Abstract
Purpose of the Review
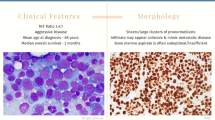
Acute erythroleukemia (AEL) is a rare form of acute myeloid leukemia recognized by erythroblastic proliferation. Many controversies remain around diagnosis influencing prognostic and therapeutic implications relating to this unique leukemia subset.
Recent Findings
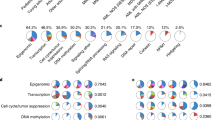
The 2016 WHO classification includes more clear and restrictive diagnostic criteria for AEL. Primary acute erythroid leukemia is associated with complex and high-risk karyotypes including chromosomes 5q and 7q abnormalities. Mutational data shows that AEL is characterized by far lower NPM1 and FLT3-ITD mutation rates and higher mutational rates in TP53 compared with other AML subtypes. Hypomethylating agents have shown therapeutic value in AEL.
Summary
In this article, we discuss the evolving diagnostic concepts of erythroleukemia, genomics, clinical outcome, and promising therapeutic targets through an appraisal of the current literature.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Schwartz SO, Critchlow J. Erythremic myelosis (DI Guglielmo’s disease); critical review with report of four cases, and comments on erythroleukemia. Blood. 1952;7(8):765–93.
Dameshek W. Some speculations on the myeloproliferative syndromes. Blood. 1951;6(4):372–5.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukemias. Br J Haematol. 1976;33:451–8.
Villeval JL, Cramer P, Lemoine F, Henri A, Bettaieb A, Bernaudin F, et al. Phenotype of early erythroblastic leukemias. Blood. 1986;68(5):1167–74.
Kowal-Vern A, Cotelingam J, Schumacher HR. The prognostic significance of proerythroblasts in acute erythroleukemia. The prognostic significance of proerythroblasts in acute erythroleukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992;98(1):34–40.
Mazzella FM, Kowal-Vern A, Shrit MA, Wibowo AL, Rector JT, Cotelingam JT. et alR. Acute erythroleukemia: evaluation of 48 cases with reference to classification, cell proliferation, cytogenetics, and prognosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;110(5):590–8.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, et al. Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med. 1985;103:626–9.
Brunning RD, Matutes E, Flandrin G, Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW. et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia not otherwise categorised., World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, 2001 Lyon, FranceI ARC Press(pg. 91-105)
Arber DA, Brunning RD, Orazi A, Porwit A, Peterson L, Thiele J, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia, not otherwise specified. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al., editors. WHO Classifiction of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC; 2008. p. 134–6.
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127(20):2391–405.
Santos FPS, Bueso-Ramos CE, Ravandi F. Acute erythroleukemia: diagnosis and management. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010;3(6):705–18.
Barnard DR, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Lange R, Woods WG. Children’s Oncology Group Comparison of childhood myelodysplastic syndrome, AML FAB M6 or M7, CCG 2891: report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;49(1):17–22.
Hasserjian RB, Zuo Z, Garcia C, Tang G, Kasyan A, Luthra R, et al. Acute erythroid leukemia: a reassessment using criteria refined in the 2008 WHO classification. Blood. 2010;115(10):1985–92.
Olopade OI, Thangavelu M, Larson RA, Mick R, Kowal-Vern A, Schumacher HR, et al. Clinical, morphologic, and cytogenetic characteristics of 26 patients with acute erythroblastic leukemia. Blood. 1992;80:2873–82.
Li H, Hasserjian RP, Kroft SH, Harrington AM, Wheaton SE, Pildain A, et al. Pure Erythroid Leukemia and Erythroblastic Sarcoma Evolving From Chronic Myeloid Neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 2016;145(4):538–51.
Domingo-Claros A, Larriba I, Rozman M, Irriguible D, Vallespí T, Aventin A, et al. Acute erythroid neoplastic proliferations. A biological study based on 62 patients. Haematologica. 2002;87(2):148–53.
• Reinig EF, Greipp PT, Chiu A, Howard MT, Reichard KK. De novo pure erythroid leukemia: refining the clinicopathologic and cytogenetic characteristics of a rare entity. Mod Pathol. 2018;31:705–17 This series of pure erythroid leukemia illustrates high rate of very complex karyotype in this disease.
Sondergaard-Petersen H Erythrophagocytosis by pathological erythroblasts in the Di Guglielmo syndrome. A study of 18 cases. Scand J Haematol. 1974;13(4):260-5. (19). Histopathology 2017, 71, 316-321
Hasserjian RP. Erythroleukemia and Its Differential Diagnosis. Surg Path Clin. 2013;6:641–59.
Greaves MF, Sieff C, Edwards PA. Monoclonal antiglycophorin as a probe for erythroleukemias. Blood. 1983;61(4):645–51.
Gupta AD, Dhond SR. Phenotypic heterogeneity of erythroblasts in erythroblastic leukemia revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Am J Hematol. 1988;29(1):12–7.
