Abstract
Purpose of Review
This review will describe the various applications, benefits, risks, and approaches of conventional irreversible electroporation (IRE), as well as highlight the new technological developments of this procedure along with their clinical applications.
Recent Findings
Minimally invasive image-guided percutaneous IRE ablation has emerged as a newer, non-thermal ablation technique for tumors in the solid organs, particularly within the liver, pancreas, kidney, and prostate. IRE allows for ablation near heat-sensitive structures, including major blood vessels and nerves, and is not susceptible to the heat sink effect. However, it is limited by certain requirements, such as the need for precise parallel placement of at least two probes with a maximum inter-probe distance of 2.5 cm to reduce the risk of arching phenomenon, the requirement for general anesthesia with muscle relaxant, and the need for cardiac synchronization. However, new technological advancements in the ablation system and image guidance tools have been introduced to improve the efficiency and efficacy of IRE.
Summary
IRE is a safe and effective treatment option for solid tumor ablation within the liver, pancreas, kidney, and prostate. Compared with other ablation techniques, IRE has several advantages, such as the absence of heat sink effect and minimal injury to blood vessels and bile ducts while activating the immune system. Novel techniques such as H-FIRE, needle placement systems, and robotics have enhanced the accuracy and performance in placement of IRE probes. IRE can be especially beneficial when combined with chemotherapy, immunomodulation, and immunotherapy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruarus AH, Vroomen LGPH, Puijk RS, Scheffer HJ, Zonderhuis BM, Kazemier G, van den Tol MP, Berger FH, Meijerink MR. Irreversible Electroporation in Hepatopancreaticobiliary Tumours. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2018;69(1):38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carj.2017.10.005.
Zhang N, Li Z, Han X, Zhu Z, Li Z, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Lv Y. Irreversible Electroporation: An Emerging Immunomodulatory Therapy on Solid Tumors. Front Immunol. 2022;12:811726. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.811726.
Narayanan G. Irreversible Electroporation. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2015;32(4):349–55. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1564706.
Fuhrmann I, Probst U, Wiggermann P, Beyer L. Navigation Systems for Treatment Planning and Execution of Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018;17:1533033818791792. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533033818791792.
Zhou L, Yin S, Chai W, Zhao Q, Tian G, Xu D, Jiang T. Irreversible electroporation in patients with liver tumours: treated-area patterns with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. World J Surg Oncol. 2020;18(1):305. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-020-02083-4.
Arena CB, Sano MB, Rossmeisl JH Jr, Caldwell JL, Garcia PA, Rylander MN, Davalos RV. High-frequency irreversible electroporation (H-FIRE) for non-thermal ablation without muscle contraction. Biomed Eng Online. 2011;10:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-925X-10-102.
Al-Sakere B, André F, Bernat C, Connault E, Opolon P, Davalos RV, Rubinsky B, Mir LM. Tumor ablation with irreversible electroporation. PloS One. 2007;2(11):e1135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001135.
Thomson KR, Kavnoudias H, Neal RE 2nd. Introduction to Irreversible Electroporation—Principles and Techniques. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;18(3):128–34. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.tvir.2015.06.002.
Timmer FEF, Geboers B, Ruarus AH, Schouten EAC, Nieuwenhuizen S, Puijk RS, de Vries JJJ, Meijerink MR, Scheffer HJ. Irreversible Electroporation for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;23(2):100675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvir.2020.100675.
Rubinsky B, Onik G, Mikus P. Irreversible electroporation: a new ablation modality—clinical implications. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2007;6(1):37–48. https://doi.org/10.1177/153303460700600106.
Zimmerman A, Grand D, Charpentier KP. Irreversible electroporation of hepatocellular carcinoma: patient selection and perspectives. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2017;4:49–58.
Bhutiani N, Philips P, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM, Potts MH, Martin RCG. Evaluation of tolerability and efficacy of irreversible electroporation (IRE) in treatment of Child-Pugh B (7/8) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HPB. 2016;18(7):593–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpb.2016.03.609.
Scheffer HJ, Vroomen LG, Nielsen K, van Tilborg AA, Comans EF, van Kuijk C, van der Meijs BB, van den Bergh J, van den Tol PM, Meijerink MR. Colorectal liver metastatic disease: efficacy of irreversible electroporation—a single-arm phase II clinical trial (COLDFIRE-2 trial). BMC Cancer. 2015;15:772. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1736-5.
Alnaggar M, Qaid AM, Chen J, Niu L, Xu K. Irreversible electroporation of malignant liver tumors: Effect on laboratory values. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(3):3881–8. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9058.
