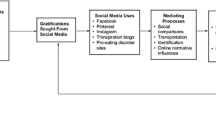
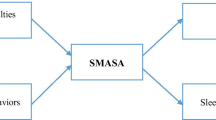
Abstract
Purpose of Review
We review recent evidence regarding the relationship between the social media (SM) habits, experiences, and the mental health of youth. We examine effects of social media use (SMU) on specific diagnoses including depression and anxiety. The relationship between psychiatric illness, specific SM experiences, and the issue of SM mental health contagion is also explored.
Recent Findings
Youth engagement in SMU has increased dramatically in recent years, concurrent with increases in prevalence of depression and anxiety. The relationship between SMU and mental illness is complex and depends on characteristics of the user (e.g., social comparison and fear of missing out (FOMO) and their SM habits and experiences (e.g., cyberbullying, and sexting,). SM engagement has distinct impacts on anxiety, depression, and suicidality. Growing evidence documents how SM may be a medium for psychiatric contagion. Research findings are largely correlational and dependent on subjective report, limiting their interpretation.
Summary
The mental health of youth is increasingly tied to their SMU, depending greatly on how youth engage with SM and resultant feedback. Future research must look to establish causality in relationships between SM and mental illness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Lenhart A, Madden M, Smith A, Purcell K, Zickuhr K. Teens, Kindness and cruelty on social network sites, The Pew Research Center. 2011.
Vogels E, Gelles-Watnick R, Massarat N. Teens, Social media and technology 2022. Pew Research Center: Internet, Science & Tech. 2022.
•• Rideout V, Peebles A, Mann S, Robb MB. Common sense census: media use by tweens and teens, 2021. Common Sense, San Francisco, CA. 2022. This is perhaps the most cited review of contemporary screen media habits in youth, including vital statistics bout social media engagement.
Lebrun-Harris LA, Ghandour RM, Kogan MD, Warren MD. Five-year trends in US Children’s Health and Well-being, 2016–2020. JAMA Pediatr. 2022;176(7):e220056. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.0056.
The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory. Social media and youth mental health. 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/about/news/2023/05/23/surgeon-general-issues-new-advisory-about-effects-social-media-use-has-youth-mental-health.html. Accessed 6/1/2023.
•• Valkenburg PM, Meier A, Beyens I. Social media use and its impact on adolescent mental health: an umbrella review of the evidence. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022;44:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.08.017. This review summarizes the state of evidence regarding the overall effects of social media engagement on mental health.
• Li X, Buxton OM, Lee S, Chang AM, Berger LM, Hale L. Sleep mediates the association between adolescent screen time and depressive symptoms. Sleep Med. 2019;57:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2019.01.029. This article highlights the importance of sleep displacement effects in the relationship between screen media habits and depression.
Miech RA, Johnston LD, Patrick ME, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the future national survey results on drug use, 1975–2022: secondary school students. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan; 2023.
Tollestrup J. Teen birth trends. In Brief Congressional Research Service 2020.
Curtin S. Motor vehicle traffic death rates among adolescents and young adults aged 15–24, by urbanicity: United States, 2000–2018. Ctr Dis Control Prev. 2020.
Hancock JT, Liu X, French M, Luo M, Mieczkowski H. Social media use and psychological well-being: a meta-analysis. In 69th Annual International Communication Association Conference (pp 24–28) 2019.
Liu D, Baumeister RF, Yang C-C, Hu B. Digital communication media use and psychological well-being: a meta-analysis. J Comput Mediat Commun. 2019;24:259–73.
Verduyn P, Gugushvili N, Massar K, Täht K, Kross E. Social comparison on social networking sites. Curr Opin Psychol. 2020;36:32–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.04.002.
Huang C. Correlations of online social network size with well-being and distress: a meta-analysis. J Psychosoc Res. 2021;15.
Huang C. A meta-analysis of the problematic social media use and mental health. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2022;68(1):12–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020764020978434.
Yin X-Q, de Vries DA, Gentile DA, Wang J-L. Cultural background and measurement of usage moderate the association between social networking sites (SNSs) usage and mental health: a meta-analysis. Soc Sci Comput Rev. 2019;37(5):631–48. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439318784908.
Rideout V, Fox S, Peebles A, Robb MB. Coping with Covid-19: how young people use digital media to manage their mental health. Common Sense Media and Hopelab. 2021.
Escobar-Viera CG, Whitfield DL, Wessel CB, Shensa A, Sidani JE, Brown AL, et al. For better or for worse? A systematic review of the evidence on social media use and depression among lesbian, gay, and bisexual minorities. JMIR mental health. 2018;5(3):e10496. https://doi.org/10.2196/10496.
