Abstract
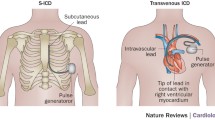
The implantable cardioverter defibrillator is today an indisputable evidence-based treatment for cardiac sudden death both in primary and secondary prevention. However, trans-venous cardioverter defibrillator implantation still carries a not negligible risk of complications both acutely and during follow-up. Trans-venous endocardial lead is the weak link of implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) technology being the source of most mechanical complications on vessels and heart structures and exposed to infection, malfunction and recalls. A totally subcutaneous defibrillation lead has recently been introduced in clinical practice. With the subcutaneous pulse generator forms a defibrillation system that leaves the vessels and the heart completely “untouched.” Subcutaneous ICD has proven to be safe and effective in many clinical trials. Patients without pacing indications and at higher risk of complications from trans-venous lead implantation represent the perfect candidates to S-ICD technology. However, with technical improvement, it is reasonable to expect a further expansion of indications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Zipes DP, Wellens HJ. Sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 1998;98(21):2334–51.
Mirowski M, Reid PR, Mower MM, et al. Termination of malignant ventricular arrhythmias with an implanted automatic defibrillator in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980;303:322–4.
Ezekowitz JA, Rowe BH, Dryden DM, et al. Systematic review: implantable cardioverter defibrillators for adults with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:251–62.
Curtis JP, Luebbert JJ, Wang Y, et al. Association of physician certification and outcomes among patients receiving an implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. JAMA. 2009;301:1661–70.
Kleemann T, Becker T, Doenges K, et al. Annual rate of transvenous defibrillation lead defects in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators over a period of >10 years. Circulation. 2007;115(19):2474–80.
Voigt A, Shalaby A, Saba S. Continued rise in rates of cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections in the United States: temporal trends and causative insights. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2010;33(4):414–9.
Wilkoff BL, Love CJ, Byrd CL, Bongiorni MG, et al. Transvenous lead extraction: heart rhythm society expert consensus on facilities, training, indications, and patient management. Heart Rhythm. 2009;6(7):1085–101.
Maytin M, Henrikson CA, Epstein LM. Lead extraction is preferred for lead revisions and system upgrades: when less is more. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010;3:413–24.
SQ-RX® pulse generator a component of the S-ICD® system user’s manual model 1010. Cameron Health Inc., San Clemente, CA, USA
Gold MR, Theuns DA, Knight BP, et al. Head-to-head comparison of arrhythmia discrimination performance of subcutaneous and transvenous ICD arrhythmia detection algorithms: the START Study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012;23:359–66.
Bardy GH, Smith WM, Hood MA, Crozier IG, Melton IC, Jordaens L, et al. An entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(1):36–44.
Olde Nordkamp LRA, Dabiri Abkenari L, Boersma LVA, et al. The entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator initial clinical experience in a large Dutch Cohort. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1933–9.
Jarman JW, Todd DM. United Kingdom national experience of entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator technology: important lessons to learn. Europace. 2013;15(8):1158–65.
Weiss R, Knight BP, Gold MR, Leon AR, Herre JM, Hood M, et al. Safety and efficacy of a totally subcutaneous implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation. 2013;128(9):944–53. International registry on S-ICD performance.
Lambiase PD, Barr C, Theuns DA, Knops R, Neuzil P, Johansen JB, et al. Worldwide experience with a totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: early results from the EFFORTLESS Investigators. Worldwide experience with a totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: early results from theEFFORTLESSS-ICD Registry. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(25):1657–65.
Randles DA, Hawkins NM, Shaw M. How many patients fulfil the surface electrocardiogram criteria for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation? Europace. 2014;16(7):1015–21.
Olde Nordkamp LRA, Warnaars JLF, Kooiman KM, et al. Which patients are not suitable for a subcutaneous ICD: incidence and predictors of failed QRS-T-wave morphology screening. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24(9):1015–20. The article analyses ECG predictors of S-ICD suitability.
De Bie MK, Thijssen J, van Rees JB, et al. Suitability for subcutaneous defibrillator implantation: results based on data from routine clinical practice. Heart. 2013;99(14):1018–23. The article analyses ECG predictors of S-ICD suitability.
Bardy GH, Lee KL, Mark DB, Poole JE, et al. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter–defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:225–37.
Peters B, Will A, Berger F, et al. Implantation of a fully subcutaneous ICD in a patient with single ventricle morphology and Eisenmenger physiology. Acta Cardiol. 2012;67(4):473–5.
Neuzil P, Petru J, et al. Subcutaneous ICD implantation in the setting of an occluded superior vena cava. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011;22:475–6.
Pettit SJ, MCLean A, Colquhoun I. Clinical experience of subcutaneous and transvenous implantable cardioverter defibrillators in children and teenagers. PACE. 2013;00:1–7.
Hanna R, Hellkamp A, Mark D, Lee K, Johnson G, Anderson A, et al. Predictors of ventricular tachyarrhythmias treated with the ICD in the sudden cardiac death in heart failure trial. Poster, ESC Congress 2012, Munich, Germany. August 26, 2012
Wathen MS, Sweeney MO, DeGroot PJ, Stark AJ, Koehler JL, Chisner MB, et al. PainFREE Investigators. Shock reduction using antitachycardia pacing for spontaneous rapid ventricular tachycardia in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2001;104:796–801.
Poole JE, Johnson GW, Hellkamp AS, Anderson J, Callans DJ, Raitt MH, et al. Prognostic importance of defibrillator shocks in patients with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1009–17.
Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ, Klein H, Wilber DJ, Cannom DS, et al. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:877–83.
Kadish A, Dyer A, Daubert JP, Quigg R, Estes NA, Anderson KP, et al. Defibrillators in Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Treatment Evaluation (DEFINITE) investigators. Prophylactic defibrillator implantation in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2151–8.
Kooiman KM, Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp L, et al. Inappropriate subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator shocks due to T-wave oversensing can be prevented. Implications for management. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11(3):426–34.
Moss AJ, Schuger C, Beck CA, Brown MW, Cannom DS, Daubert JP, et al. Reduction in inappropriate therapy and mortality through ICD programming. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2275–83.
Olde Nordkamp LR, Knops RE, Bardy GH, Blaauw Y, Boersma LV, Bos JS, et al. Rationale and design of the PRAETORIAN trial: a prospective, RAndomizEd comparison of subcuTaneOus and tRansvenous ImplANtable cardioverter- defibrillator therapy. Am Heart J. 2012;163:753–60.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Maria Grazia Bongiorni, Stefano Viani, Giulio Zucchelli, Andrea Di Cori, Luca Segreti, Luca Paperini, Dianora Levorato, Adriano Boem, Giulia Branchitta, Diana Andreini and Ezio Soldati declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Management of Heart Failure
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bongiorni, M.G., Viani, S., Zucchelli, G. et al. Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators: Indications and Limitations. Curr Heart Fail Rep 12, 79–86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11897-014-0242-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11897-014-0242-4