Abstract
Purpose of Review
To review the concept of erectile hydraulics and the scientific advances in modern inflatable penile prosthesis implant.
Recent Findings
Penile erection requires the presence of nitric oxide, relaxation of the penile vasculature, and engorgement of corpora cavernosa sinusoids. It is generally accepted that the development of erectile dysfunction is frequently attributed to both psychogenic factors as well as physiological alterations in neural, vascular, hormonal and endothelial function. Despite the advent of oral and intracavernosal erectile drugs, penile prosthesis implant remains a relevant and desired option as many men became refractory to medical therapy and/or seek a more effective and permanent solution.
Summary
The inflatable penile prosthesis is considered a superior option to malleable prosthesis as it closely replicates a normal penile erection. While the ideal penile prosthesis is probably yet to be developed, scientific advances in prosthesis design, device technology, and surgical techniques have made the penile prosthesis more natural, durable and reliable device.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Lue TF, Giuliano F, Montorsi F, et al. Summary of the recommendations on sexual dysfunctions in men. J Sex Med. 2004 Jul;1(1):6–23.
Hartmann U. Sigmund Freud and his impact on our understanding of male sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2009;6(8):2332–9.
Lue TF, Zeineh SJ, Schmidt RA, Tanagho EA. Neuroanatomy of penile erection: its relevance to iatrogenic impotent. J Urol. 1984;131(2):273–80.
Aboseif SR, Lue TF. Hemodynamics of penile erection. Urol Clin North Am. 1988;15(1):1–7.
Chung E, De Young L, Brock GB. Investigative models in erectile dysfunction: a state-of-the-art review of current animal models. J Sex Med. 2011;8(121):3291–305.
Lue TF. Erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1802–13.
Andersson KE, Wagner G. Physiology of penile erection. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:191–236.
Yiee JH, Baskin LS. Penile embryology and anatomy. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010;10:1174–9.
Moscovici J, Galinier P, Hammoudi S, Lefebvre D, Juricic M, Vaysse P. Contribution to the study of the venous vasculature of the penis. Surg Radiol Anat. 1999;21:193–9.
Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2005;32(4):379-v.
Meldrum DR, Burnett AL, Dorey G, Esposito K, Ignarro LJ. Erectile hydraulics: maximizing inflow while minimizing outflow. J Sex Med. 2014;11:1208–20.
Andersson KE. Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:417–50.
Lavoisier O, Courtois F, Barres D, Blanchard M. Correlation between intracavernous pressure and contraction of ischiocavernosus muscle in man. J Urol. 1986;136:936–9.
Bosch RJ, Benard F, Aboseif SR, et al. Penile detumescence: characterization of three phases. J Urol. 1991;146:867–71.
Lue TF, Takamura T, Schmidt RA, et al. Hemodynamics of erection in the monkey. J Urol. 1983;130:1237–41.
de Saenz Tejada I, Angulo J, Sellek S, et al. Pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2005;2:26–39.
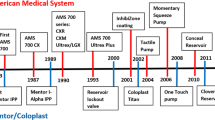
•• Chung E. Penile prosthesis implant: scientific advances and technological innovations over the last four decades. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6(1):37–45. This study provides a comprehensive review on the advances of malleable and inflatable penile prosthesis implant in the last 4 decades
Gee WF. A history of surgical treatment of impotence. Urology. 1975;5:401–5.
Frumkin AP. Reconstruction of the male genitalia. Am Rev Soviet Med. 1944;2:14–7.
Goodwin WE, Scott WW. Phalloplasty. J Urol. 1952;68(6):903–8.
Beheri GE. Surgical treatment of impotence. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1966;38(2):92–7.
Lash H. Silicone implant for impotence. J Urol. 1968;100(5):709–10.
Pearman RO. Treatment of organic impotence by implantation of a penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1967;97(4):716–9.
Scott FB, Bradley WE, Timm GW. Management of erectile impotence: use of implantable inflatable prosthesis. Urology. 1973;2:80–2. (*)
Randrup ER. Clinical experience with 180 inflatable penile prostheses. South Med J. 1995;88(1):47–51.
Riehmann M, Gasser TC, Bruskewitz RC. The Hydroflex penile prosthesis: a test case for the introduction of new urological technology. J Urol. 1993;149(5 Pt 2):1304–7.
