Abstract
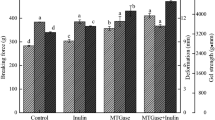
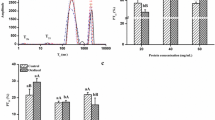
The objectives of this study were to investigate the changes and the relationship between structure and physiochemical properties of low sodium salt substitutes (NaCl partially replaced by KCl, CaCl2, and MgCl2) on grass carp myofibrillar protein gels mediated by microbial transglutaminase during cold-set gels and to provide more information about the gel characteristics. The gel strength, water holding capacity, whiteness, rheological characteristics, differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), and Raman spectra of cold-set gels were determined. The Raman spectra data were fitted to four secondary structures (α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil). The gel properties of cold-set gels varied both with the low sodium salt types and incubation time. Myofibrillar protein (MP) gels added with NaCl and KCl had significantly higher water holding capacity than the MgCl2, CaCl2, and control groups. Additionally, the results showed that the gel strength and G’ value increased with the incubating time. No significant difference was detected in whiteness between the NaCl group and partial substituted groups. Cold-set gels added with the same molar amount of NaCl and KCl had fairly similar gel properties. There is a strong correlation between structural properties and gel properties of MP gels determined by DSC during the cold-set gelation process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, S., Zhang, W., Rajput, N., Khan, M. A., Li, C. B., & Zhou, G. H. (2015). Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on the quality of chicken breast meat. Food Chemistry, 173(8), 808–814.
Alix, A. J. P., Pedanou, G., & Berjot, M. (1988). Fast determination of the quantitative secondary structure of proteins by using some parameters of the Raman amide I band. Journal of Molecular Structure, 174(174), 159–164.
Alting, A. C., Hamer, R. J., Cgd, K., Pacques, M., & Visschers, R. W. (2003). Number of thiol groups rather than the size of the aggregates determines the hardness of cold set whey protein gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 17(4), 469–479.
Baratli, Y., Charles, A. L., Wolff, V., Ben, T. L., Smiri, L., Bouitbir, J., Zoll, J., Piquard, F., Tebourbi, O., & Sakly, M. (2013). Impact of iron oxide nanoparticles on brain, heart, lung, liver and kidneys mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes activities and coupling. Toxicology in Vitro, 27(8), 2142–2148.
Barbut, S., & Findlay, C. J. (2010). Influence of sodium, potassium and magnesium chloride on thermal properties of beef muscle. Journal of Food Science, 56(1), 180–182.
Beaulieu, J. C. (2010). Color, flavor, texture, and nutritional quality of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: desirable levels, instrumental and sensory measurement, and the effects of processing. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 50(5), 369–389.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1–2), 248–254.
Cai, L., Feng, J., Regenstein, J., Lv, Y., & Li, J. (2017). Confectionery gels: effects of low calorie sweeteners on the rheological properties and microstructure of fish gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids, 67, 157–165.
Dejong, G. A. H., & Koppelman, S. J. (2002). Transglutaminase catalyzed reactions: impact on food applications. Journal of Food Science, 67(8), 2798–2806.
Estevez, M., Ventanas, S., & Cava, R. (2010). Protein oxidation in frankfurters with increasing levels of added rosemary essential oil: effect on color and texture deterioration. Journal of Food Science, 70(7), 427–432.
Fan, M., Hu, T., Zhao, S., Xiong, S., Xie, J., & Huang, Q. (2017). Gel characteristics and microstructure of fish myofibrillar protein/cassava starch composites. Food Chemistry, 218, 221–230.
Greiff, K., Aursand, I. G., Erikson, U., Josefsen, K. D., & Rustad, T. (2015). Effects of type and concentration of salts on physicochemical properties in fish mince. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 64(1), 220–226.
Han, L., Zhang, L., Li, Q., & Luo, Y. (2017). Comparison of gel properties and biochemical characteristics of myofibrillar protein from bighead carp ( Aristichthys nobilis ) affected by frozen storage and a hydroxyl radical-generation oxidizing system. Food Chemistry, 223, 96–103.
Hong, G. P., & Koobok, C. (2010). Effects of microbial transglutaminase and sodium alginate on cold-set gelation of porcine myofibrillar protein with various salt levels. Food Hydrocolloids, 24(4), 444–451.
Hong, G. P., Chun, J. Y., Lee, S. K., & Choi, M. J. (2012). Effects of non-meat protein binders and acidification on the efficiency of cold-set pork restructuring by high pressure. Hangug Chugsan Sigpum Haghoeji = Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources., 32(3), 301–307.
Horita, C. N., Morgano, M. A., Celeghini, R. M. S., et al. (2011). Physico-chemical and sensory properties of reduced-fat mortadella prepared with blends of calcium, magnesium and potassium chloride as partial substitutes for sodium chloride. Meat Science, 89(4), 426–433.
Kang, Z. L., Wang, P., Xu, X. L., Zhu, C. Z., Li, K., & Zhou, G. H. (2014). Effect of beating processing, as a means of reducing salt content in frankfurters: a physico-chemical and Raman spectroscopic study. Meat Science, 98(2), 17–177.
