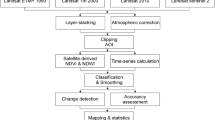
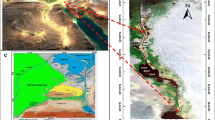
Abstract
Saltmarsh land-cover (SLC) ecosystems, composed of unvegetated mudflats, saltmarshes, mangroves, and/or seagrass communities, are vulnerable to climate-induced impacts, such as sea level rise. Extracting a seamless and consistent waterline from satellite imagery is a major challenge because of environmental factors, such as turbidity, water depth and multiple types of underwater vegetation cover that introduce noise in the extraction of information. Hence, a water index, derived from multi-temporal Landsat 8 (OLI) data, acquired under different tides is proposed for mapping land-water across SLC wetlands by tracking waterlines. This provided inundation maps and defined eco-zones to specify south-eastern Bangladesh wetland composition. The NDWI_1 (McFeeters’s water index) applied to 42 OLI images and derived land-water difference maps generated inundation gradient maps with an overall classification accuracy of 87.8%. The simple intersection and union of region-of-interests extracted from the tide heights above the mean low-water springs enabled the mapping of four categories of wetland composition based on hydroperiods: a) irregularly inundated (II), regularly inundated (RI), irregularly exposed (IE; high floodplain), and subtidal (river bed and deep water sea). For all of the three study sites, mangrove, seagrass, non-mangrove and agriculture were all prominent on the IE eco-zone, while only saltmarsh was dominant on the II eco-zone. These maps of SLC wetland will enrich previous concepts of eco-zonation models that include salinity, erosion, accretion and rate of sea level rise as factors, suggesting that inundation extent and tidal phase complexities should be considered in the remote sensing of SLC composition for improved models of SLC vegetation response to climate change.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, MSH.
References
Abu Hena MK, Aysha A, Ashraful MAKK et al (2010) Distribution of aquatic macrophytes in the coastal area of Salimpur, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Chiang Mai Univ J Nat Sci 9:273–279
Acharya TD, Lee DH, Yang IT, Lee JK (2016) Identification of Water bodies in a landsat 8 OLI Image using a J48 decision tree. Sensors 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071075
Acharya TD, Subedi A, Lee DH (2018) Evaluation of water indices for surface water extraction in a landsat 8 scene of Nepal. Sensors 18:2580
Al Azad ASMA, Mita KS, Zaman MW et al (2018) Impact of tidal phase on inundation and thrust force due to storm surge. J Mar Sci Eng 6:110
Alam SMR, Hossain MS (2021) A rule-based classification method for mapping saltmarsh land-cover in South-Eastern Bangladesh from Landsat-8 OLI. Can J Remote Sens 47:356–380. https://doi.org/10.1080/07038992.2020.1789852
Alam SMR, Hossain MS (2023) Probabilities of acquiring cloud-free and low-tide landsat observations for mapping saltmarsh over south-eastern Bangladesh from 1980 to 2019. Mar Geod: 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490419.2023.2200212
Almonacid-Caballer J, Sánchez-García E, Pardo-Pascual JE et al (2016) Evaluation of annual mean shoreline position deduced from Landsat imagery as a mid-term coastal evolution indicator. Mar Geol 372:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2015.12.015
Aristizabal F, Judge J, Monsivais-Huertero A (2020) High-resolution inundation mapping for Heterogeneous Land covers with synthetic aperture radar and Terrain Data. Remote Sens 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060900
Bai J, Chen X, Li J et al (2011) Changes in the area of inland lakes in arid regions of central Asia during the past 30 years. Environ Monit Assess 178:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1686-y
Barbier EB, Hacker SD, Kennedy C et al (2011) The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol Monogr 81:169–193
Best ÜSN, Van der Wegen M, Dijkstra J et al (2018) Do salt marshes survive sea level rise? Modelling wave action, morphodynamics and vegetation dynamics. Environ Model Softw 109:152–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.08.004
Billah MM, Zamal H, Kamal AHM et al (2016) Saltmarsh and seagrass beds on the south-eastern coast of Bangladesh: vegetation characteristics and adjacent fisheries diversity. Zool Ecol 26:313–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/21658005.2016.1225364
Bishop-Taylor R, Sagar S, Lymburner L et al (2019a) Sub-pixel Waterline extraction: characterising accuracy and sensitivity to indices and Spectra. Remote Sens 11:2984
Bishop-Taylor R, Sagar S, Lymburner L, Beaman RJ (2019b) Between the tides: modelling the elevation of Australia’s exposed intertidal zone at continental scale. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 223:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.03.006
Coleman AM, Diefenderfer HL, Ward DL, Borde AB (2015) A spatially based area–time inundation index model developed to assess habitat opportunity in tidal–fluvial wetlands and restoration sites. Ecol Eng 82:624–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.05.006
