Abstract
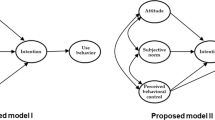
This study employed the theory of planned behavior to explore the relationship between criminal intention and criminal behavior and the factors influencing them. The present study focused on injury, theft, and drug use, the three most prominent types of criminal behavior in Taiwan. An anonymous online questionnaire survey of male adults was conducted with 864 valid responses returned. The responses revealed that attitudes toward crime, subjective norms, and perceived behavior control effectively predict the intention to injure, steal, or use drugs. Criminal intention effectively predicts the occurrence and the frequency of injury to others, theft, and drug use. Planning and anticipated regret do not moderate the relationship between criminal intention and criminal behavior. The implications of the findings and their practical application are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham C, Sheeran P (2004) Deciding to exercise: the role of anticipated regret. B J Health Psychol 9:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910704773891096
Ajzen I (1985) From intentions to actions: a theory of planned behavior. In: Kuhl J, Beckmann J (eds) Action-control: From cognition to behavior. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 11–39
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 50:179–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Allan JL, Johnston M, Campbell N (2011) Missed by an inch or a mile? Predicting the size of intention-behaviour gap from measures of executive control. Psychol Health 26:635–650. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870441003681307
Allom V, Mullan B, Sebastian J (2013) Closing the intention–behaviour gap for sunscreen use and sun protection behaviours. Psychol Health 28:477–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2012.745935
Arnold M (2019) Development of a hearing help-seeking questionnaire based on the theory of planned behavior. Int J Audiol 58(5):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1080/14992027.2018.1535720
Arrizabalaga-López M et al (2018) A randomized controlled trial of a program based on the theory of planned behavior to promote fruit and vegetable intake among school children: Profruve study protocol. BMC Public Health 18(1): 827. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5748-3
Arslan M, Şar S (2018) Examination of environmentally friendly “green” logistics behavior of managers in the pharmaceutical sector using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Res Soc Adm Pharm 14(11):1007–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.002
Beck L, Ajzen I (1991) Predicting dishonest actions using the theory of planned behavior. J Res Pers 25:285–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-6566(91)90021-H
Bruijn GJ, Kremers SJ, Vet E, Nooijer J, Mechelen W, Brug J (2007) Does habit strength moderate the intention-behaviour relationship in the theory of planned behaviour? the case of fruit consumption. Psychol Health 22:899–916. https://doi.org/10.1080/14768320601176113
Chiou HJ (2004) Principles and practice of structural equation modeling with LISREL (p.9.2). Yeh-Yeh Book Gallery
Conner M, Godin G (2007) Temporal stability of behavioral intention as a moderator of intention-health behaviour relationships. Psychol Health 22:875–897. https://doi.org/10.1080/14768320601070449
Conner M, Sandberg T, McMillan B, Higgins A (2006) Role of anticipated regret, intentions and intention stability in adolescent smoking initiation. Br J Health Psychol 11:85–101. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910705X40997
Cousson-Gélie F et al (2018) Preventing tobacco in vocational high schools: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial of P2P, a peer to peer and theory planned behavior-based program. BMC Public Health 18(1): 494. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5226-y
Dibonaventura MD, Chapman GB (2005) Moderators of the intention–behavior relationship in influenza vaccinations: intention stability and unforeseen barriers. Psychol Health 20:761–774. https://doi.org/10.1080/14768320500183368
Didarloo A, Khalili S, Aghapour AA, Moghaddam-Tabrizi F, Mousavi SM (2022) Determining intention, fast food consumption and their related factors among university students by using a behavior change theory. BMC Public Health 22(1):314. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12696-x
Fan CW, Chen IH, Ko NY, Yen CF, Lin CY, Griffiths MD et al (2021) Extended theory of planned behavior in explaining the intention to COVID-19 vaccination uptake among mainland Chinese university students: An online survey study. Hum Vacc Immunother 17(10):3413–3420. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2021.1933687
Fang HS, Tai CN (2009) The study of the situations soliciting the aggressive behavior for school children with aggressive behaviors. J Couns Guid 20:113–145. https://doi.org/10.6308/JCG.20.02
Gibson LP, Magnan RE, Kramer EB, Bryan AD (2021) Theory of planned behavior analysis of social distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic: Focusing on the intention-behavior gap. Ann Behav Med 55(8):805–812.https://doi.org/10.1093/abm/kaab041
Godin G, Conner M, Sheeran P (2005) Bridging the intention-behaviour ‘gap’: The role of moral norm. Br J Soc Psychol 44:497–512. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466604X17452
Gollwitzer PM (1999) Implementation intentions: strong effects of simple plans. Am Psychol 54:493–503. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.54.7.493