Franken LC, van Veldhuisen E, Ruarus AH, Coelen RJS, Roos E, van Delden OM, Besselink MG, Klümpen HJ, van Lienden KP, van Gulik TM, Meijerink MR, Erdmann JI. Outcomes of Irreversible Electroporation for Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma: A Prospective Pilot Study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2022;33(7):805-813.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2022.03.024.
Peng H, Shen J, Long X, Zhou X, Zhang J, Xu X, Huang T, Xu H, Sun S, Li C, Lei P, Wu H, Zhao J. Local Release of TGF-β Inhibitor Modulates Tumor-Associated Neutrophils and Enhances Pancreatic Cancer Response to Combined Irreversible Electroporation and Immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(10):e2105240. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202105240.
Wah TM, Lenton J, Smith J, Bassett P, Jagdev S, Ralph C, Vasudev N, Bhattarai S, Kimuli M, Cartledge J. Irreversible electroporation (IRE) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC): a mid-term clinical experience. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(10):7491–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-07846-5.
Wang Z, Lu J, Huang W, et al. A retrospective study of CT-guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation (IRE) ablation: clinical efficacy and safety. BMC Cancer. 2021;21:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-07820-w.
Ng H, Wang K, Cartledge J, et al. Ureteric Injury after Image-Guided Ablation of Renal Cell Cancer with Irreversible Electroporation. JVIR. 2020;32(2):P322-324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2020.09.015.
Wang H, Xue W, Yan W, et al. Extended Focal Ablation of Localized Prostate Cancer With High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Surg. 2022;157(8):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2022.2230.
Geboers B, Scheffer HJ, Graybill PM, Ruarus AH, Nieuwenhuizen S, Puijk RS, van den Tol PM, Davalos RV, Rubinsky B, de Gruijl TD, Miklavčič D, Meijerink MR. High-Voltage Electrical Pulses in Oncology: Irreversible Electroporation, Electrochemotherapy, Gene Electrotransfer, Electrofusion, and Electroimmunotherapy. Radiology. 2020;295(2):254–72. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020192190.
Galvanize Therapeutics, Inc. Aliya System. https://galvanizetx.com/aliya-system. Accessed 20 June 2023.
Endovascular Today. Galvanize Therapeutics’ Aliya PEF System Studied in Solid Tumors. https://evtoday.com/news/galvanize-therapeutics-aliya-pef-system-studied-in-solid-tumors. Accessed 20 June 2023.
Beyer LP, Pregler B, Michalik K, Niessen C, Dollinger M, Müller M, Schlitt HJ, Stroszczynski C, Wiggermann P. Evaluation of a robotic system for irreversible electroporation (IRE) of malignant liver tumors: initial results. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017;12(5):803–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1485-1.
de Baere T, Roux C, Noel G, Delpla A, Deschamps F, Varin E, Tselikas L. Robotic assistance for percutaneous needle insertion in the kidney: preclinical proof on a swine animal model. Eur Radiol Exp. 2022;6(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41747-022-00265-1.
Guiu B, De Baère T, Noel G, et al. Feasibility, safety and accuracy of a CT-guided robotic assistance for percutaneous needle placement in a swine liver model. Sci Rep. 2021;11:5218. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84878-3.
Epione. Quantum Surgical. https://www.quantumsurgical.com/epione/ [Accessed 25 June 2023].
de Baère T, Roux C, Deschamps F, Tselikas L, Guiu B. Evaluation of a New CT-Guided Robotic System for Percutaneous Needle Insertion for Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors: A Prospective Pilot Study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2022;45(11):1701–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-022-03267-z.
Sun S, Liu Y, He C, Hu W, Liu W, Huang X, et al. Combining NanoKnife With M1 Oncolytic Virus Enhances Anticancer Activity in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021;502:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.018.
Qian J, Chen T, Wu Q, Zhou L, Zhou W, Wu L, et al. Blocking Exposed PD-L1 Elicited by Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Field Reverses Dysfunction of CD8 T Cells in Liver Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020;495:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.09.015.
Burbach BJ, O’Flanagan SD, Shao Q, Young KM, Slaughter JR, Rollins MR, Street TJL, Granger VE, Beura LK, Azarin SM, Ramadhyani S, Forsyth BR, Bischof JC, Shimizu Y. Irreversible electroporation augments checkpoint immunotherapy in prostate cancer and promotes tumor antigen-specific tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3862. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24132-6.
Acknowledgements
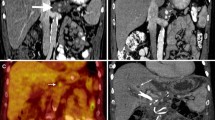
The authors thank Dr. Govindarajan Narayanan, MD, from the Miami Cancer Institute for providing a case of the successful treatment of renal cell carcinoma through irreversible electroporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, J.H., Fang, A., Khorshidi, F. et al. New Developments in Image-Guided Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation of Solid Tumors. Curr Oncol Rep 25, 1213–1226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-023-01452-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-023-01452-y