Craft C (2016) Inland marshes. In: Craft CBT-C (ed) Creating and restoring wetlands. Elsevier, Boston, pp 95–127
Crosby SC, Sax DF, Palmer ME et al (2016) Salt marsh persistence is threatened by predicted sea-level rise. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 181:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.08.018
Dai C, Howat IM, Larour E, Husby E (2019) Coastline extraction from repeat high resolution satellite imagery. Remote Sens Environ 229:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.04.010
David PG (1996) Changes in plant communities relative to hydrologic conditions in the Florida Everglades. Wetlands 16:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160642
Dong Y, Liu Y, Hu C, Xu B (2019) Coral reef geomorphology of the Spratly Islands: a simple method based on time-series of Landsat-8 multi-band inundation maps. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 157:137–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.09.011
Feyisa GL, Meilby H, Fensholt R, Proud SR (2014) Automated water extraction index: a new technique for surface water mapping using landsat imagery. Remote Sens Environ 140:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.029
Gao B-C, Li R-R (2018) FVI-A floating Vegetation Index formed with three Near-IR channels in the 1.0–1.24 µm spectral range for the detection of Vegetation floating over Water surfaces. Remote Sens 10:1421
Green EP, Edwards AJ, Mumby PJ (2000) Mapping bathymetry. In: Green EP, Mumby PJ, Edwards AJ, Clark CD (eds) Remote sensing handbook for Tropical Coastal Management. UNESCO, Paris, pp 219–233
Guarnieri A, Vettore A, Pirotti F et al (2009) Retrieval of small-relief marsh morphology from terrestrial laser scanner, optimal spatial filtering, and laser return intensity. Geomorphology 113:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.06.005
Guo M, Li J, Sheng C et al (2017) A review of wetland remote sensing. Sensors (Switzerland) 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040777
Hagenaars G, de Vries S, Luijendijk AP et al (2018) On the accuracy of automated shoreline detection derived from satellite imagery: a case study of the sand motor mega-scale nourishment. Coast Eng 133:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2017.12.011
Harris AR, Mason IM (1989) Lake area measurement using AVHRR a case study. Int J Remote Sens 10:885–895. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431168908903928
Hena MKAKA, Short FTT, Sharifuzzaman SMM et al (2007) Salt marsh and seagrass communities of Bakkhali Estuary, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2007.01.022
Hooke JM (1984) Changes in river meanders: a review of techniques and results of analyses. Prog Phys Geogr Earth Environ 8:473–508. https://doi.org/10.1177/030913338400800401
Huang C, Chen Y, Zhang S, Wu J (2018) Detecting, extracting, and monitoring surface water from space using optical sensors: a review. Rev Geophys 56:333–360. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000598
Hughes MG, Rogers K, Wen L (2019) Saline wetland extents and tidal inundation regimes on a micro-tidal coast, New South Wales, Australia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 227:106297
Huq AM (1986) Plants names of Bangladesh (native and scientific). Bangladesh National Herbarium, BARC, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Islam AS, Bala SK, Haque MA (2010) Flood inundation map of Bangladesh using MODIS time-series images. J Flood Risk Manag 3:210–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-318X.2010.01074.x
Jia M, Wang Z, Wang C et al (2019) A new vegetation index to detect periodically submerged mangrove forest using single-tide Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens 11:2043
Jia M, Wang Z, Mao D et al (2021) Rapid, robust, and automated mapping of tidal flats in China using time series Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens Environ 255:112285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2021.112285
Jiang H, Feng M, Zhu Y et al (2014) An automated method for extracting Rivers and Lakes from Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens 6:5067–5089
Jun C, Ban Y, Li S (2014) Open access to Earth land-cover map. Nature 514:434. https://doi.org/10.1038/514434c
Jupp DLB (1988) Background and extensions to depth of penetration (DOP) mapping in shallow coastal waters. In: Proceedings of Remote Sensing of the Coastal Zone International Symposium, Gold Coast, Australia. Gold Coast, Queensland, p IV.2.1–19
Kefelegn H (2019) Mathematical formulations for Three Components of Hydroperiod in Tidal wetlands. Wetlands 39:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-018-1113-7
Kelly JT, Gontz AM (2018) Using GPS-surveyed intertidal zones to determine the validity of shorelines automatically mapped by Landsat water indices. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 65:92–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.10.007