Hagger MS, Chan DKC, Protogerou C, Chatzisarantis NLD (2016) Using meta-analytic path analysis to test theoretical predictions in health behavior: an illustration based on meta-analyses of the theory of planned behavior. Prev Med 89:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.05.020
Hair J, Black W, Babin B, Anderson R, Tatham R (2006) Multivariate Data Analysis, 6th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Hall PA, Zehr CE, Ng M, Zanna MP (2012) Implementation intentions for physical activity in supportive and unsupportive environmental conditions: an experimental examination of intention–behavior consistency. J Exp Soc Psychol 48:432–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2011.09.004
Hameed J, Waris I, Haq MAU (2019) Predicting eco-conscious consumer behavior using theory of planned behavior in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res (International) 26(15):15535–15547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04967-9
Haydon HM, Obst PL, Lewis I (2018) Examining women’s alcohol consumption: the theory of planned behavior and self-identity. Subst Use & Misuse 53(1):128–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2017.1327972
Hrubes D, Ajzen I, Daigle J (2001) Predicting hunting intentions and behavior: an application of the theory of planned behavior. Leis Sci 23:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/014904001316896855
Huang JY (2017) Relationship between child sexual aggression intention and practice and its impact factors. Bull Educ Psychol 49:193–214. https://doi.org/10.6251/BEP.201712-49(2).0002
Hussain SA, Alhabash S (2021) Nostalgic emotional valence and its effects on help-seeking in depression: an application of the theory of planned behavior. Health Communication 36(13):1731–1742. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2020.1794549
Jolliffe D, Farrington DP, Hawkins JD, Catalano RF, Hill KG, Kosterrman R (2003) Predictive, concurrent, prospective and retrospective validity of self-reported delinquency. Crim Behav Ment Health 13:179–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbm.541
Koss MP, Gidycz CA, Wisniewski N (1987) The scope of rape: incidence and prevalence of sexual aggression and victimization in a national sample of higher education students. J Consult Clin Psychol 55–170. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.55.2.162
Krueger J (1998) Enhancement bias in descriptions of self and others. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 24(5):505–516. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167298245006
Lareyre O, Gourlan M, Stoebner-Delbarre A, Cousson-Gélie F (2021) Characteristics and impact of theory of planned behavior interventions on smoking behavior: a systematic review of the literature. Prev Med 143
Lawental M, Kipnis A, Rigg K (2018) Binge drinking among young adults in Israel: application of the theory of planned behavior. Psychol Health Med 23(9):1060–1068. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2018.1467025
Lin CY, Updegraff JA, Pakpour AH (2016) The relationship between the theory of planned behavior and medication adherence in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behavior 61:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.05.030
Little TD, Cunningham WA, Shahar G, Widaman KF (2002) To parcel or not to parcel: exploring the question, weighing the merits. Struct Equ Modeling: A Multidiciplanary Journal 9:151–173. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15328007SEM0902_1
Martin RJ et al (2010) Using the theory of planned behavior to predict gambling behavior. Psychol Addict Behav 24(1):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018452
McEachan RRC, Conner M, Taylor NJ, Lawton RJ (2011) Prospective prediction of health-related behaviours with the theory of planned behaviour: a meta-analysis. Health Psychol Rev 5:97–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2010.521684
National Police Agency, Ministry of Interior (2020). Criminal Profile of Suspect. Retrieved September 21, 2020, from website: https://www.npa.gov.tw/NPAGip/wSite/ct?xItem=94251&ctNode=12768&mp=1
Norman P, Conner M (2005) The theory of planned behavior and exercise: evidence for the mediation and moderating roles of planning on intention-behavior relationships. J Sport Exerc Psychol 27:488–504. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsep.27.4.488
Prestwich A, Perugini M, Hurling R (2008) Goal desires moderate intention-behavior relations. Br J Soc Psychol 47:49–71. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466607X218221
Qi X, Ploeger A (2019) Explaining consumers’ intentions towards purchasing green food in Qingdao, China: the amendment and extension of the theory of planned behavior. Appetite 133:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2018.12.004
Reuter T, Ziegelmann JP, Wiedemann AU, Lippke S (2008) Dietary planning as a mediator of the intention–behavior relation: an experimental-causal-chain design. Applied Psychology: an International Review 57:194–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-0597.2008.00364.x
Reuter T, Ziegelmann JP, Wiedemann AU, Lippke S, Schüz B, Aiken LS (2010) Planning bridges the intention-behaviour gap: age makes a difference and strategy use explains why. Psychol Health 25:873–887. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870440902939857
Rhodes R, Bruijn G (2013) How big is the physical activity intention-behaviour gap? A meta-analysis using the action control framework. Br J Health Psychol. 18:296–309. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12032
