Abstract
Purpose of Review
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common aggressive lymphoma in adults. Although curable in the majority of cases, a substantial portion of patients will experience disease relapse and will die from their lymphoma. This review is aimed at summarizing the role of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT) in patients with relapsed DLBCL with a focus on its role in the era of CAR T-cell therapy
Recent Findings
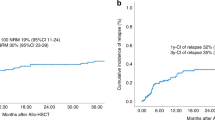
Allo-HSCT is primarily reserved for patients who experience disease progression or relapse after CAR T-cell therapy, largely due to the high non-relapse mortality (NRM) associated with the procedure. Disease status at the time of allo-HSCT is prognostic with complete remission (CR) associated with better outcomes. Reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) is likely as effective as myeloablative conditioning (MAC) with less toxicity. In patients with multiply relapsed disease, including after auto-HSCT and CAR T-cell therapy, approximately one-third can be cured with allo-HSCT.
Summary
Allo-HSCT should be considered a treatment modality for fit adults without major comorbid conditions whose disease can be controlled with emerging treatment modalities (e.g., bispecifics, antibody-drug conjugates).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Bartlett NL, Wilson WH, Jung S-H, Hsi ED, Maurer MJ, Pederson LD, et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R compared with R-CHOP as frontline therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: clinical outcomes of the phase III intergroup trial alliance/CALGB 50303. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2019;37:1790–9.
Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Somers R, Van Der Lelie H, Bron D, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1540–5.
Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, Singh Gill D, Linch DC, Trneny M, et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4184–90.
Locke FL, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Perales M-A, Kersten M-J, Oluwole OO, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:640–54.
Kamdar M, Solomon SR, Arnason J, Johnston PB, Glass B, Bachanova V, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;399:2294–308.
Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet Lond Engl. 2020;396:839–52.
Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Jacobson CA, Miklos DB, Lekakis LJ, Oluwole OO, et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:31–42.
Schuster SJ, Tam CS, Borchmann P, Worel N, McGuirk JP, Holte H, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas (JULIET): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1403–15.
Sehn LH, Salles G. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:842–58.
Westin J, Sehn LH. CAR T cells as a second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: a paradigm shift? Blood. 2022;139:2737–46.
Poeschel V, Held G, Ziepert M, Witzens-Harig M, Holte H, Thurner L, et al. Four versus six cycles of CHOP chemotherapy in combination with six applications of rituximab in patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma with favourable prognosis (FLYER): a randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2019;394:2271–81.
Persky DO, Li H, Stephens DM, Park SI, Bartlett NL, Swinnen LJ, et al. Positron emission tomography-directed therapy for patients with limited-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results of intergroup national clinical trials network study S1001. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2020;38:3003–11.
Tilly H, Morschhauser F, Sehn LH, Friedberg JW, Trněný M, Sharman JP, et al. Polatuzumab vedotin in previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:351–63.
Jones RJ, Ambinder RF, Piantadosi S, Santos GW. Evidence of a graft-versus-lymphoma effect associated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1991;77:649–53.
van Besien KW, de Lima M, Giralt SA, Moore DM Jr, Khouri IF, Rondón G, et al. Management of lymphoma recurrence after allogeneic transplantation: the relevance of graft-versus-lymphoma effect. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997;19:977–82.
Bishop MR, Dean RM, Steinberg SM, Odom J, Pavletic SZ, Chow C, et al. Clinical evidence of a graft-versus-lymphoma effect against relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:1935–40.
Urbano-Ispizua A, Pavletic SZ, Flowers ME, Klein JP, Zhang M-J, Carreras J, et al. The impact of graft-versus-host disease on the relapse rate in patients with lymphoma depends on the histological subtype and the intensity of the conditioning regimen. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:1746–53.
Chopra R, Goldstone AH, Pearce R, Philip T, Petersen F, Appelbaum F, et al. Autologous versus allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a case-controlled analysis of the European Bone Marrow Transplant Group Registry data. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 1992;10:1690–5.
Lazarus HM, Zhang M-J, Carreras J, Hayes-Lattin BM, Ataergin AS, Bitran JD, et al. A comparison of HLA-identical sibling allogeneic versus autologous transplantation for diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a report from the CIBMTR. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16:35–45.
Robinson SP, Boumendil A, Finel H, Blaise D, Poiré X, Nicolas-Virelizier E, et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: efficacy in the rituximab era and comparison to first allogeneic transplants. A report from the EBMT Lymphoma Working Party. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:365–71.