Kirwan ML, Megonigal JP (2013) Tidal wetland stability in the face of human impacts and sea-level rise. Nature 504:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12856
Kirwan ML, Walters DC, Reay WG, Carr JA (2016) Sea level driven marsh expansion in a coupled model of marsh erosion and migration. Geophys Res Lett 43:4366–4373. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL068507
Kumbier K, Hughes MG, Rogers K, Woodroffe CD (2021) Inundation characteristics of mangrove and saltmarsh in micro-tidal estuaries. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 261:107553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2021.107553
Kwak TJ, Zedler JB (1997) Food web analysis of southern California coastal wetlands using multiple stable isotopes. Oecologia 110:262–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050159
Laborde H, Douzal V, Ruiz Piña HA et al (2017) Landsat-8 cloud-free observations in wet tropical areas: a case study in South East Asia. Remote Sens Lett 8:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2017.1297543
Lamb BT, Tzortziou MA, McDonald KC (2019) Evaluation of approaches for mapping tidal wetlands of the Chesapeake and Delaware bays. Remote Sens 11:2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11202366
Lee J-S, Kim J-W, Lee SH et al (2016) Zonation and soil factors of salt marsh halophyte communities. J Ecol Environ 40:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41610-016-0010-3
Lewis DB, Jimenez KL, Abd-Elrahman A et al (2021) Carbon and nitrogen pools and mobile fractions in surface soils across a mangrove saltmarsh ecotone. Sci Total Environ 798:149328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149328
Li W, Du Z, Ling F et al (2013) A comparison of land surface water mapping using the normalized difference water index from TM, ETM plus and ALI. Remote Sens 5:5530–5549. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5115530
Liu Z, Huang F, Li L, Wan E (2002) Dynamic monitoring and damage evaluation of Flood in north-west Jilin with remote sensing. Int J Remote Sens 23:3669–3679. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160010006953
Liu Y, Hu C, Dong Y et al (2019) Geometric accuracy of remote sensing images over oceans: the use of global offshore platforms. Remote Sens Environ 222:244–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.01.002
Lopes CL, Mendes R, Caçador I, Dias JM (2020) Assessing salt marsh extent and condition changes with 35 years of Landsat imagery: Tagus Estuary case study. Remote Sens Environ 247:111939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111939
Mao D, Wang Z, Du B et al (2020) National Wetland mapping in China: a new product resulting from object-based and hierarchical classification of Landsat 8 OLI images. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 164:11–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.03.020
Marani M, Da Lio C, D’Alpaos A (2013) Vegetation engineers marsh morphology through multiple competing stable states. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:3259–3263. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1218327110
Mazumder D, Saintilan N, Williams RJ (2006) Trophic relationships between itinerant fish and crab larvae in a temperate Australian saltmarsh. Mar Freshw Res 57:193–199
McFeeters SK (1996) The use of the normalized difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int J Remote Sens 17:1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169608948714
McKinley E, Ballinger RC, Beaumont NJ (2018) Saltmarshes, ecosystem services, and an evolving policy landscape: a case study of Wales, UK. Mar Policy 91:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2018.01.021
Meng L, Huang Y, Zhu N et al (2021) Mapping properties of vegetation in a tidal salt marsh from multi-spectral satellite imagery using the SCOPE model. Int J Remote Sens 42:422. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2020.1809737
Miller CB, Rodriguez AB, Bost MC (2021) Sea-level rise, localized subsidence, and increased storminess promote saltmarsh transgression across low-gradient upland areas. Quat Sci Rev 265:107000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.107000
Minello TJ, Rozas LP, Baker R (2012) Geographic Variability in Salt Marsh flooding patterns may affect Nursery Value for Fishery species. Estuaries Coasts 35:501–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-011-9463-x
Mitsch WJ, Gosselink JG (2007) Wetlands, 4th edn. John Wiley and Sons Inc, Hoboken
Morris JT, Sundareshwar PV, Nietch CT et al (2002) Responses of coastal wetlands to rising sea level. Ecology 83:2869–2877. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[2869:ROCWTR]2.0.CO;2
Muala E, Mohamed YA, Duan Z, Van der Zaag P (2014) Estimation of Reservoir discharges from Lake Nasser and Roseires Reservoir in the Nile Basin using Satellite Altimetry and Imagery Data. Remote Sens 6:7522–7545