Garand R, Duchayne E, Blanchard D, Robillard N, Kuhlein E, Fenneteau O, et al. Minimally differentiated erythroleukaemia (AML M6 ‘variant’): a rare subset of AML distinct from AML M6. Groupe Français d'Hématologie Cellulaire. Br J Haematol. 1995;90(4):868–75.
• Lee WY, Weinberg OW, Pinkus GS. GATA1 Is a sensitive and specific Nuclear marker for erythroid and megakaryocytic lineages. Am J Clin Pathol. 2017;147(4):420–6 This study shows that blasts in acute erythroleukemia exhibit intense nuclear GATA1 positivity.
Wong E, Ling V, Westerman D, Morgan S, Juneja S. How unique is pure erythroid leukaemia? A retrospective analysis of seven cases and review of the literature. JCP. 2015;68:301–5.
• Wang SA, Patel KP, Pozdnyakova O, Peng J, Zuo Z, Dal Cin P, et al. Acute erythroid leukemia with <20% bone marrow blasts is clinically and biologically similar to myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts. Mod Pathol. 2016;29:1221–31 The results of this study supports WHO change in definition of acute erythroid leukemia.
Lessard M, Struski S, Leymarie V, Flandrin G, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Mozziconacci MJ, et al. Cytogenetic study of 75 erythroleukemias. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005;163:113–22.
Grossmann V, Bacher U, Haferlach C, Schnittger S, Pötzinger F, Weissmann S, et al. Acute erythroid leukemia (AEL) can be separated into distinct prognostic subsets based on cytogenetic and molecular genetic characteristics. Leukemia. 2013;27(9):1940–3.
Cervera N, Carbuccia N, Garnier S, Guille A, Adélaïde J, Murati A, et al. Molecular characterization of acute erythroid leukemia (M6-AML) using targeted next-generation sequencing. Leukemia. 2016;30:966–70.
Ko PS, Liu YC, Yeh CM, Gau JP, Yu YB, Hsiao LT, et al. The uniqueness of morphological features of pure erythroid leukemia in myeloid neoplasm with erythroid predominance: A reassessment using criteria revised in the 2016 World Health Organization classification. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0172029.
• Rose D, Haferlach T, Schnittger S, Perglerová K, Kern W, Haferlach C. Subtype-specific patterns of molecular mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2017;31(1):11–7 This study illustrates mutation profile in acute erythroleukemia.
•• Montalban-Bravo G, Benton CB, Wang SA, Ravandi F, Kadia T, Cortes J, et al. More than 1 TP53 abnormality is a dominant characteristic of pure erythroid leukemia. Blood. 2017;129(18):2584–7 This study illustrates high rate of TP53 mutations in acute erythroleukemia.
•• Iacobucci I, Wen J, Meggendorfer M, Choi JK, et al. Genomic subtyping and therapeutic targeting of acute erythroleukemia. Nat Genet. 2019;51:694–704 This large study compares genomic features of pediatric and adult acute erythroleukemia.
Panagopoulos I, Micci F, Thorsen J, Haugom L, Buechner J, Kerndrup G, et al. Fusion of ZMYND8 and RELA genes in acute erythroid leukemia. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63663.
Colita A, Belhabri A, Chelghoum Y, Charrin C, Fiere D, Thomas X. Prognostic factors and treatment effects on survival in acute myeloid leukemia of M6 subtype: a retrospective study of 54 cases. Ann Oncol. 2001;12(4):451–5.
Santos F, Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, Koller C, Beran M, O'Brien S, et al. Adult Acute Erythroleukemia: An Analysis of 108 patients treated at a single institution. Leukemia. 2009;23(12):227–80.
Greco R, Petrungaro A, Recchia AG, De Stefano L, Bossio S, Palummo A, et al. Treatment Acute Myeloid Leukemia Using Cytoreductive Chemotherapy Cytarabine (Ara-C) Followed Azacitidine (AZA) Maintenance: A Real Life Single Center Experience. Blood. 2016;128(22):5204.
Welch JS, Petti AA, Miller CA, Fronick CC, O'Laughlin M, Fulton RS, et al. TP53 and Decitabine in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes. NEJM. 2016;375(21):2023–36.
•• Almeida AM, Prebet T, Itzykson R, Ramos F, Al-Ali H, Shammo J, et al. Clinical Outcomes of 217 Patients with Acute Erythroleukemia According to Treatment Type and Line: A Retrospective Multinational Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):837 This study supports use of HMAs in acute erythroleukemia.
Peng J, Hasserjian RP, Tang G, Patel KP, Goswami M, Jabbour EJ, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes following therapy with hypomethylating agents (HMAs): development of acute erythroleukemia may not influence assessment of treatment response. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016;57(4):812–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
Neither of the authors has any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Leukemia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinberg, O.K., Arber, D.A. Erythroleukemia: an Update. Curr Oncol Rep 23, 69 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-021-01060-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-021-01060-8