Wilson SK, Cleves M, Delk 2nd JR. Long-term results with Hydroflex and Dynaflex penile prostheses: device survival comparison to multicomponent inflatables. J Urol. 1996;155(5):1621–3.
Levine LA, Estrada CR, Morgentaler A. Mechanical reliability and safety of, and patient satisfaction with, the Ambicor inflatable penile prosthesis: results of a 2 center study. J Urol. 2001;166:932–7.
Timm GW, Bradley WF, Scott FB. Experimental evaluation of an implantable externally controllable urinary sphincter. Investig Urol. 1974;11:326–30.
Scott FB, Bradley WE, Timm GW. Treatment of urinary incontinence by implantable prosthetic sphincter. Urology. 1973;1:252–6.
Henry GD. Historical review of penile prosthesis design and surgical techniques: part 1 of a three-part review series on penile prosthetic surgery. J Sex Med. 2009;6(3):675–81.
Wilson SK, Delk 2nd JR. Historical advances in penile prostheses. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12(4):S101–7.
Data on file at AMS database. www.AmericanMedicalSystems.com
Salem EA, Wilson SK, Neeb A, Delk JR, Cleves MA. Mechanical reliability of AMS 700 CX improved by parylene coating. J Sex Med. 2009;6(9):2615–20.
Merrill DC, Javaheri P. Mentor inflatable penile prosthesis. Preliminary clinical results in 30 patients. Urology. 1984;23(5 Spec No):72–4.
Hakky T, Ferguson D, Spiess PE, et al. Thre-dimensional mapping and comparative analysis of the distal human corpus cavernosum and the inflatable penile prosthesis. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:567–70.
Mulcany JJ. Use of CX cylinders in association with AMS700 inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1988;140(6):1420–1.
Negro CL, Paradiso M, Rocca A, Bardari F. Implantation of AMS 700 LGX penile prosthesis preserves penile length without the need for penile lengthening procedures. Asian J Androl. 2016;18(1):114–7.
McKim SE, Carson 3rd CC. AMS 700 inflatable penile prosthesis with InhibiZone. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2010;7(3):311–7.
Carson 3rd CC. Efficacy of antibiotic impregnation of inflatable penile prostheses in decreasing infection in original implants. J Urol. 2004;171:1661–4.
Wolter CE, Hellstrom WJ. The hydrophilic-coated inflatable penile prosthesis: 1-year experience. J Sex Med. 2004;1:221–4.
Ziegelmann MJ, Viers BR, Lomas DJ, Westerman ME, Trost LW. Ectopic penile prosthesis reservoir placement: an anatomic cadaver model of the high submuscular technique. J Sex Med. 2016;13(9):1425–31.
Chung PH, Morey AF, Tausch TJ, Simhan J, Scott JF. High submuscular placement of urologic prosthesis balloons and reservoirs: 2-year experience and patient reported outcomes. Urology. 2014;84:1535–40.
Wilson SK, Henry GD, Delk Jr JR, Cleves MA. The Mentor alpha 1 penile prosthesis with reservoir lock-out valve: effective prevention of auto-inflation with improved capability for ectopic reservoir placement. J Urol. 2002;168:1475–8.
Knoll LD, Henry G, Culkin D, et al. Physician and patient satisfaction with the new AMS 700 momentary squeeze inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med. 2009;6:1773–8.
Shaw T, Garber BB. Coloplast titan inflatable penile prosthesis with one-touch release pump: review of 100 cases and comparison with genesis pump. J Sex Med. 2011;8(1):310–4.
Ohl DA, Brock G, Ralph D, et al. Prospective evaluation of patient satisfaction, and surgeon and patient trainer assessment of the Coloplast titan one touch release three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med. 2012;9(9):2467–74.
• Pastuszak AW, Lentz AC, Farooq A, Jones L, Bella AJ. Technological improvements in three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis design over the past 40 years. J Sex Med. 2015;12(7):415–21. This study highlights technological advances in three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis over the last 40 years
Acknowledgments
Boston Scientific/AMS and Coloplast Corporations for sharing their database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Eric Chung has received honorarium from Boston Scientific and Coloplast Corporation.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Preclinical and Psychophysiology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, E. Translating Penile Erectile Hydraulics to Clinical Application in Inflatable Penile Prosthesis Implant. Curr Sex Health Rep 9, 84–89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11930-017-0107-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11930-017-0107-4