•• Rideout VJ, Fox S. Digital health practices, social media use, and mental well-being among teens and young adults in the U.S. San Francisco, CA: Hopelab and Well Being Trust. 2018. This work illustrates how young people grappling with depression engage with social media to address their illness, and their resultant experiences.
Pfeifer JH, Allen NB. Puberty initiates cascading relationships between neurodevelopmental, social, and internalizing processes across adolescence. Biol Psychiat. 2021;89(2):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.09.002.
Sherman LE, Greenfield PM, Hernandez LM, Dapretto M. Peer influence via instagram: effects on brain and behavior in adolescence and young adulthood. Child Dev. 2018;89(1):37–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12838.
Sherman LE, Payton AA, Hernandez LM, Greenfield PM, Dapretto M. The power of the like in adolescence: effects of peer influence on neural and behavioral responses to social media. Psychol Sci. 2016;27(7):1027–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797616645673.
Crone EA, Konijn EA. Media use and brain development during adolescence. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):588. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03126-x.
Krayer A, Ingledew DK, Iphofen R. Social comparison and body image in adolescence: a grounded theory approach. Health Educ Res. 2007;23(5):892–903. https://doi.org/10.1093/her/cym076.
Pedalino F, Camerini AL. Instagram use and body dissatisfaction: the mediating role of upward social comparison with peers and influencers among young females. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031543.
Telzer EH, Nesi J, Prinstein MJ. Handbook of adolescent digital media use and mental health. Handbook of adolescent digital media use and mental health. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2022.
Beyens I, Frison E, Eggermont S. “I don’t want to miss a thing”: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;64:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.083.
Lopes LS, Valentini JP, Monteiro TH, Costacurta MCF, Soares LON, Telfar-Barnard L, et al. Problematic social media use and its relationship with depression or anxiety: a systematic review. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2022;25(11):691–702. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2021.0300.
Daly M. Prevalence of depression among adolescents in the U.S. From 2009 to 2019: analysis of trends by sex, race/ethnicity, and income. J Adolesc Health. 2022;70(3):496–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.08.026.
Wilson S, Dumornay NM. Rising rates of adolescent depression in the United States: challenges and opportunities in the 2020s. J Adolesc Health. 2022;70(3):354–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.12.003.
• Twenge JM, Joiner TE, Rogers ML, Martin GN. Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clin Psychol Sci. 2017;6(1):3–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702617723376. Article highlighting important data relating to the advent of increased screen media and national date regarding suicide.
Woods HC, Scott H. #Sleepyteens: social media use in adolescence is associated with poor sleep quality, anxiety, depression and low self-esteem. J Adolesc. 2016;51:41–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.05.008.
Alonzo R, Hussain J, Stranges S, Anderson KK. Interplay between social media use, sleep quality, and mental health in youth: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev. 2021;56:101414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2020.101414.
Shafi RMA, Nakonezny PA, Miller KA, Desai J, Almorsy AG, Ligezka AN, et al. An exploratory study of clinical and physiological correlates of problematic social media use in adolescents. Psychiatry Res. 2021;302:114020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114020.
Liu L, Villavicencio F, Yeung D, Perin J, Lopez G, Strong KL, et al. National, regional, and global causes of mortality in 5–19-year-olds from 2000 to 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2022;10(3):e337–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(21)00566-0.
Yard E, Radhakrishnan L, Ballesteros MF. Emergency department visits for suspected suicide attempts among persons aged 12–25 years before and during the COVID-19 pandemic — United States, January 2019–May 2021. CDC - MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:888–94. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7024e1.
Ruch DA, Heck KM, Sheftall AH, Fontanella CA, Stevens J, Zhu M, et al. Characteristics and precipitating circumstances of suicide among children aged 5 to 11 years in the United States, 2013–2017. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):e2115683. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.15683.
Belfort EL, Miller L. Relationship between adolescent suicidality, self-injury, and media habits. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2018;27(2):159–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2017.11.004.
Nesi J, Burke TA, Bettis AH, Kudinova AY, Thompson EC, MacPherson HA, et al. Social media use and self-injurious thoughts and behaviors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;87:102038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102038.
Ferguson CJ. Links between screen use and depressive symptoms in adolescents over 16 years: Is there evidence for increased harm? Dev Sci. 2021;24(1):e13008. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.13008.
Swedo EA, Beauregard JL, de Fijter S, Werhan L, Norris K, Montgomery MP, et al. Associations between social media and suicidal behaviors during a youth suicide cluster in Ohio. J Adolesc Health. 2021;68(2):308–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.05.049.
Glover J, Ariefdjohan M, Fritsch SL. #KidsAnxiety and the digital world. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2022;31(1):71–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2021.06.004.
