Abstract
Purpose of Review
Intranasal corticosteroid sprays have been available as over-the-counter (OTC) medications since 2013. As such, clinicians need to be up-to-date with the risks and the safety of INS, as patients may have concerns and detailed questions. The following is a review of the recent medical literature regarding the safety profile, adverse reactions, and special populations using INS.
Recent Findings
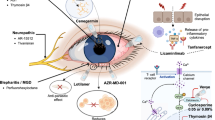
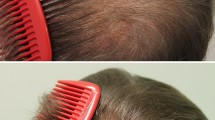
The latest research on intranasal steroid sprays (INS) continue to confirm that INS rarely have significant local side effects, such as severe and persistent epistaxis. Recent studies looking at systemic side effects such as hypothalamic pituitary axis suppression, growth effects, and ocular effects do not indicate any new concerns nor have found significant differences from the past literature. The use of combination INS and topical antihistamine medications did not reveal any new safety issues. Use of INS with topical decongestants found some limited effects of tachyphylaxis and rebound congestion. Studies continue to support the use of newer INS for children and continued monitoring of growth in this population. The HIV population should avoid use of INS with the prescription of ritonavir, given demonstration of adrenal suppression.
Summary
This updated perspective has found that newer generation INS should be used at the lowest effective dose for the selected population, that clinicians can inform patients using the OTC INS preparations that there are very few safety concerns, and that regular follow-up visits can provide further reassurance with physical examinations and address patient’s questions. Future research regarding the safety of INS should study newer preparations when developed and if used in combination with other topical agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Jang TY, Kim YH. Recent updates on the systemic and local safety of intranasal steroids. Curr Drug Metab. 2016;17(10):992–6.
D'Alonzo GE Jr. Scope and impact of allergic rhinitis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2002;102(6 Suppl 2):S2–6.
van Bavel JH, Ratner PH, Amar NJ, Hampel FC Jr, Melchior A, Dunbar SA, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily treatment with beclomethasone dipropionate nasal aerosol in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012;33(5):386–96.
• Dykewicz MS, Wallace DV, Baroody F, Bernstein J, Craig T, Finegold I, et al. Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: an evidence-based focused 2017 guideline update. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;119(6):489–511.e41 Important update for treatment of allergic rhinitis.
Badorrek P, Hohlfeld JM, Krug N, Joshi A, Raut A. Efficacy and safety of a novel nasal steroid, S0597, in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;115(4):325–9.e1.
Thennati R, Khanna A, Khanna M, Sonaiya T, Mehta T, Mehta K, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of compound SFDAC by intranasal administration of multiple escalating dose in healthy male subjects. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2014;3(6):428–38.
Storms WW, Segall N, Mansfield LE, Amar NJ, Kelley L, Ding Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of beclomethasone dipropionate nasal aerosol in pediatric patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013;111(5):408–14.e1.
• Lightman S, Scadding GK. Should intranasal corticosteroids be used for the treatment of ocular symptoms of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis? A review of their efficacy and safety profile. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;158(4):317–25 Article reviewing ocular issues pertaining to INS.
Blaiss MS. Safety update regarding intranasal corticosteroids for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2011;32(6):413–8.
Day JH, Andersson CB, Briscoe MP. Efficacy and safety of intranasal budesonide in the treatment of perennial rhinitis in adults and children. Ann Allergy. 1990;64(5):445–50.
Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, Brook I, Ashok Kumar K, Kramper M, et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;152(2 Suppl):S1–S39.
Snidvongs K, Thanaviratananich S. Update on intranasal medications in rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017 Jul;17(7):47.
Orgel HA, Meltzer EO, Bierman CW, Bronsky E, Connell JT, Lieberman PL, et al. Intranasal fluocortin butyl in patients with perennial rhinitis: a 12-month efficacy and safety study including nasal biopsy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991;88(2):257–64.
Blaiss MS. Over-the-counter intranasal corticosteroids: why the time is now. Pro Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013;111(5):316–8.
Allen A, Murdoch RD, Bareille P, Burns O, Hughes S, Gupta A, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of once-daily intranasal fluticasone furoate and levocabastine administered alone or simultaneously as fluticasone furoate/levocabastine fixed-dose combination. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2016 May;5(3):225–31.
