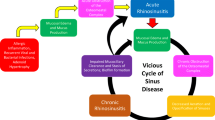
Abstract
Purpose of Review
In the clinical practice, patients affected by chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) commonly complain of otologic symptoms. This review aims to describe the available literature evidence assessing the relationship between CRS and ear illnesses published in the last 5 years.
Recent Findings
Available evidence suggests a higher prevalence of otologic symptoms in patients suffering from CRS, affecting up to 87% of patients. These symptoms may be related to Eustachian tube dysfunction, which improves after treatment for CRS. A few studies suggested a potential but not confirmed role of CRS in cholesteatoma, chronic otitis media, and sensorineural hypoacusis. A special type of otitis media with effusion (OME) may occur in patients with CRS, which seems to respond well to new biologic therapy.
Summary
Ear symptoms appear to be highly prevalent in patients with CRS. So far, the available evidence is robust only for Eustachian tube dysfunction, which has been shown to be particularly impaired in CRS patients. Additionally, the Eustachian tube function appears to improve after treatment for CRS. Finally, interesting preliminary data were described for eosinophilic otitis media, as it appears to respond well to the treatment with biologics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ahmad JG, Marino MJ, Luong AU. Unified airway disease: future directions. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2023;56(1):181–95.
Maniakas A, Desrosiers M, Asmar MH, Al Falasi M, Endam LM, Hopkins C, et al. Eustachian tube symptoms are frequent in chronic rhinosinusitis and respond well to endoscopic sinus surgery. Rhinology. 2018;56(2):118–21.
Chang MT, Hosseini DK, Song SH, Nayak JV, Patel ZM, Lee JY, et al. The effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;163(3):603–10.
Teo NW, Mace JC, Smith TL, Hwang PH. Impact of endoscopic sinus surgery on otologic symptoms associated with chronic rhinosinusitis. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;3(1):24–31.
• Chen T, Shih MC, Edwards TS, Nguyen SA, Meyer TA, Soler ZM, et al. Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) in chronic rhinosinusitis with comparison to primary ETD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022;12(7):942–51. Up to date, this is the only metanalysis assessing eustachian tube dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis.
Cole RA. Chronic otitis media, mastoiditis and petrositis. In: Cummings Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2015. p. 2139–55.
Jung SY, Kim D, Park DC, Lee EH, Choi YS, Ryu J, et al. Immunoglobulins and transcription factors in otitis media. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):3201.
Singh GB, Malhotra S, Yadav SC, Kaur R, Kwatra D, Kumar S. The role of biofilms in chronic otitis media-active squamosal disease: an evaluative study. Otol Neurotol. 2021;42(9):e1279–85.
Kim SK, Park MW, Min C, Park IS, Park B, Byun SH, et al. Increased risk of chronic otitis media in chronic rhinosinusitis patients: a longitudinal follow-up study using a national health screening cohort. Rhinology. 2021;59(3):292–300.
Hong SN, Lee WH, Lee SH, Rhee CS, Lee CH, Kim JW. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is associated with chronic otitis media in the elderly. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274(3):1463–70.
Son DS, Cho MS, Kim DK. Chronic rhinosinusitis could increase the risk of cholesteatoma of middle ear. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023;13(2):168–71.
Kuo CL, Yen YC, Chang WP, Shiao AS. Association between middle ear cholesteatoma and chronic rhinosinusitis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;143(8):757–63.
Chen WC, Yang KL, Lin WC, Fang KC, Wu CN, Luo SD. Clinical outcomes of Eustachian tube dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis following endoscopic sinus surgery. J Chin Med Assoc. 2022;85(7):782–7.
Choi KY, Jang S, Seo G, Park SK. Effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on Eustachian tube function in adult sinusitis patients: a prospective case-control study. J Clin Med. 2021;10(20):4689.
Wu AW, Walgama ES, Higgins TS, Borrelli M, Vardanyan N, Hopp S, et al. Eustachian tube quality of life and severity of disease in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2020;34(4):532–6.
Higgins T, Cappello Z, Wu AW, Ting JY, Sindwani R. Predictors of eustachian tube dysfunction improvement and normalization after endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 2020;130(12):E721–6.
Schilder AGM, Bhutta MF, Butler CC, Holy C, Levine LH, Kvaerner KJ, et al. Eustachian tube dysfunction: consensus statement on definition, types, clinical presentation and diagnosis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015;40(5):407–11.
Smith ME, Tysome JR. Tests of Eustachian tube function: a review. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015;40(4):300–11.
Vandersteen C, Castillo L, Roger C, Savoldelli C, Guevara N. Tubomanometry: an effective and promising assessment of Eustachian tube dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2021;138(1):7–12.
