Abstract
Medical treatments for lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia are frequently associated with changes in sexual function. While these medications are generally well-tolerated and have both reduced and delayed more invasive surgical options, the ramifications of long-term chronic use are largely unknown. Sexual side effects of these medications are frequently either reported as part of a short-term initial drug study or have inflexible endpoints that are not able to gauge more subtle changes in sexual performance. This review will delineate the currently known effects of these medications on sexual function and will consider mechanisms of dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Price DT, Schwinn DA, Lomasney JW, Allen LF, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Identification, quantification, and localization of mRNA for three distinct alpha 1 adrenergic receptor subtypes in human prostate. J Urol. 1993;150:546–51.
Malloy BJ, Price DT, Price RR, Bienstock AM, Dole MK, Funk BL, et al. Alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in human detrusor. J Urol. 1998;160:937–43.
Smith M, Schambra U, Wilson K, et al. Alpha1-adrenergic receptors in human spinal cord: specific localized expression of mRNA encoding alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtypes at four distinct levels. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;63:254.
Roehrborn CG. Efficacy of alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers in the treatment of male lower urinary tract symptoms. Rev Urol. 2009;11:S1–8.
McVary KT, Roehrborn CG, Avins AL, Barry MJ, Bruskewitz RC, Donnell RF, et al. Update on AUA guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2011;185:1793–803. The most recent addition of the AUA guidelines provide an excellent overview of all treatment options including surgical options. Required reading for urologists treating male voiding dysfunction.
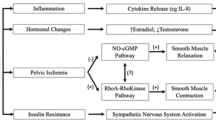
Andersson K-E. The pharmacological perspective: role for the sympathetic nervous system in micturition and sexual function. PCPD. 1999;2:S5–8.
Nagai A, Hara R, Yokoyama T, Jo Y, Fujii T, Miyaji Y. Ejaculatory dysfunction caused by the new alpha1-blocker silodosin: a preliminary study to analyze human ejaculation using color Doppler ultrasonography. Int J Urol. 2008;15:915–8.
Hisasue S, Furuya R, Itoh N, Kobayashi K, Furuya S, Tsukamoto T. Ejaculatory disorder caused by alpha-1 adrenoceptor antagonists is not retrograde ejaculation but a loss of seminal emission. Int J Urol. 2006;13:1311–6.
Kobayashi K, Masumori N, Hisasue S, Kato R, Hashimoto K, Itoh N, et al. Inhibition of Seminal emission is the main cause of anejaculation induced by a new highly selective alpha1A-blocker in normal volunteers. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2185–90.
Beretta G, Chelo E, Fanciullacci F, Zanollo A. Effect of an alpha-blocking agent (phenoxybenzamine) in the management of premature ejaculation. Acta Eur Fertil. 1986;17:43–5.
Hedlund H, Andersson K-E, Larsson B. Effect of drugs interacting with adrenoreceptors and muscarinic receptors in the epididymal and prostatic parts of the human isolated vas deferens. J Auton Pharmacol. 1985;5:261–70.
Moriyama N, Nasu K, Takeuchi T, Akiyama K, Murata S, Nishimatsu H, et al. Quantification and distribution of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype mRNAs in human vas deferens: comparison with those of epididymal and pelvic portions. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;122:1009–14.
Marks LS, Gittelman MC, Hill LA, Volinn W, Hoel G. Rapid efficacy of the highly selective alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor antagonist silodosin in men with signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia: pooled results of 2 phase 3 studies. J Urol. 2013;189:S122–8.
Höfner K, Claes H, De Reijke TM, Folkestad B, Speakman MJ. Tamsulosin 0.4 mg once daily: effect on sexual function in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol. 1999;36:335–41.
Narayan P, Tewari A. A second phase III multicenter placebo controlled study of 2 dosages of modified release tamsulosin in patients with symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. United States 93-01 Study Group. J Urol. 1998;160:1701–6.
Shelbaia A, Elsaied WM, Elghamrawy H, Abdullah A, Salaheldin M. Effect of selective alpha-blocker tamsulosin on erectile function in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2013;82:130–5.
Wilt T, MacDonald R, Rutks I. Tamsulosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev 2002, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD002081.