Murray NJ, Phinn SR, DeWitt M et al (2019) The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature 565:222–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0805-8
Murray NJ, Phinn SR, Clemens RS et al (2012) Continental Scale Mapping of Tidal Flats across East Asia using the Landsat Archive. Remote Sens 4:3417–3426
Muslim AMM, Hossain MS, Razman N et al (2019) Shoreline mapping: how do fuzzy sigmoidal, bayesian, and Demspter-Shafer classifications perform for different types of coasts? Remote Sens Lett 10:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2018.1523583
Nahrawi H, Leclerc MY, Pennings S et al (2020) Impact of tidal inundation on the net ecosystem exchange in daytime conditions in a salt marsh. Agric for Meteorol 294:108133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.108133
Nardin W, Locatelli S, Pasquarella V et al (2016) Dynamics of a fringe mangrove forest detected by landsat images in the Mekong River Delta, Vietnam. Earth Surf Process Landforms 41:2024–2037. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3968
Narron CR, O’Connell JL, Mishra DR et al (2022) Flooding in Landsat across tidal systems (FLATS): an index for intermittent tidal filtering and frequency detection in salt marsh environments. Ecol Indic 141:109045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109045
Nguyen H-H, McAlpine C, Pullar D et al (2013) The relationship of spatial–temporal changes in fringe mangrove extent and adjacent land-use: case study of Kien Giang coast, Vietnam. Ocean Coast Manag 76:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2013.01.003
Nuttle WK (1997) Measurement of wetland hydroperiod using harmonic analysis. Wetlands 17:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160720
O’Connell JL, Mishra DR, Cotten DL et al (2017) The tidal Marsh Inundation Index (TMII): an inundation filter to flag flooded pixels and improve MODIS tidal marsh vegetation time-series analysis. Remote Sens Environ 201:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.08.008
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076
Ouyang X, Lee SY (2014) Updated estimates of carbon accumulation rates in coastal marsh sediments. Biogeosciences 11:5057–5071. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-5057-2014
Pardo-Pascual JE, Sánchez-García E, Almonacid-Caballer J et al (2018) Assessing the accuracy of automatically extracted shorelines on microtidal beaches from Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens 10:326
Pearson ES, Hartley HO (1972) Biometrika tables for statisticians, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Pennings SC, Callaway RM (1992) Salt Marsh Plant Zonation: the relative importance of competition and physical factors. Ecology 73:681–690. https://doi.org/10.2307/1940774
Rinaldo A, Belluco E, D’Alpaos A et al (2004) Tidal Networks: form and Function. In: Fagherazzi S, Marani M, Blum LK (eds) The ecogeomorphology of tidal marshes. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp 75–91
Rodriguez AB, McKee BA (2021) Salt Marsh formation. In: FitzGerald DM, Hughes ZJ (eds) Salt marshes: function, Dynamics, and stresses. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 31–52
Rogers AS, Kearney MS (2004) Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh thematic mapper scenes using spectral indices. Int J Remote Sens 25:2317–2335. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160310001618103
Rogers K, Lymburner L, Salum R et al (2017) Mapping of mangrove extent and zonation using high and low tide composites of Landsat data. Hydrobiologia 803:49–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3257-5
Rokni K, Ahmad A, Selamat A, Hazini S (2014) Water feature extraction and change detection using Multitemporal Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens 6:4173–4189
Romano F, Manuel del J, Andrea R, Ignacio R-I (2012) Hydroperiod regime controls the organization of plant species in wetlands. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:19596–19600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1218056109
Rosbakh S, Phartyal SS, Poschlod P (2020) Seed germination traits shape community assembly along a hydroperiod gradient. Ann Bot 125:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcz139
Rowan GSL, Kalacska M (2021) A review of remote sensing of submerged aquatic vegetation for non-specialists. Remote Sens 13:623
Ryu JH, Won JS, Min KD (2002) Waterline extraction from landsat TM data in a tidal flat a case study in Gomso Bay, Korea. Remote Sens Environ 83:442–456
Sagar S, Roberts D, Bala B, Lymburner L (2017) Extracting the intertidal extent and topography of the Australian coastline from a 28 year time series of landsat observations. Remote Sens Environ 195:153–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.04.009
Saintilan N, Rogers K, Mazumder D, Woodroffe C (2013) Allochthonous and autochthonous contributions to carbon accumulation and carbon store in southeastern Australian coastal wetlands. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 128:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2013.05.010
