Abstract
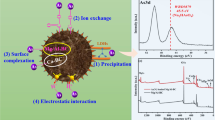
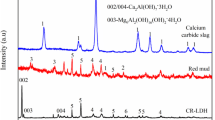
A novel Fe-Al double hydroxides adsorbent (DHs-FeAl) was synthesized utilizing red mud (RM), and then the arsenic(As)V adsorption characteristics of DHs-FeAl were evaluated. The iron-containing acid leaching residue (Fe = 63.55%) generated during the production of DHs-FeAl can be used directly as a raw material for iron metallurgy. Optimized conditions for As(V) adsorption were observed to be pH = 4.0–9.0, 1.0 g/L adsorbent dosage, 50 mg/L initial As(V) concentration, 720 min, and ambient temperature. The adsorption capacity of DH-FeAl for As(V) was up to 117.73 mg/g, as determined by fitting adsorption equilibrium data using the Langmuir–Freundlich isothermal model (R2 > 99%). According to the adsorption thermodynamic and kinetic results, the As(V) adsorption process, controlled by coupled external and internal diffusion, was dominated by physisorption and supplemented by inner-sphere complexation and hydroxide ion exchange. When the DHs-FeAl was regenerated with an NaOH-NaCl binary solution after adsorbing As(V), the adsorbent still had a good adsorption capacity for the first three cycles. Based on the results, it was possible and efficient to adsorb As(V) using DHs-FeAl. The research complied with the notions of reusing resources and treating waste with waste.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Q e :
-
Apparent adsorbed amount of As(V) (mg/g)
- C 0 :
-
Initial concentration of As(V) (mg/L)
- C e :
-
Equilibrium concentration of As(V) (mg/L)
- V :
-
The volume of the solution (L)
- m :
-
Dosage of the adsorbent (g)
- %R e :
-
The percentage removal of As (V)
- Q max :
-
The capacity of saturated adsorption (mg/g)
- K L :
-
Langmuir constant (L/mg)
- K F :
-
Freundlich affinity coefficient ((mg/g)/(mg/L)1/n)
- n :
-
Freundlich constants
- K d :
-
Thermodynamic equilibrium constant
- ΔG θ :
-
Standard Gibbs free energy (kJ mol−1)
- ΔH θ :
-
Standard enthalpy (kJ mol−1)
- ΔS θ :
-
Standard entropy (J mol−1 K−1)
- R :
-
Gas constant (8.314 J mol−1 K−1)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- Q t :
-
Adsorption capacity at a certain time (mg/g)
- k 1 :
-
The rate constant of the PFO (min−1)
- k 2 :
-
The rate constant of the PSO (g/mg min)
- Q fast :
-
Adsorption capacity during fast phase (mg/g)
- k fast :
-
Fast phase constant (min−1)
- k slow :
-
Slow phase constant (min−1)
- C :
-
Webber–Morris constant
- k p :
-
Webber–Morris rate constant (mg g−1 min−1/2)
- %R d :
-
Desorption percentage
- C d :
-
As(V) concentration in regeneration eluent (mg/g)
- C w :
-
As(V) concentration in wash water (mg/g)
References
A. Deditius, Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 79, 1–16 https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.110.7.1905 (2015).
P. Drahota and M. Filippi, Environ. Int. 35, 1243–1255 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.07.004 (2009).
R.D. Koons and C.A. Peters, J. Anal. Toxicol. 18, 36–40 https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/18.1.36 (1994).
B.S. Rathi and P.S. Kumar, J. Hazard. Mater. 418, 126299 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126299 (2021).
M. Argos, T. Kalra, and P.J. Rathouz, Lancet 376, 252–258 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60481-3 (2010).
K. Hayat, S. Menhas, J. Bundschuh, and H.J. Chaudhary, J. Clean. Prod. 151, 427–438 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.084 (2017).
J.V. Bothe and P.W. Brown, Environ. Sci. Technol. 33, 3806–3811 https://doi.org/10.1021/es980998m (1999).
C.B. Tabelin, R.D. Corpuz, T. Iarashi, M. Ito, N. Hiroyoshi, and M. Villacorte-Tabelin, Chemosphere 233, 946–953 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.020 (2019).
Z.L. Tang, X.C. Tang, H.N. Liu, and Z.Y. Xiao, Sep. Purif. Technol. 295, 121276 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121276 (2022).
J.M. Byrne and A. Kappler, Microb. Biotechnol. 10, 1098–1101 https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12742 (2017).
D.E. Giles, M. Mohapatra, and T.B. Issa, J. Environ. Manage. 92, 3011–3022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.07.018 (2011).
Y. Mamindy-Pajany, C. Hurel, N. Marmier, and M. Roméoet, Desalination 281, 93–99 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.07.046 (2011).
M.C.S. Faria, R.S. Rosemberg, C.A. Bomfeti, D.S. Monteiro, F. Barbosa, L.C.A. Oliveira, M. Rodriguez, M.C. Pereira, and J.L. Rodrigues, Chem. Eng. J. 237, 47–54 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.006 (2014).
T.K. Das and A.N. Bezbaruah, Sci. Total. Environ. 764, 142914 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142914 (2020).
M. Pigna, G.S.R. Krishnamurti, and A. Violante, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 70, 2017–2027 https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0373 (2006).