Robinson SP, Goldstone AH, Mackinnon S, Carella A, Russell N, de Elvira CR, et al. Chemoresistant or aggressive lymphoma predicts for a poor outcome following reduced-intensity allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation: an analysis from the Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2002;100:4310–6.
Corradini P, Dodero A, Farina L, Fanin R, Patriarca F, Miceli R, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation following reduced-intensity conditioning can induce durable clinical and molecular remissions in relapsed lymphomas: pre-transplant disease status and histotype heavily influence outcome. Leukemia. 2007;21:2316–23.
van Kampen RJW, Canals C, Schouten HC, Nagler A, Thomson KJ, Vernant J-P, et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation as salvage therapy for patients with diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma relapsing after an autologous stem-cell transplantation: an analysis of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1342–8.
Glass B, Hasenkamp J, Wulf G, Dreger P, Pfreundschuh M, Gramatzki M, et al. Rituximab after lymphoma-directed conditioning and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (DSHNHL R3): an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:757–66.
Rigacci L, Puccini B, Dodero A, Iacopino P, Castagna L, Bramanti S, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma relapsed after autologous stem cell transplantation: A GITMO study. Ann Hematol. 2012;91:931–9.
• Bento L, Gutiérrez A, Novelli S, Montoro J, Piñana JL, López-Corral L, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation as a curative option in relapse/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: Spanish multicenter GETH/GELTAMO study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021;56:1919–28. Spanish multicenter retrospective study showing contemporary outcomes of allo-HSCT for relapsed DLBCL.
Faulkner RD, Craddock C, Byrne JL, Mahendra P, Haynes AP, Prentice HG, et al. BEAM-alemtuzumab reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation for lymphoproliferative diseases: GVHD, toxicity, and survival in 65 patients. Blood. 2004;103:428–34.
•• Dreger P, Sureda A, Ahn KW, Eapen M, Litovich C, Finel H, et al. PTCy-based haploidentical vs matched related or unrelated donor reduced-intensity conditioning transplant for DLBCL. Blood Adv. 2019;3:360–9. Registry study from CIBMTR and EBMT of outcomes after reduced-intensity conditioning for relapsed DLBCL using various donor options.
Sirvent A, Dhedin N, Michallet M, Mounier N, Faucher C, Yakoub-Agha I, et al. Low nonrelapse mortality and prolonged long-term survival after reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: report of the Société Française de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie Cellulaire. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16:78–85.
Fenske TS, Ahn KW, Graff TM, DiGilio A, Bashir Q, Kamble RT, et al. Allogeneic transplantation provides durable remission in a subset of DLBCL patients relapsing after autologous transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2016;174:235–48.
Bacher U, Klyuchnikov E, Le-Rademacher J, Carreras J, Armand P, Bishop MR, et al. Conditioning regimens for allotransplants for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: myeloablative or reduced intensity? Blood. 2012;120:4256–62.
Rezvani AR, Norasetthada L, Gooley T, Sorror M, Bouvier ME, Sahebi F, et al. Non-myeloablative allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation for relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a multicentre experience. Br J Haematol. 2008;143:395–403.
Kekre N, Marquez-Malaver FJ, Cabrero M, Piñana J, Esquirol A, Soiffer RJ, et al. Fludarabine/busulfan versus fludarabine/melphalan conditioning in patients undergoing reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22:1808–15.
Ghosh N, Ahmed S, Ahn KW, Khanal M, Litovich C, Aljurf M, et al. Association of reduced-intensity conditioning regimens with overall survival among patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma undergoing allogeneic transplant. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:1011–8.
Epperla N, Ahn KW, Khanal M, Litovich C, Ahmed S, Ghosh N, et al. Impact of reduced-intensity conditioning regimens on outcomes in diffuse large B cell lymphoma undergoing allogeneic transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27:58–66.
Thomson KJ, Morris EC, Bloor A, Cook G, Milligan D, Parker A, et al. Favorable long-term survival after reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation for multiple-relapse aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:426–32.
Izumi K, Kanda J, Nishikori M, Arai Y, Ishikawa T, Yoshioka S, et al. Outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplantation for DLBCL: a multi-center study from the Kyoto Stem Cell Transplantation Group. Ann Hematol. 2019;98:2815–23.
Dreger P, Fenske TS, Montoto S, Pasquini MC, Sureda A, Hamadani M, et al. Cellular immunotherapy for refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma in the chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T cell era: still a role for allogeneic transplantation? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26:e77–85.