Saintilan N, Rogers K, McKee KL (2019) The shifting saltmarsh-mangrove ecotone in Australasia and the Americas. In: Perillo GME, Wolanski E, Cahoon DR, Hopkinson CSBT-CW (eds) Coastal wetlands. Elsevier, 2nd edn, pp 915–945
Slagter B, Tsendbazar N-E, Vollrath A, Reiche J (2020) Mapping wetland characteristics using temporally dense Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data: A case study in the St. Lucia wetlands, South Africa. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 86:102009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2019.102009
Sani DA, Hashim M, Hossain MS (2019) Recent advancement on estimation of blue carbon biomass using satellite-based approach. Int J Remote Sens 40:7679–7715. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2019.1601289
Shafiqul Islam M, Pervez A, Aminur Rahman M, Habibur Rahman Molla M (2021) Eco-engineering of coastal environment through saltmarsh restoration towards climate change impact mitigation and community adaptation in Bangladesh. Reg Stud Mar Sci 46:101880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101880
Silva TSF, Costa MPF, Melack JM, Novo EMLM (2008) Remote sensing of aquatic vegetation: theory and applications. Environ Monit Assess 140:131–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9855-3
Silvestri S, Defina A, Marani M (2005) Tidal regime, salinity and salt marsh plant zonation. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 62:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2004.08.010
Souza Filho PWM, do Farias Martins ES, da Costa FR (2006) Using mangroves as a geological indicator of coastal changes in the Bragança macrotidal flat, Brazilian Amazon: A remote sensing data approach. Ocean Coast Manag 49:462–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2006.04.005
Stankovic M, Ambo-Rappe R, Carly F et al (2021) Quantification of blue carbon in seagrass ecosystems of Southeast Asia and their potential for climate change mitigation. Sci Total Environ 783:146858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146858
Sun C, Fagherazzi S, Liu Y (2018) Classification mapping of salt marsh vegetation by flexible monthly NDVI time-series using landsat imagery. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 213:61–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2018.08.007
Sun C, Li J, Liu Y et al (2021) Plant species classification in salt marshes using phenological parameters derived from Sentinel-2 pixel-differential time-series. Remote Sens Environ 256:112320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2021.112320
Thom RM, Diefenderfer HL, Adkins JE et al (2010) Guidelines, processes and tools for coastal ecosystem restoration, with examples from the United States. Plankt Benthos Res 5:185–201. https://doi.org/10.3800/pbr.5.185
Tian J, Wang L, Yin D et al (2020) Development of spectral-phenological features for deep learning to understand Spartina alterniflora invasion. Remote Sens Environ 242:111745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111745
Tiner RW, Milton GR (2016) Estuarine Marsh: an overview. In: Finlayson CM, Milton GR, Prentice RC, Davidson NC (eds) The Wetland Book. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 1–18
USGS (2019) Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook. https://d9-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/s3fs-public/atoms/files/LSDS-1574_L8_Data_Users_Handbook-v5.0.pdf. Accessed 6 Jul 2022
Valderrama-Landeros L, Flores-Verdugo F, Rodríguez-Sobreyra R et al (2021) Extrapolating canopy phenology information using Sentinel-2 data and the Google Earth Engine platform to identify the optimal dates for remotely sensed image acquisition of semiarid mangroves. J Environ Manage 279:111617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111617
van der Walt S, Schönberger JL, Nunez-Iglesias J et al (2014) scikit-image: image processing in Python. PeerJ 2:e453. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.453
Visser F, Buis K, Verschoren V, Meire P (2015) Depth estimation of submerged aquatic vegetation in Clear Water streams using low-Altitude Optical Remote sensing. Sensors 15:25287–25312
Wang SR, Di Iorio D, Cai W-J, Hopkinson CS (2018a) Inorganic carbon and oxygen dynamics in a marsh-dominated estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 63:47–71. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10614
Wang X, Liu Y, Ling F, Xu S (2018b) Fine spatial resolution coastline extraction from Landsat-8 OLI imagery by integrating downscaling and pansharpening approaches. Remote Sens Lett 9:314–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2017.1420928
Wang X, Gao X, Zhang Y, et al (2019) Land-cover classification of coastal wetlands using the RF algorithm for worldview-2 and landsat 8 images. Remote Sens 11:1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11161927