Kirby RS, Roehrborn C, Boyle P, Bartsch G, Jardin A, Cary MM, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of doxazosin and finasteride, alone or in combination, in treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Prospective European Doxazosin and Combination Therapy (PREDICT) trial. Urology. 2003;61:119–26.
Lepor H, Williford WO, Barry MJ, Brawer MK, Dixon CM, Gormley G, et al. The efficacy of terazosin, finasteride, or both in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:533–9.
van Moorselaar RJ, Hartung R, Emberton M, Harving N, Matzkin H, Elhilali M, et al. Alfuzosin 10 mg once daily improves sexual function in men with lower urinary tract symptoms and concomitant sexual dysfunction. BJU Int. 2005;95:603–8.
van Kerrebroeck P, Jardin A, Laval KU, van Cangh P. Efficacy and safety of a new prolonged release formulation of alfuzosin 10 mg once daily versus alfuzosin 2.5 mg thrice daily and placebo in patients with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. ALFORTI Study Group. Eur Urol. 2000;37:306–13.
Wiser HJ, Kӧhler TS. Sexual impact of the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Curr Urol Rep. 2010;11:228–35.
McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole Jr GL, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al. The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2387–98.
Kawabe K, Yoshida M, Homma Y. Silodosin, a new alpha1A-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study in Japanese men. BJU Int. 2006;98:1019–24.
Hellstrom WJ, Sikka SC. Effects of acute treatment with tamsulosin versus alfuzosin on ejaculatory function in normal volunteers. J Urol. 2006;176:1529–33.
Karadag E, Oner S, Budak YU, Atahan O. Randomized crossover comparison of tamsulosin and alfuzosin in patients with urinary disturbances caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int Urol Nephrol. 2011;43:949–54.
Chapple CR, Montorsi F, Tammela TL, Wirth M, Koldewijn E, Fernández FE. Silodosin therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms in men with suspected benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled clinical trial performed in Europe. Eur Urol. 2011;59:342–52.
Gacci M, Ficarra V, Sebastianelli A, Corona G, Serni S, Shariat SF, et al. Impact of medical treatments for male lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia on ejaculatory function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med. 2014;11:1554–66. Recently published review and meta-analysis of the effects of BPH medications on ejaculatory function with findings of increased EjD with increasing AB receptor specificity and a significant incidence of EjD with 5-ARIs.
Giuliano F, Oelke M, Jungwirth A, Hatzimouratidis K, Watts S, Cox D, et al. Tadalafil once daily improves ejaculatory function, erectile function, and sexual satisfaction in men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction: results from a randomized, placebo- and tamsulosin-controlled, 12-week double-blind study. J Sex Med. 2013;10:857–65.
Fwu CW, Eggers PW, Kirkali Z, McVary KT, Burrows PK, Kusek JW. Change in sexual function in men with lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia associated with long-term treatment with doxazosin, finasteride and combined therapy. J Urol. 2013;191(6):1828–34. This is an analysis of the secondary outcomes from MTOPS data that used a state of the art validated questionnaire for sexual function at the time. This study found an overall decrease in sexual function in the placebo group that was worsened by BPH medications.
Kaufman M, Pinsky L. The dissociation of testosterone- and 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone-receptor complexes formed within cultured human genital skin fibroblasts. J Steroid Biochem. 1983;18:121–5.
Gormley GJ, Stoner E, Bruskewitz RC, Imperato-McGinley J, Walsh P, McConnell JD, et al. The effect of finasteride in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:1185–91.
McVary KT. A review of combination therapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Ther. 2007;29:387–98.
McConnell JD, Bruskewitz R, Walsh P, Andriole GL, Lieber M, Holtgrewe L, et al. The effect of finasteride on the risk of acute urinary retention and the need for surgical treatment among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:557–63.
Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K, Andriole GL. Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types 1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2002;60:434–41.
Thigpen AE, Silver RI, Guileyardo JM, Casey ML, McConnell JD, Russell DW. Tissue distribution and ontogeny of steroid 5 alpha-reductase isozyme expression. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:903–10.