• Dreger P, Dietrich S, Schubert M-L, Selberg L, Bondong A, Wegner M, et al. CAR T cells or allogeneic transplantation as standard of care for advanced large B-cell lymphoma: an intent-to-treat comparison. Blood Adv. 2020;4:6157–68. Intention-to-treat analysis of CAR T-cell therapy vs allo-HSCT for relapsed DLBCL showing similar outcomes.
Hamadani M, Gopal AK, Pasquini M, Kim S, Qiu X, Ahmed S, et al. Allogeneic transplant and CAR-T therapy after autologous transplant failure in DLBCL: a noncomparative cohort analysis. Blood Adv. 2022;6:486–94.
Vercellino L, Di Blasi R, Kanoun S, Tessoulin B, Rossi C, D’Aveni-Piney M, et al. Predictive factors of early progression after CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020;4:5607–15.
Spiegel JY, Dahiya S, Jain MD, Tamaresis J, Nastoupil LJ, Jacobs MT, et al. Outcomes of patients with large B-cell lymphoma progressing after axicabtagene ciloleucel therapy. Blood. 2021;137:1832–5.
Di Blasi R, Le Gouill S, Bachy E, Cartron G, Beauvais D, Le Bras F, et al. Outcomes of patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma after failure of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy: a DESCAR-T analysis. Blood. 2022;140:2584–93.
Chong EA, Alanio C, Svoboda J, Nasta SD, Landsburg DJ, Lacey SF, et al. Pembrolizumab for B-cell lymphomas relapsing after or refractory to CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy. Blood. 2022;139:1026–38.
Gouni S, Rosenthal AC, Crombie JL, Ip A, Kamdar MK, Hess B, et al. A multicenter retrospective study of polatuzumab vedotin in patients with large B-cell lymphoma after CAR T-cell therapy. Blood Adv. 2022;6:2757–62.
• Shadman M, Gauthier J, Hay KA, Voutsinas JM, Milano F, Li A, et al. Safety of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant in adults after CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapy. Blood Adv. 2019;3:3062–9. Retrospective study of feasibility and safety of allo-HSCT after CAR T-cell therapy failure.
Iacoboni G, Iraola-Truchuelo J, Mussetti A, Fernández-Caldas P, Navarro Garcés V, Martin Lopez AA, et al. Salvage treatment with novel agents is preferable to standard chemotherapy in patients with large B-cell lymphoma progressing after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Blood. 2022;140:378–80.
•• Zurko J, Ramdial J, Shadman M, Ahmed S, Szabo A, Iovino L, et al. Allogeneic transplant following CAR T-cell therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2023;108:98–109. Largest multicenter experience of outcomes of allo-HSCT after CAR T-cell therapy failure in DLBCL.
Holtan S. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil as the new standard for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis in reduced intensity conditioning: results from phase III BMT CTN 1703. ASH. 2022; [cited 2023 Jan 6]. Available from: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2022/webprogram/Paper171463.html
Penack O, Peczynski C, Mohty M, Yakoub-Agha I, Styczynski J, Montoto S, et al. How much has allogeneic stem cell transplant-related mortality improved since the 1980s? A retrospective analysis from the EBMT. Blood Adv. 2020;4:6283–90.
Ahmed N, Kumar A, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, DeFilipp Z, Herrera A, Hashmi S, et al. ASTCT Committee on Practice Guidelines survey on evaluation & management of diffuse large b-cell lymphoma after failure of chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy (CAR-T) therapy. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:523–9.
Dickinson MJ, Carlo-Stella C, Morschhauser F, Bachy E, Corradini P, Iacoboni G, et al. Glofitamab for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2220–31.
Nastoupil LJ, Jain MD, Feng L, Spiegel JY, Ghobadi A, Lin Y, et al. Standard-of-care axicabtagene ciloleucel for relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma: results from the US lymphoma CAR T consortium. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:3119–28.
Han S, Zhou L, Chen Y, Zhou X, Guo Z, Yang J, et al. The role of allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation as consolidation after anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in adults with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a prospective cohort study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022;57:513–6.
Ramos CA. Should CD19 CAR-T cells for ALL be followed by allogeneic stem cell transplant? Transplant Cell Ther Off Publ Am Soc Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:1–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors had access to the data and a role in writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hilal, T., Mountjoy, L.J. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Evolving Role in the Era of CAR T-Cell Therapy. Curr Oncol Rep 25, 599–607 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-023-01403-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-023-01403-7