Tangbumrungtham N, Patel VS, Thamboo A, Patel ZM, Nayak JV, Ma Y, et al. The prevalence of Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018;8(5):620–3.
Daval M, Picard H, Bequignon E, Bedbeder P, Coste A, Ayache D, et al. Chronic otitis media with effusion in chronic sinusitis with polyps. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018;97(8):E13–8.
Chen X, Dang H, Chen Q, Chen Z, Ma Y, Liu X, et al. Endoscopic sinus surgery improves Eustachian tube function in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a multicenter prospective study. Rhinology. 2021;59(6):560–6.
Lyly A, Genberg E, Kauppi P, Virkkula P, Lee SE, Laidlaw TM, et al. Real-life experience of biologic treatment for asthma on chronic rhinosinusitis: a Finnish cohort. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022;7:1–12.
Ohta N, Ishida A, Kurakami K, Suzuki Y, Kakehata S, Ono J, et al. Expressions and roles of periostin in otolaryngological diseases. Allergol Int. 2014;63(2):171–80.
•• Bartier S, Béquignon E, Thibaut de Ménonville C, Verillaud B, Evrard D, Léger M, et al. Otitis media in severe asthma associated with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a new therapeutic target for biologics. J Asthma. 2022;1–6. This study has the largest sample size reporting the use of biologic therapy to treat eosinophilic otitis media, an illness currently no recognized as indication for biologic therapy.
• Iino Y, Tomioka-Matsutani S, Matsubara A, Nakagawa T, Nonaka M. Diagnostic criteria of eosinophilic otitis media, a newly recognized middle ear disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011;38(4):456–61. This study is the basis for the diagnosis of eosinophilic otitis media.
Ohira S, Komori M, Matsui H, Furuya H, Kajiwara R, Matsuura K, et al. Anatomical features around Eustachian tube in eosinophilic otitis media with eosinophilic sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2021;131(10):E2689–95.
Yoshida N. Intractable otitis media - pathogenesis and treatment of Eosinophilic otitis media (EOM) and otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) -associated vasculitis (OMAAV). Auris Nasus Larynx. 2022;S0385–8146(22):00191–2.
Shevchik E, Svistushkin V, Nikiforova G, Zolotova A. Eosinophilic otitis media: modern aspects of pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022;74(Suppl 1):132–40.
Seo Y, Nonaka M, Yamamura Y, Pawankar R, Tagaya E. Optimal control of asthma improved eosinophilic otitis media. Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(1): e5.
•• De Corso E, Montuori C, Settimi S, Mele DA, Cantiani A, Corbò M, et al. Efficacy of biologics on refractory eosinophilic otitis media associated with bronchial asthma or severe uncontrolled CRSwNP. J Clin Med. 2022;11(4):926. This study has the second largest sample size reporting the use of biologic therapy to treat eosinophilic otitis media, however is the largest using a specific questionnaire to assess chronic otitis media response.
Kagoshima H, Hori R, Kojima T, Okanoue Y, Tagushi A, Yamamoto H, et al. Successful treatment of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis and eosinophilic otitis media using the anti-IL-5 receptor monoclonal antibody benralizumab: a case report. Respir Med Case Repo. 2020;17(30): 101135.
Shimizu H, Kato H, Yoshioka S, Okazawa M. Rapid and remarkable effectiveness of benralizumab for treating severe bronchial asthma with intractable eosinophilic rhinosinusitis and eosinophilic otitis media: a case report. Respir Med Case Rep. 2021;32:101336.
Chikumoto A, Oishi K, Hamada K, Hirano T, Kakugawa T, Kanesada K, et al. Sequential biotherapy targeting IL-5 and IL-4/13 in patients with eosinophilic asthma with sinusitis and otitis media. Biomolecules. 2022;12(4):522.
van der Lans RJL, van Spronsen E, Fokkens WJ, Reitsma S. Complete remission of severe eosinophilic otitis media with dupilumab: a case report. Laryngoscope. 2021;131(12):2649–51.
Iino Y, Sekine Y, Yoshida S, Kikuchi S. Dupilumab therapy for patients with refractory eosinophilic otitis media associated with bronchial asthma. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021;48(3):353–60.
Gill AS, Hwang J, Beliveau AM, Alt JA, Strong EB, Wilson MD, et al. The impact of medical comorbidities on patient satisfaction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2021;12:34894211015736.
Lin X, Shan X, Lin S, Shu B, Wang Y, Xiao W. Is Sensorineural hearing loss related to chronic rhinosinusitis caused by outer hair cell injury? Med Sci Monit. 2019;22(25):627–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Calvo-Henriquez, C., Di Corso, E., Alobid, I. et al. Pathophysiological Link Between Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Ear Disease. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 23, 389–397 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-023-01072-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-023-01072-3