Ahmadiafshar A, Ahmadiafshar S. Efficacy and safety of inhaled and intranasal corticosteroids. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2014;13(2):83–7.
Davies RJ, Nelson HS. Once-daily mometasone furoate nasal spray: efficacy and safety of a new intranasal glucocorticoid for allergic rhinitis. Clin Ther. 1997;19(1):27–38.
Nowicka A, Samolinski B. Is the use of intranasal glucocorticosteroids (inGCSs) in children safe? Otolaryngol Pol. 2015;69(1):1–10.
• Lipworth BJ, Jackson CM. Safety of inhaled and intranasal corticosteroids: lessons for the new millennium. Drug Saf. 2000;23(1):11–33 Broad review of the safety of INS.
Blaiss MS. Safety considerations of intranasal corticosteroids for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007;28(2):145–52.
Sastre J, Mosges R. Local and systemic safety of intranasal corticosteroids. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2012;22(1):1–12.
Lanier B, Kai G, Marple B, Wall GM. Pathophysiology and progression of nasal septal perforation. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007;99(6):473–9 quiz 80–1, 521.
Dosen LK, Haye R. Nasal septal perforation 1981–2005: changes in etiology, gender and size. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2007;7:1.
• Salib RJ, Howarth PH. Safety and tolerability profiles of intranasal antihistamines and intranasal corticosteroids in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Drug Saf. 2003;26(12):863–93 Good review of safety of INS for particular populations (children, elderly, pregnancy).
• Bensch GW. Safety of intranasal corticosteroids. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016;117(6):601–5 Important overview article.
• Passalacqua G, Albano M, Canonica GW, Bachert C, Van Cauwenberge P, Davies RJ, et al. Inhaled and nasal corticosteroids: safety aspects. Allergy. 2000;55(1):16–33 Useful overview of safety of INS.
Klossek JM, Laliberte F, Laliberte MF, Mounedji N, Bousquet J. Local safety of intranasal triamcinolone acetonide: clinical and histological aspects of nasal mucosa in the long-term treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis. Rhinology. 2001;39(1):17–22.
Mehta DK. British National Formulary, number 432002 March 31, 2002.
Manji J, Singh G, Okpaleke C, Dadgostar A, Al-Asousi F, Amanian A, et al. Safety of long-term intranasal budesonide delivered via the mucosal atomization device for chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017;7(5):488–93.
Welch MJ, Bronsky E, Findlay S, Pearlman DS, Southern DL, Storms WW, et al. Long-term safety of triamcinolone acetonide nasal aerosol for the treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis. Clin Ther. 1994;16(2):253–62.
Skoner DP, Gentile D, Angelini B, Kane R, Birdsall D, Banerji D. The effects of intranasal triamcinolone acetonide and intranasal fluticasone propionate on short-term bone growth and HPA axis in children with allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003 Jan;90(1):56–62.
Schenkel EJ, Skoner DP, Bronsky EA, Miller SD, Pearlman DS, Rooklin A, et al. Absence of growth retardation in children with perennial allergic rhinitis after one year of treatment with mometasone furoate aqueous nasal spray. Pediatrics. 2000;105(2):E22.
Moller C, Ahlstrom H, Henricson KA, Malmqvist LA, Akerlund A, Hildebrand H. Safety of nasal budesonide in the long-term treatment of children with perennial rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003;33(6):816–22.
Toogood JH, Jennings B, Crepea SB, Johnson JD. Efficacy of safety of concurrent use of intranasal flunisolide and oral beclomethasone aerosols in treatment of asthmatics with rhinitis. Clin Allergy. 1982;12(1):95–105.
Skoner DP, Rachelefsky GS, Meltzer EO, Chervinsky P, Morris RM, Seltzer JM, et al. Detection of growth suppression in children during treatment with intranasal beclomethasone dipropionate. Pediatrics. 2000;105(2):E23.
Mansfield LE, Mendoza CP. Medium and long-term growth in children receiving intranasal beclomethasone dipropionate: a clinical experience. South Med J. 2002;95(3):334–40.
