–4549.
Ibarz, A., & Esplugas, S. (1989). Ingeniería fotoquímica. Aplicación a la industria alimentaria. Theknos, 110, 8–14.
Ibarz, A., Pagán, J., Panadés, R., & Garza, S. (2005). Photochemical destruction of color compounds in fruit juices. Journal of Food Engineering., 69(2), 155–160.
Kennedy, J. F., Rivera, Z. S., Lloyd, L. L., Warner, F. P., & Jumel, K. (1990). Studies on non-enzymic browning in orange juice using a model system based on freshly squeezed orange juice. Journal of Science of Food and Agriculture, 52(1), 85–95.
Khadem-Hosseini, A., Mirabedini, S. M., & Pazokifard, S. (2016). Photocatalytic activity and colloidal stability of various combinations of TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposites. Journal of Materials Science, 51(6), 3219–3230.
Kim, Y., Choi, Y., Kim, S., Park, J., Chung, M., Song, K. B., Hwang, I., Kwon, K., & Park, J. (2009). Disinfection of iceberg lettuce by titanium dioxide-UV photocatalytic reaction. Journal of Food Protection, 72(9), 1916–1922.
Kim, Y., Jeong, S., Back, K., Park, K., Chung, M., & Kang, D. (2013a). Effect of various conditions on inactivation of escherichia coli O157:H7, salmonella typhimurium, and listeria monocytogenes in fresh-cut lettuce using ultraviolet radiation. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 166(3), 349–355.
Kim, S., Ghafoor, K., Lee, J., Feng, M., Hong, J., Lee, D., et al. (2013b). Bacterial inactivation in water, DNA strand breaking, and membrane damage induced by ultraviolet-assisted titanium dioxide photocatalysis. Water Research, 47(13), 4403–4411.
Koutchma, T., Keller, S., Chirtel, S., & Parisi, B. (2004). Ultraviolet disinfection of juice products in laminar and turbulent flow reactors. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 5(2), 179–189.
Koutchma, T., Forney, L. J., & Moraru, C. I. (2009). Ultraviolet light in food technology; principles and applications. Scitech Book News 33(2) Portland: Ringgold Inc.
Koutchma, T., Popović, V., Ros-Polski, V., & Popielarz, A. (2016). Effects of ultraviolet light and high-pressure processing on quality and health-related constituents of fresh juice products. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 1–24.
Kuhn, H. J., Braslavsky, S. E., & Schmidt, R. (2004). Chemical actinometry (IUPAC technical report). Pure Applied Chemistry, 76(12), 2105–2146.
McCullagh, C., Robertson, J. M., Bahnemann, D. W., & Robertson, P. K. (2007). The application of TiO 2 photocatalysis for disinfection of water contaminated with pathogenic micro-organisms: a review. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 33(3), 359–375.
Müller, A., Günthner, K. A., Stahl, M. R., Greiner, R., Franz, C. M. A. P., & Posten, C. (2015). Effect of physical properties of the liquid on the efficiency of a UV-C treatment in a coiled tube reactor. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 29, 240–246.
Nualkaekul, S., & Charalampopoulos, D. (2011). Survival of Lactobacillus plantarum in model solutions and fruit juices. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 146(2), 111–117.
Ohno, T., Sarukawa, K., Tokieda, K., & Matsumura, M. (2001). Morphology of a TiO2 photocatalyst (Degussa, P-25) consisting of anatase and rutile crystalline phases. Journal of Catalysis, 203(1), 82–86.
Ohtani, B., Ogawa, Y., & Nishimoto, S. (1997). Photocatalytic activity of amorphous−anatase mixture of titanium(IV) oxide particles suspended in aqueous solutions. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 101(19), 3746–3752.
Oms-Oliu, G., Odriozola-Serrano, I., Soliva-Fortuny, R., Elez-Martínez, P., & Martín-Belloso, O. (2012). Stability of health-related compounds in plant foods through the application of non-thermal processes. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 23(2), 111–123.
Orlowska, M., Koutchma, T., Kostrzynska, M., & Tang, J. (2015). Surrogate organisms for pathogenic O157: H7 and non-O157 Escherichia coli strains for apple juice treatments by UV-C light at three monochromatic wavelengths. Food Control, 47, 647–655.
Oteiza, J. M., Giannuzzi, L., & Zaritzky, N. (2010). Ultraviolet treatment of orange juice to inactivate E. coli O157:H7 as affected by native microflora. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3(4), 603–614.
Pala, Ç. U., & Toklucu, A. K. (2013). Effects of UV-C light processing on some quality characteristics of grape juices. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(3), 719–725.
Park, D., Shahbaz, H. M., Kim, S. H., Lee, M., Lee, W., Oh, J. W., Lee, D. U., & Park, J. (2016). Inactivation efficiency and mechanism of UV-TiO2 photocatalysis against murine norovirus using a solidified agar matrix. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 238, 256–264.
Ramesh, T., Nayak, B., Amirbahman, A., Tripp, C. P., & Mukhopadhyay, S. (2016). Application of ultraviolet light assisted titanium dioxide photocatalysis for food safety: a review. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 38, 105–115.