Normington K, Russell DW. Tissue distribution and kinetic characteristics of rat steroid 5 alpha-reductase isozymes. Evidence for distinct physiological functions. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:19548–54.
Iehlé C, Radvanyi F, de Medina Gil Diez S, Ouafik LH, Gérard H, Chopin D, et al. Differences in steroid 5alpha-reductase iso-enzymes expression between normal and pathological human prostate tissue. J Steroid Biochem Mol Bio. 1999;68:189–95.
Godoy A, Kawinski E, Li Y, Oka D, Alexiev B, Azzouni F, et al. 5alpha-reductase type 3 expression in human benign and malignant tissues: a comparative analysis during prostate cancer progression. Prostate. 2011;71:1033–46.
Yamana K, Labrie F, Luu-The V. Human type 3 5α-reductase is expressed in peripheral tissues at higher levels than types 1 and 2 and its activity is potently inhibited by finasteride and dutasteride. Horm Mol Biol Clin Invest. 2010;2:293–9.
Uemura M, Tamura K, Chung S, Honma S, Okuyama A, Nakamura Y, et al. Novel 5 alpha-steroid reductase (SRD5A3, type-3) is overexpressed in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:81–6.
Steiner JF. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Finasteride. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996;30:16–27.
Bonkhoff H, Stein U, Aumuller G, Remberger K. Differential expression of 5 alpha-reductase isoenzymes in the human prostate and prostatic carcinomas. Prostate. 1996;29:261–7.
Schirar A, Bonnefond C, Meusnier C, Devinoy E. Androgens modulate nitric oxide synthase messenger ribonucleic acid expression in neurons of the major pelvic ganglion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1997;138:3093–102.
Gur S, Kadowitz PJ, Hellstrom WJ. Effects of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors on erectile function, sexual desire and ejaculation. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2013;12:81–90. Thought provoking expert opinion paper examining both basic science and clinical studies. The paper proposes many interesting hypotheses for the effects of 5-ARIs on sexual function.
Kunelius P, Lukkarinen O, Hannuksela ML, Itkonen O, Tapanainen JS. The effects of transdermal dihydrotestosterone in the aging male: a prospective, randomized, double blind study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1467–72.
Foresta C, Caretta N, Garolla A, Rossato M. Erectile function in elderly: role of androgens. J Endocrinol Invest. 2003;26:77–81.
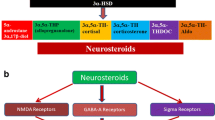
Dubrovsky BO. Steroids, neuroactive steroids and neurosteroids in psychopathology. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2005;29:169–92.
Belelli D, Lambert JJ. Neurosteroids: endogenous regulators of the GABA(A) receptor. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:565–75.
Lephart ED. Age-related changes in brain and pituitary 5 alpha-reductase with finasteride (Proscar) treatment. Neurobiol Aging. 1995;16:647–50.
Melcangi RC, Caruso D, Abbiati F, Giatti S, Calabrese D, Piazza F, et al. Neuroactive steroid levels are modified in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of post-finasteride patients showing persistent sexual side effects and anxious/depressive symptomatology. J Sex Med. 2013;10:2598–603.
Traish AM, Hassani J, Guay AT, Zitzmann M, Hansen ML. Adverse side effects of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors therapy: persistent diminished libido and erectile dysfunction and depression in a subset of patients. J Sex Med. 2011;8:872–84.
Na Y, Ye Z, Zhang S. Efficacy and safety of dutasteride in Chinese adults with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study with an open-label extension. Clin Drug Investig. 2012;32:29–39.
Clark RV, Hermann DJ, Cunningham GR, Wilson TH, Morrill BB, Hobbs S. Marked suppression of dihydrotestosterone in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia by Dutasteride, a dual 5α-reductase inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2179–84.
Debruyne F, Barkin B, van Erps P, Reis M, Tammela T, Roehrborn C. Efficacy and safety of the long-term treatment with the dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor Dutasteride in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2004;46:488–95.
Andriole GL, Bostwick DG, Brawley OW, Gomella LG, Marberger M, Montorsi F, et al. Effect of Dutasteride on the risk of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1192–202.
Marberger MJ. Long-term effects of finasteride in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. PROWESS Study Group. Urology. 1998;51:677–86.