N. Inchaurrondo, C. di Luca, F. Mori, A. Pintar, G. Žerjav, M. Valiente, and C. Palet, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7, 102901 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102901 (2019).
S.H. Wang, H.X. Jin, Y. Deng, and Y.D. Xiao, J. Clean. Prod. 289, 125136 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125136 (2021).
Z.B. Liu and H.X. Li, Hydrometallurgy 155, 29–43 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.03.018 (2015).
Y. Liu, C. Lin, and Y. Wu, J. Hazard. Mater. 146, 255–261 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.015 (2007).
D.D. Frey, F. Engelhardt, and E.M. Greitzer, Res. Eng. Des. 14, 65–74 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00163-002-0026-9 (2003).
A.A. Khan and R.P. Singh, Colloids Surf. 24, 33–42 https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6622(87)80259-7 (1987).
B. Liu, Z. Liu, H. Wu, S. Pan, X. Cheng, Y. Sun, and Y. Xu, Sci. Total. Environ. 742, 141508 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140508 (2020).
Y. Yu, L. Yu, K. Shih, and J.P. Chen, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 521, 252–260 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.02.046 (2018).
K. Kitahama, R. Kiriyama, and Y. Baba, B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 31, 322–324 https://doi.org/10.1107/S056774087500266X (1975).
K.L. Muedi, H.G. Brink, V. Masindi, and J.P. Maree, J. Hazard. Mater. 414, 125491 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125491 (2021).
S. Ghosh, R. Prabhakar, and S. Samadder, Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 21, 121–138 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1622-3 (2019).
Y.K. Penke, G. Anantharaman, J. Ramkumar, and K.K. Kar, J. Hazard. Mater. 364, 519–530 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.069 (2019).
B.N. Mahato and T. Krithiga, Mater. Today: Proc. 17, 303–312 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.434 (2019).
F. Wu, C. Zhao, G. Qu, Z. Yan, Y. Zeng, B. Chen, Y. Hu, W. Ji, Y. Li, and H. Tang, RSC Adv. 11, 6577–6585 https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra09339d (2021).
J. Ju, Z. He, R. Liu, H. Liu, X. Zhang, and J. Qu, Environ. Eng. Sci. 32(7), 613–621 https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2014.0245 (2014).
X. Yu, Y. Wei, C. Liu, J. Ma, H. Liu, S. Wei, W. Deng, J. Xiang, and S. Luo, Chemosphere 222, 258–266 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.130 (2019).
X. Ge, Y. Ma, X. Song, G. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and H. Zhao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 13480–13490 https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01275 (2017).
N. Jain and A. Maiti, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 3230–3242 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10745-9 (2021).
V.K. Tchieda, E. D’Amato, A. Chiavola, M. Parisi, A. Chianese, M. Amamra, and A. Kanaev, Clean 44, 496–505 https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201400599 (2016).
A. Maiti, J.K. Basu, and S. De, Chem. Eng. J. 191, 1–12 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.01.031 (2012).
S.I. Lyubchik, A.I. Lyubchik, O.L. Galushko, L.P. Tikhonova, J. Vital, I.M. Fonseca, and S.B. Lyubchik, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 242, 151–158 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2004.04.066 (2004).
C.K. Jain, D.C. Singhal, and M.K. Sharma, J. Hazard. Mater. 114, 231–239 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.09.001 (2004).
H.N. Tran, S.J. You, A. Hosseini-Bandegharaei, and H.P. Chao, Water Res. 120, 88–116 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014 (2017).
T. Mahlangu, R. Das, L.K. Abi, M. Onyango, S.S. Ray, and A. Maity, Chem. Eng. J. 360, 423–434 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.231 (2019).
Y. Zhang, X. She, X. Gao, C. Shan, C. Shan, and B. Pan, Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 365–372 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05177 (2019).
G. Nie, B. Pan, S. Zhang, and B. Pan, J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 6201–6209 https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3119154 (2013).
Q. Hu, Y. Liu, X. Gu, and Y. Zhao, Chemosphere 181, 328–336 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.049 (2017).
J.R.T. Johnson and I. Panas, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. Chem Chem Phys 3(24), 5482–5488 https://doi.org/10.1039/B106318A (2001).
M. Karanac, M. Đolić, Z. Veličković, A. Kapidžić, V. Ivanovski, M. Mitrić, and A. Marinković, J. Environ. Manage. 224, 263–276 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.051 (2018).
Y. Babaee, C.N. Mulligan, and M.S. Rahaman, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 93, 63–71 https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5320 (2018).
P. Singh, P. Pal, P. Mondal, G. Saravanan, P. Nagababu, S. Majumdar, N. Labhsetwar, and S. Bhowmick, Chem. Eng. J. 412, 128667 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128667 (2021).
G.S. Murugesan, M. Sathishkumar, and K. Swaminathan, Bioresour. Technol. 97, 483–487 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.03.008 (2006).
S.J. Mills, A.G. Christy, J.M.R. Génin, T. Kameda, and F. Colombo, Mineral. Mag. 76, 1289–1336 https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.2012.076.5.10 (2012).
T. Türk, T. Boyraz, and İ Alp, Environ. Geochem. Health 42, 1335–1345 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00420-5 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21276286 and No. 21476268) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central South University (No.2023ZZTS0456).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Tang, X., Tang, Z. et al. High-Performance Fe-Al Double Hydroxide Prepared by Red Mud for Arsenic Removal. JOM (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06301-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-06301-8