Abstract
Background
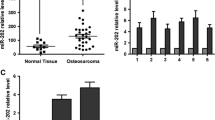
Recent studies have shown that microRNA-21 (miR-21) is overexpressed in solid tumors and implicated in the modulation of drug-induced resistance.
Methods
In this study, we investigated the anti-tumor effects of miR-21 on the sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells to CDDP.
Results
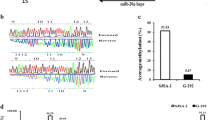
Changes in the sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells to CDDP were examined after transfection with miR-21 mimics or anti-miR-21 or bcl-2 siRNA in combination with CDDP. Osteosarcoma cells transfected with miR-21 mimics were significantly resistant to CDDP, while suppression of miR-21 in osteosarcoma cells led to enhanced CDDP cytotoxicity. Moreover, the miR-21-induced changes in chemoresponse were ameliorated by down-regulation of bcl-2 by its siRNA.
Conclusion
The miR-21 in osteosarcoma cells is a significant modulator of the anti-tumor effect of CDDP by regulating the expression of bcl-2, and the study reveals a novel mechanism of osteosarcoma drug resistance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pillai RS (2005) MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA 11:1753–1761
Zamore PD, Haley B (2005) Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science 309:1519–1524
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF et al (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303:83–86
Croce CM, Calin GA (2005) miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 122:6–7
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG et al (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:7065–7070
Diederichs S, Haber DA (2006) Sequence variations of microRNAs in human cancer: alterations in predicted secondary structure do not affect processing. Cancer Res 66:6097–6104
Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP et al (2006) MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol 24:4677–4684
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG et al (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2257–2261
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H et al (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133:647–658
Giovannetti E, Funel N, Peters GJ et al (2010) MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res 70:4528–4538
Bourguignon LY, Spevak CC, Wong G et al (2009) Hyaluronan–CD44 interaction with protein kinase C (epsilon) promotes oncogenic signaling by the stem cell marker Nanog and the production of microRNA-21, leading to down-regulation of the tumor suppressor protein PDCD4, anti-apoptosis, and chemotherapy resistance in breast tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284:26533–26546
Shi L, Chen J, Yang J et al (2010) MiR-21 protected human glioblastoma U87MG cells from chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide induced apoptosis by decreasing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. Brain Res 1352:255–264
Li Y, Li W, Yang Y et al (2009) MicroRNA-21 targets LRRFIP1 and contributes to VM-26 resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res 1286:13–18
Bacci G, Ruggieri P, Picci P et al (1996) Intra-arterial versus intravenous cisplatinum (in addition to systemic Adriamycin and high dose methotrexate) in the neoadjuvant treatment of osteosarcoma of the extremities. Results of a randomized study. J Chemother 8:70–81
Jaffe N, Knapp J, Chuang VP et al (1983) Osteosarcoma: intra-arterial treatment of the primary tumor with cis-diammine-dichloroplatinum II (CDP). Angiographic, pathologic, and pharmacologic studies. Cancer 51:402–407
Jaffe N (1993) Pediatric osteosarcoma: treatment of the primary tumor with intraarterial cis-diamminedichloroplatinum-II (CDP)—advantages, disadvantages, and controversial issues. Cancer Treat Res 62:75–84
Giaccone G (2000) Clinical perspectives on platinum resistance. Drugs 59:9–17
Huang Y, Anderle P, Bussey KJ et al (2004) Membrane transporters and channels: role of the transportome in cancer chemosensitivity and chemoresistance. Cancer Res 64:4294–4301
McLornan DP, McMullin MF, Johnston P et al (2007) Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in acute myeloid leukaemia. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 3:363–377
Bazarbashi S, Abdelsalam M, Amin T et al (2008) Phase II trial of neoadjuvant cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and interferon-alpha in operable squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Chemotherapy 54:315–322
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS et al (2008) MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1–9
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N et al (2008) Effects of miR-34a on cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377:114–119
Bai S, Nasser MW, Wang B et al (2009) MicroRNA-122 inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib. J Biol Chem 284:32015–32027
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Giovannini C et al (2009) MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 69:5761–5767
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H et al (2010) MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to the anti-tumour effect of interferon-a/5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 103:1617–1626
Bai H, Xu R, Cao Z et al (2011) Involvement of miR-21 in resistance to daunorubicin by regulating PTEN expression in the leukaemia K562 cell line. FEBS Lett 585:402–408
Yang J, Zhang W (2013) New molecular insights into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 25:398–406
Ji T, Lin C, Krill LS et al (2013) Flavokawain B, a kava chalcone, inhibits growth of human osteosarcoma cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Cancer 12:55
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H et al (2007) miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 26:2799–2803
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Wuhan City (Hubei, China) Health Bureau project (No: WX13C34).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziyan, W., Yang, L. MicroRNA-21 regulates the sensitivity to cisplatin in a human osteosarcoma cell line. Ir J Med Sci 185, 85–91 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-014-1225-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-014-1225-x