Weinstein S, Qaqundah P, Georges G, Nayak A. Efficacy and safety of triamcinolone acetonide aqueous nasal spray in children aged 2 to 5 years with perennial allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with an open-label extension. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009;102(4):339–47.
Gradman J, Caldwell MF, Wolthers OD. A 2-week, crossover study to investigate the effect of fluticasone furoate nasal spray on short-term growth in children with allergic rhinitis. Clin Ther. 2007 Aug;29(8):1738–47.
Ratner P, Darken P, Wingertzahn M, Shah T. Ciclesonide and beclomethasone dipropionate coadministration: effect on cortisol in perennial allergic rhinitis. J Asthma. 2007;44(8):629–33.
LaForce C, Journeay GE, Miller SD, Silvey MJ, Wu W, Lee LA, et al. Ocular safety of fluticasone furoate nasal spray in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis: a 2-year study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013;111(1):45–50.
Meltzer EO, Bernstein DI, Prenner BM, Berger WE, Shekar T, Teper AA. Mometasone furoate nasal spray plus oxymetazoline nasal spray: short-term efficacy and safety in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013;27(2):102–8.
Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008;63(Suppl 86):8–160.
•• Baena-Cagnani CE. Safety and tolerability of treatments for allergic rhinitis in children. Drug Saf. 2004;27(12):883–98 Key review of the safety aspects of INS in children.
Dibildox J. Safety and efficacy of mometasone furoate aqueous nasal spray in children with allergic rhinitis: results of recent clinical trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108(1 Suppl):S54–8.
Berard A, Sheehy O, Kurzinger ML, Juhaeri J. Intranasal triamcinolone use during pregnancy and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138(1):97–104 e7.
• Alhussien AH, Alhedaithy RA, Alsaleh SA. Safety of intranasal corticosteroid sprays during pregnancy: an updated review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;275(2):325–33 Key review of safety of INS in pregnancy.
• Foisy MM, Yakiwchuk EM, Chiu I, Singh AE. Adrenal suppression and Cushing's syndrome secondary to an interaction between ritonavir and fluticasone: a review of the literature. HIV Med. 2008;9(6):389–96 Looks at issues with INS in HIV+ populations.
Garbe E, LeLorier J, Boivin JF, Suissa S. Inhaled and nasal glucocorticoids and the risks of ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. JAMA. 1997;277(9):722–7.
Grossman J, Gates D. Mometasone furoate nasal spray for the treatment of elderly patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010 May;104(5):452–3.
• Dykewicz MS, Kaiser HB, Nathan RA, Goode-Sellers S, Cook CK, Witham LA, et al. Fluticasone propionate aqueous nasal spray improves nasal symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis when used as needed (prn). Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003;91(1):44–8 Article showing some efficacy of INS even given PRN.
Minshall E, Ghaffar O, Cameron L, O'Brien F, Quinn H, Rowe-Jones J, et al. Assessment by nasal biopsy of long-term use of mometasone furoate aqueous nasal spray (Nasonex) in the treatment of perennial rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;118(5):648–54.
Pipkorn U, Pukander J, Suonpaa J, Makinen J, Lindqvist N. Long-term safety of budesonide nasal aerosol: a 5.5-year follow-up study. Clin Allergy. 1988;18(3):253–9.
Chong LY, Head K, Hopkins C, Philpott C, Burton MJ, Schilder AG. Different types of intranasal steroids for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;4:CD011993.
• Blaiss MS. Efficacy, safety, and patient preference of inhaled nasal corticosteroids: a review of pertinent published data. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2001;22(6 Suppl 1):S5–10 Review of published studies on safety.
• Khanna P, Shah A. Assessment of sensory perceptions and patient preference for intranasal corticosteroid sprays in allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol. 2005;19(3):316–21 Details how sensory aspects differ between medications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Rhinitis, Conjunctivitis, and Sinusitis
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(MOV 60.9 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonnell, J., Weller, K. & Pien, L.C. Safety of Intranasal Steroids: an Updated Perspective. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 20, 69 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-020-00960-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-020-00960-2