Bhattacharya S, Bashar MA, Srivastava A, Singh A. Nomophobia: no mobile phone phobia. J Fam Med Prim Care. 2019;8(4):1297–300. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_71_19.
• Ohannessian CM, Fagle T, Salafia C. Social media use and internalizing symptoms during early adolescence: the role of co-rumination. J Affect Disord. 2021;280(Pt A):85–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.10.079. This study examined longitudinal data of social media use, risk of co-rumination and internalising symptoms.
Franchina V, Vanden Abeele M, van Rooij AJ, Lo Coco G, De Marez L. Fear of missing out as a predictor of problematic social media use and phubbing behavior among Flemish adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102319.
Englander E, Donnerstein E, Kowalski R, Lin C, Parti K. Defining cyberbullying. Pediatrics. 2017;140:S148–51. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-1758U.
Englander E. Back to the drawing board with cyberbullying. JAMA Pediatr. 2019;173(6):513–4. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.0690.
• Li C, Wang P, Martin-Moratinos M, Bella-Fernández M, Blasco-Fontecilla H. Traditional bullying and cyberbullying in the digital age and its associated mental health problems in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-022-02128-x. Recent meta-analysis examining relationship of cyberbullying and psychopathology including suicide risk.
Alhajji M, Bass S, Dai T. Cyberbullying, mental health, and violence in adolescents and associations with sex and race: data from the 2015 youth risk behavior survey. Glob Pediatr Health. 2019;6:2333794x19868887. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333794x19868887.
Mori C, Park J, Temple JR, Madigan S. Are youth sexting rates still on the rise? A meta-analytic update. J Adolesc Health. 2022;70(4):531–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.10.026.
Handschuh C, La Cross A, Smaldone A. Is sexting associated with sexual behaviors during adolescence? A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2019;64(1):88–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmwh.12923.
Raine G, Khouja C, Scott R, Wright K, Sowden AJ. Pornography use and sexting amongst children and young people: a systematic overview of reviews. Syst Rev. 2020;9(1):283. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01541-0.
Gassó AM, Klettke B, Agustina JR, Montiel I. Sexting, mental health, and victimization among adolescents: a literature review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132364.
Gámez-Guadix M, de Santisteban P. “Sex pics?”: longitudinal predictors of sexting among adolescents. J Adolesc Health. 2018;63(5):608–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.05.032.
Doyle C, Douglas E, O’Reilly G. The outcomes of sexting for children and adolescents: a systematic review of the literature. J Adolesc. 2021;92:86–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2021.08.009.
Rice E, Gibbs J, Winetrobe H, Rhoades H, Plant A, Montoya J, et al. Sexting and sexual behavior among middle school students. Pediatrics. 2014;134(1):e21–8. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-2991.
Klettke B, Hallford DJ, Clancy E, Mellor DJ, Toumbourou JW. Sexting and psychological distress: the role of unwanted and coerced sexts. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2019;22(4):237–42. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2018.0291.
Suto DJ, Macapagal K, Turban JL. Geosocial networking application use among sexual minority adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021;60(4):429–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2020.11.018.
PlushCare.: how accurate is mental health advice on TikTok? 2022. https://plushcare.com/blog/tiktok-mental-health/. Accessed 16 Feb 2023.
American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. Safe reporting guidelines for media. https://afsp.org/safereporting/. Accessed 27 Nov 2023.
• Samuels MA. Tik Tok Tics. Am J Med. 2022;135(8):933–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.02.040. Using unorthodox methods, this study describes an important online phenomenon and highlights how tics portrayed on vastly popular social media posts differ greatly from those seen in Tourette’s Disorder.
Lewis SP, Seko Y. A double-edged sword: a review of benefits and risks of online nonsuicidal self-injury activities. J Clin Psychol. 2016;72(3):249–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.22242.
Littman L. Parent reports of adolescents and young adults perceived to show signs of a rapid onset of gender dysphoria. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(8):e0202330. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202330.
Shafi RMA, Nakonezny PA, Miller KA, Desai J, Almorsy AG, Ligezka AN, et al. Altered markers of stress in depressed adolescents after acute social media use. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;136:149–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.01.055.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Family media plan https://www.healthychildren.org/English/fmp/Pages/MediaPlan.aspx. Accessed 16 May 2023.
American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. Screen Media Resource Center. https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Resource_Centers/Screen_Media_Resource_Center/Home.aspx. Accessed 16 June 2023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Weigle, P.E., Shafi, R.M.A. Social Media and Youth Mental Health. Curr Psychiatry Rep 26, 1–8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-023-01478-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-023-01478-w