Wang X, Xiao X, Zou Z et al (2020) Mapping coastal wetlands of China using time series Landsat images in 2018 and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 163:312–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.03.014
White SM, Madsen EA (2016) Tracking tidal inundation in a coastal salt marsh with Helikite airphotos: influence of hydrology on ecological zonation at Crab Haul Creek, South Carolina. Remote Sens Environ 184:605–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.08.005
Williams WT (1961) Salt marshes and Salt deserts. Nature 192:833. https://doi.org/10.1038/192833a0
Wong JXW, Van Colen C, Airoldi L (2015) Nutrient levels modify saltmarsh responses to increased inundation in different soil types. Mar Environ Res 104:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.12.003
Wulder MA, Loveland TR, Roy DP et al (2019) Current status of Landsat program, science, and applications. Remote Sens Environ 225:127–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.02.015
Xie H, Luo X, Xu X et al (2016) Evaluation of Landsat 8 OLI imagery for unsupervised inland water extraction. Int J Remote Sens 37:1826–1844. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1168948
Xu H (2006) Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int J Remote Sens 27:3025–3033. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160600589179
Yan D, Li J, Yao X, Luan Z (2022) Integrating UAV data for assessing the ecological response of Spartina alterniflora towards inundation and salinity gradients in coastal wetland. Sci Total Environ 814:152631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152631
Yang X, Lu X (2014) Drastic change in China’s lakes and reservoirs over the past decades. Sci Rep 4:6041. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06041
Yousefi S, Moradi H, Telvari A, Vafakhah M (2015) Monitoring of fluvial systems by RS and GIS (case study: Talar River, Iran). J Selçuk Univ Nat Appl Sci 4:60–72
Yousefi S, Pourghasemi HR, Hooke J et al (2016) Changes in morphometric meander parameters identified on the Karoon River, Iran, using remote sensing data. Geomorphology 271:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.07.034
Zhang X, Treitz PM, Chen D et al (2017) Mapping mangrove forests using multi-tidal remotely-sensed data and a decision-tree-based procedure. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 62:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.06.010
Zhang X, Liu L, Chen X et al (2021) GLC\_FCS30: global land-cover product with fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst Sci Data 13:2753–2776. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-13-2753-2021
Zhang Z, Xu N, Li Y, Li Y (2022) Sub-continental-scale mapping of tidal wetland composition for East Asia: a novel algorithm integrating satellite tide-level and phenological features. Remote Sens Environ 269:112799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2021.112799
Zhao B, Guo H, Yan Y et al (2008) A simple waterline approach for tidelands using multi-temporal satellite images: a case study in the Yangtze Delta. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 77:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2007.09.022
Zhao J, Barnes B, Melo N et al (2013) Assessment of satellite-derived diffuse attenuation coefficients and euphotic depths in south Florida coastal waters. Remote Sens Environ 131:38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.12.009
Zhao C, Qin C-Z, Teng J (2020) Mapping large-area tidal flats without the dependence on tidal elevations: a case study of Southern China. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 159:256–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.022
Zheng Z, Zhou Y, Tian B, Ding X (2016) The spatial relationship between salt marsh vegetation patterns, soil elevation and tidal channels using remote sensing at Chongming Dongtan Nature Reserve, China. Acta Oceanol Sin 35:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-016-0831-z
Zhou Y, Dong J, Xiao X et al (2017) Open Surface Water Mapping algorithms: a comparison of Water-related spectral indices and sensors. Water 9:256
Zhu X, Hou Y, Weng Q, Chen L (2019) Integrating UAV optical imagery and LiDAR data for assessing the spatial relationship between mangrove and inundation across a subtropical estuarine wetland. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 149:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.01.021
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Postgraduate Research Grant (PGRG) scheme (Vot number: 55203) from the Centre for Research and Innovation Management (CRIM), Universiti Malaysia Terengganu (UMT), Malaysia. Landsat data were downloaded from USGS Earthexplorer portal (http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, S.R., Hossain, M.S. Using a water index approach to mapping periodically inundated saltmarsh land-cover vegetation and eco-zonation using multi-temporal Landsat 8 imagery. J Coast Conserv 28, 19 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-023-01019-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-023-01019-w