Kaufman KD, Olsen EA, Whiting D. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:578–89.
Leyden J, Dunlap F, Miller B, Winters P, Lebwohl M, Hecker D, et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with frontal male pattern hair loss. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:930–7.
Whiting DA, Olsen EA, Savin R, Halper L, Rodgers A, Wang L, et al. Male Pattern Hair Loss Study Group. Efficacy and tolerability of finasteride 1 mg in men aged 41 to 60 years with male pattern hair loss. Eur J Dermatol. 2003;13:150–60.
Byrnes CA, Morton AS, Liss CL, Lippert MC, Gillenwater JY. Efficacy, tolerability, and effect on health-related quality of life of Finasteride versus placebo in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: A community-based study. Clin Ther. 1995;17:956–69.
Lowe FC, McConnell JD, Hudson PB, Romas NA, Boake R, Lieber M, et al. Long-term 6-year experience with Finasteride in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2003;61:791–6.
Tenover JL, Pagano GA, Morton AS, Liss CL, Byrnes CA. Efficacy and tolerability of Finasteride in symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: A primary care study. Clin Ther. 1997;19:243–58.
Thompson IM, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Miller GJ, Ford LG, et al. The influence of finasteride on the development of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:214–5.
Nickel J, Curtis MD, Fradet Y, Boake R, Pommerville PJ. Efficacy and safety of finasteride therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a 2-year randomized controlled trial (the PROSPECT study). Can Med Assoc J. 1996;155:1251–9.
Nickel JC, Gilling P, Tammela TL, Morrill B, Wilson TH, Rittmaster RS. Comparison of dutasteride and finasteride for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Enlarged Prostate International Comparator Study (EPICS). BJU Int. 2011;108:388–94.
Amory JK, Wang C, Swerdloff RS, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ, et al. The effect of 5alpha-reductase inhibition with dutasteride and finasteride on semen parameters and serum hormones in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1659–65.
Wessels H, Roy J, Bannow J, Grayhack J, Matsumoto AM, Tenover L, et al. Incidence and severity of sexual adverse experiences in Finasteride and placebo-treated men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2003;61:579–84.
Mondaini N, Gontero P, Giubilei G, Lombardi G, Cai T, Gavazzi A, et al. Finasteride 5 mg and sexual side effects: how many of these are related to a nocebo phenomenon? J Sex Med. 2007;4:1708–12.
Irwig MS, Kolukula S. Persistent sexual side effects of finasteride for male pattern hair loss. J Sex Med. 2011;8:1747–53.
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. Public Assessment Report Decentralised Procedure. Finasteride 1 mg film-coated tablets. 2009. Available at: http://www.mhra.gov.uk/home/groups/par/documents/websiteresources/con054522.pdf (accessed June 1, 2014).
US Food and Drug Administration. Questions and answers: Finasteride label changes. 2012. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/safety/medwatch/safetyinformation/ucm303257.htm (accessed June 1, 2014).
Di Loreto C, La Marra F, Mazzon G, Belgrano E, Trombetta C, Cauci S. Immunohistochemical evaluation of the androgen receptor and nerve structure density in human prepuce from patients with persistent sexual side effects after Finasteride use for androgenic alopecia. PLoS One. 2014;9:e100237.
Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damiao R, Major-Walker K, Nandy I, et al. The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study. Eur Urol. 2010;57:123–31.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Dr. R. Charles Welliver Jr. reports other financial or material support from American Medical Systems, Coloplast, and Sophiris.
Dr. Michael Butcher and Dr. Yogitha Potini each declare no potential conflict of interest.
Dr. Kevin T. McVary reports personal fees from Allergan, Lilly/ICOS, Watson Pharmaceuticals, NeoTract, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), and Sophiris, outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. McVary has patents pending for 1) Thermal-Activated Penile Prosthesis Using a Shape-Memory Biomaterial. Dr. McVary is a section editor for Current Urology Reports.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welliver, C., Butcher, M., Potini, Y. et al. Impact of Alpha Blockers, 5-alpha Reductase Inhibitors and Combination Therapy on Sexual Function. Curr Urol Rep 15, 441 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-014-0441-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-014-0441-2