Rhodes RE (2014) Bridging the physical activity intention-behaviour gap: contemporary strategies for the clinician. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39:105–107. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2013-0166
Rhodes RE, Plotnikoff RC, Courneya KS (2008) Predicting the physical activity intention–behavior profiles of adopters and maintainers using three social cognition models. Ann Behav Med 36:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-008-9071-6
Rich A, Brandes K, Mullan B, Hagger MS (2015) Theory of planned behavior and adherence in chronic illness: a meta-analysis. J Behav Med. 38(4):673–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-015-9644-3
Richard R, Van der Plight J, De Vries NK (1996) Anticipated regret and time perspective: changing sexual risk-taking behavior. J Behav Decis Mak 9:185–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0771(199609)9:3%3c185::AID-BDM228%3e3.0.CO;2-5
Sandberg T, Conner M (2008) Anticipated regret as an additional predictor in the theory of planned behaviour: a meta-analysis. Br J Soc Psychol 47:589–606. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466607X258704
Schwarzer R, Luszczynska A, Ziegelmann JP, Scholz U, Lippke S (2008) Social-cognitive predictors of physical exercise adherence: three longitudinal studies in rehabilitation. Health Psychol 27:854–863. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.27.1(Suppl.).S54
Sheeran P (2002) Intention-behaviour relations: a conceptual and empirical review. In: Stroebe W, Hewstone M (eds) European Review of Social Psychology, 12. Wiley, London, pp 1–36
Sheeran P, Maki A, Montanaro E, Avishai-Yitshak A, Bryan A, Klein WM et al (2016) The impact of changing attitudes, norms, and self-efficacy on health-related intentions and behavior: a meta-analysis. Health Psychol 35(11):1178–1188. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0000387
Siegel LJ (2016) Criminology: The core (6th Ed.) (p. 381). CENGAGE Learning
Skinner BF (1938) The behavior of organisms: An experimental analysis. Appleton-Century, New York
Sniehotta FF, Scholz U, Schwarzer R (2005) Bridging the intention–behaviour gap: planning, self-efficacy, and action control in the adoption and maintenance of physical exercise. Psychol Health 20:143–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870440512331317670
Taylor SE, Peplau LA, Sears DO (1997) Social psychology, 9th edn. Prentice Hall, NJ, pp 141–142
Thoma BC, Huebner DM (2018) Parent-adolescent communication about sex and condom use among young men who have sex with men: an examination of the theory of planned behavior. Ann Behav Med 52(11):973–987. https://doi.org/10.1093/abm/kay002
Tochkov K (2009) The effects of anticipated regret on risk preferences of social and problem gamblers. Judgm Decis Mak 4:227–234
Tseng YF, Wang KL, Lin CY, Lin YT, Pan HC, Chang CJ (2018) Predictors of smoking cessation in Taiwan: using the theory of planned behavior. Psychol Health Med 23(3):270–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2017.1378820
Turchik JA, Gidycz CA (2012) Exploring the intention-behavior relationship in the prediction of sexual risk behaviors: can it be strengthened? J Sex Res 49:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224499.2011.578220
Wang S, Wang J, Yang S, Li J, Zhou K (2020) From intention to behavior: comprehending residents’ waste sorting intention and behavior formation process. Waste Manage 113:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.05.031
Wikipedia (2020) Zhengjie (Taiwan). Retrieved August 5, from website: https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%84%AD%E6%8D%B7_(%E8%87%BA%E7%81%A3)
Wu AMS, Tang CS (2012) Problem gambling of Chinese college students: application of the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Gambling Study 28:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-011-9250-4
Yu SC, Yu MN (2006) Comparison of internet and paper-and-pencil questionnaires in Taiwan using multi-sample invariance approach. Psychol Testing 53:103–127. https://doi.org/10.7108/PT.200606.0103
Zeelenberg M (1999) Anticipated regret, expected feedback and behavioral decision making. J Behav Decis Mak 12:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0771(199906)12:2%3c93::AID-BDM311%3e3.0.CO;2-S
Zhao X, Dichtl FF, Foran HM (2022) Predicting smoking behavior: iIntention and future self-continuity among Austrians. Psychol Health Med 27(5):1042–1051. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2020.1842898
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology (grant number: MOST 106–2410-H-364 -002-SSS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan (REC number: 10605ES031). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This study used anonymous self-reporting online questionnaire to collect data. All the participants are Taiwanese. The contents of the questionnaire were not connected to personal information. Under informed consent, the participants decided whether they would participate in the survey.
Informed Consent
The informed consent was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of National.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, JY., Chen, CA. Relationship Between Criminal Intention and Criminal Behavior. J Police Crim Psych 38, 555–566 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11896-023-09576-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11896-023-09576-4