Koli, J. M., Basu, S., Nayak, B. B., Patange, S. B., Pagarkar, A. U., & Gudipati, V. (2012). Functional characteristics of gelatin extracted from skin and bone of Tiger-toothed croaker (Otolithes ruber) and pink perch (Nemipterus japonicus). Food and Bioproducts Processing, 90(3), 555–562.
Koob, C., Miy, G., & Xiong, Y. (2009). Effect of soy protein substitution for sodium caseinate on the transglutaminate-induced cold and thermal gelation of myofibrillar protein. Food Research International, 42(8), 941–948.
Lee, K. Y., Shim, J., Bae, I. Y., Cha, J., Park, C. S., & Lee, H. G. (2003). Characterization of gellan/gelatin mixed solutions and gels. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 36(8), 795–802.
Liu, R., Zhao, S. M., Xie, B. J., & Xiong, S. B. (2011). Contribution of protein conformation and intermolecular bonds to fish and pork gelation properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 898–906.
Lorenzo, J. M., Cittadini, A., Bermúdez, R., Munekata, P. E., & Domínguez, R. (2015). Influence of partial replacement of NaCl with KCl, CaCl2 and MgCl2 on proteolysis, lipolysis and sensory properties during the manufacture of dry-cured lacón. Food Control, 55, 90–96.
Mahawanich, T., Lekhavichitr, J., & Duangmal, K. (2010). Original article: gel properties of red tilapia surimi: effects of setting condition, fish freshness and frozen storage. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 45(9), 1777–1786.
Martinezalvarez, O., & Gomezguillen, M. C. (2005). The effect of brine composition and pH on the yield and nature of water-soluble proteins extractable from brined muscle of cod (Gadus morhua). Food Chemistry, 92(1), 71–77.
Nam, M. K., Lee, H. C., Hong, Y. J., Jang, J. Y., Choi, E. H., Chung, C. W., Jeon, S., Kim, J. M., Kang, S., & Rhim, H. (2017). The new approach for establishing the cellular response guideline for medical applications of argon-plasma jet: mitochondria and colorimetric polydiacetylene as innovative parameters. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 13(1), 77–83.
Peipei, Z., Tan, H., Shaolong, F., Qi, X., Ting, Z., Moxi, Z., Xueqi, C., Xingjian, H., Xiaonan, L., & Siyi, P. (2016). Effect of high intensity ultrasound on transglutaminase-catalyzed soy protein isolate cold set gel. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 29, 380–389.
Sun, X. D., & Holley, R. A. (2011). Factors influencing gel formation by myofibrillar proteins in muscle foods. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 10(1), 33–51.
Sun, W., Zhao, Q., Zhao, M., Yang, B., Cui, C., & Ren, J. (2011). Structural evaluation of myofibrillar proteins during processing of Cantonese sausage by Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(20), 11070–11077.
Sun, L., Sun, J., Thavaraj, P., Yang, X., & Guo, Y. (2017). Effects of thinned young apple polyphenols on the quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi during cold storage. Food Chemistry, 224, 372–381.
Thorarinsdottir, K. A., Arason, S., Geirsdottir, M., Bogason, S. G., & Kristbergsson, K. (2002). Changes in myofibrillar proteins during processing of salted cod (Gadus morhua) as determined by electrophoresis and differential scanning calorimetry. Food Chemistry, 77(3), 377–385.
Tornberg, E. (2005). Effects of heat on meat proteins—implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Science, 70(3), 493–508.
Xia, X., Kong, B., Xiong, Y., & Ren, Y. (2010). Decreased gelling and emulsifying properties of myofibrillar protein from repeatedly frozen-thawed porcine longissimus muscle are due to protein denaturation and susceptibility to aggregation. Meat Science, 85(3), 481–489.
Xiong, Y. L., & Brekke, C. J. (1989). Changes in protein solubility and gelation properties of chicken myofibrils during storage. Journal of Food Science, 54(5), 1141–1146.
Yang, H., Zhang, W., Li, T., Zheng, H., Khan, M. A., Xu, X., Sun, J., & Zhou, G. (2016). Effect of protein structure on water and fat distribution during meat gelling. Food Chemistry, 204, 239–246.
Yi, Z., He, S., & Simpson, B. K. (2017). A cold active transglutaminase from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): purification, characterization and application in the modification of cold-set gelatin gel. Food Chemistry, 232, 155–162.
Zhao, Y. Y., Wang, P., Zou, Y. F., Li, K., Kang, Z. L., Xu, X. L., & Zhou, G. H. (2014). Effect of pre-emulsification of plant lipid treated by pulsed ultrasound on the functional properties of chicken breast myofibrillar protein composite gel. Food Research International, 58(4), 98–104.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31401478), the National Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2015M570760), the Postdoctoral Special Funding of Chongqing City (Xm2015021), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (20170540006), the Open Fund by Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health (20171003), and the Graduate Innovation Fund of Bohai University of Liaoning Province of China (YJC20170027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Feng, J., Cao, A. et al. Effect of Partial Substitutes of NaCl on the Cold-Set Gelation of Grass Carp Myofibrillar Protein Mediated by Microbial Transglutaminase. Food Bioprocess Technol 11, 1876–1886 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2149-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2149-7