Rivas, A., Rodrigo, D., Martínez, A., Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V., & Rodrigo, M. (2006). Effect of PEF and heat pasteurization on the physical–chemical characteristics of blended orange and carrot juice. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 39(10), 1163–1170.
Santhirasegaram, V., Razali, Z., George, D. S., & Somasundram, C. (2015). Comparison of UV-C treatment and thermal pasteurization on quality of Chokanan mango (Mangifera indica L.) juice. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 94, 313–321.
Sauer, A., & Moraru, C. I. (2009). Inactivation of escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and escherichia coli O157:H7 in apple juice and apple cider, using pulsed light treatment. Journal of Food Protection, 72(5), 937–944.
Shahbaz, H. M., Kim, S., Hong, J., Kim, J. U., Lee, D., Ghafoor, K., & Park, J. (2016a). Effects of TiO2-UVC photocatalysis and thermal pasteurization on microbial inactivation and quality characteristics of the Korean rice-and-malt drink sikhye. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 51(1), 123–132.
Shahbaz, H. M., Yoo, S., Seo, B., Ghafoor, K., Kim, J. U., Lee, D., & Park, J. (2016b). Combination of TiO2-UV photocatalysis and high hydrostatic pressure to inactivate bacterial pathogens and yeast in commercial apple juice. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(1), 182–190.
Shan, A. Y., Ghazi, T. I. M., & Rashid, S. A. (2010). Immobilization of titanium dioxide onto supporting materials in heterogeneous photocatalysis: a review. Applied Catalysis A, 389(1–2), 1–8.
Singleton, V. L., & Rossi, J. A. (1965). Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture, 16, 144–158.
U.S. FDA (2004) Guidance for industry: juice HACCP hazards and controls guidance 1st Edn. https://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/GuidanceDocumentsRegulatoryInformation/Juice/ucm072557.htm. Accessed 02 Jan 2018.
U.S. FDA (2015a). 21 CFR 73.575. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=73.575 Accessed 27 Oct 2015.
U.S. FDA (2015b). Kinetics of microbial inactivation for alternative food processing technologies—ultraviolet light. Retrieved 08/30, 2016, from http://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodScienceResearch/SafePracticesforFoodProcesses/ucm103137.htm. Accessed 30 Aug 2016.
U.S. FDA (2016). Guidance for industry: juice HACCP hazards and controls guidance first edition; final guidance. http://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/GuidanceDocumentsRegulatoryInformation/Juice/ucm072557.htm. Accessed 11 Dec 2016.
U.S. FDA (2016a). 21CFR172.480. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=172.480. Accessed 09 Dec 2016.
U.S. FDA (2016b). 21CFR73.575. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=73.575. Accessed 09 Dec 2016.
Unluturk, S., & Atilgan, M. R. (2015). Microbial safety and shelf life of UV-C treated freshly squeezed white grape juice. Journal of Food Science, 80(8), M1831–M1841.
WHO (2015). Food safety fact sheet N°399. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs399/en. Accessed 01 Aug 2016.
Worobo, R. W. (2000). Efficacy of the CiderSure 3500 ultraviolet light unit in apple cider (pp. 1–6). Ithaca: Cornell University, Department of Food Science and Technology.
Yaparatne, S., Tripp, C. P., & Amirbahman, A. (2018). Photodegradation of taste and odor compounds in water in the presence of immobilized TiO2-SiO2 photocatalysts. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 346, 208–217.
Yemmireddy, V. K., & Hung, Y. C. (2015). Selection of photocatalytic bactericidal titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles for food safety applications. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 61(1), 1–6.
Yemmireddy, V. K., & Hung, Y. C. (2017). Using photocatalyst metal oxides as antimicrobial surface coatings to ensure food safety—opportunities and challenges. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 16(4), 617–631.
Yoo, S., Ghafoor, K., Kim, J. U., Kim, S., Jung, B., Lee, D., & Park, J. (2015a). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on orange fruit surfaces and in juice using photocatalysis and high hydrostatic pressure. Journal of Food Protection, 78(6), 1098–1105.
Yoo, S., Ghafoor, K., Kim, S., Sun, Y. W., Kim, J. U., Yang, K., Lee, D., Shahbaz, H. M., & Park, J. (2015b). Inactivation of pathogenic bacteria inoculated onto a Bacto™ agar model surface using TiO2-UVC photocatalysis, UVC and chlorine treatments. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 119(3), 688–696.
Yu, J., Zhao, X., & Zhao, Q. (2000). Effect of surface structure on photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films, 379(1–2), 7–14.
Zhang, C., Trierweiler, B., Li, W., Butz, P., Xu, Y., Rüfer, C. E., Ma, Y., & Zhao, X. (2011). Comparison of thermal, ultraviolet-c, and high pressure treatments on quality parameters of watermelon juice. Food Chemistry, 126(1), 254–260.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the United States Department of Agriculture, National Institute of Food and Agriculture (USDA NIFA) Hatch No: ME021408, Maine Agricultural and Forest Experiment Station, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, T., Yaparatne, S., Tripp, C.P. et al. Ultraviolet Light-Assisted Photocatalytic Disinfection of Escherichia coli and Its Effects on the Quality Attributes of White Grape Juice. Food Bioprocess Technol 11, 2242–2252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2182-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2182-6