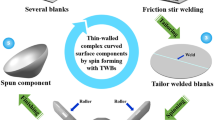
Abstract
A novel hybrid manufacturing technique combining friction stir welding and spinning provides a promising approach to forming large-diameter thin-walled axisymmetric components while minimizing process scrap. By integrating experimental and numerical methods, the feasibility of the hybrid manufacturing technique for producing thin-walled axisymmetric components with the 2195 Al-Li alloy was explored. The results indicate that the welding seam of the spun components restricts plastic deformation, which leads to flange swing. The movement of the welding seam occurs during spinning, and the movement direction is consistent with the rotation direction of the spun components. The microhardness of the components in the welding zone was found to increase by 21% on average after spinning. Moreover, the yield strength in the welding zone increased by over 60% and the tensile strength by over 12%. These results suggest that the hybrid manufacturing technique is a feasible way to produce large-diameter thin-walled axisymmetric components. Since the process scraps can be re-utilized using this method, it thus provides a potential route for sustainability in the recycling and remanufacturing of aluminum alloys.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Medjahed, B.C. Li, L.G. Hou, R.Z. Wu, A. Zegaoui, M. Derradji, and H. Benyamina, JOM 71, 4. (2019).
M. Zhan, J. Guo, M.W. Fu, P.F. Gao, H. Long, and F. Ma, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 257, 15. (2018).
E. Balducci, L. Ceschini, and S. Messieri, JOM 70, 11. (2018).
X.C. Meng, Y.X. Huang, J. Cao, J.J. Shen, and J.F. dos Santos, Prog. Mater. Sci. 115, 20. (2020).
Q.X. Xia, G.F. Xiao, H. Long, X.Q. Cheng, and X.F. Sheng, Int. J. Mach. Tools. Manuf. 85, 100. (2014).
X.S. Yang, W.J. Huang, X.H. Zhu, R. Zhang, F. Guo, and L. Hu, Met. Mater. Int. 27, 4793. (2021).
S. Chen, X.H. Zhan, Y.Q. Zhao, Y.F. Wu, and D.T. Liu, Met. Mater. Int. 27, 1671. (2021).
C.C. Wong, T.A. Dean, and J. Lin, Int. J. Mach. Tools. Manuf. 43, 1419. (2003).
D.Y. Yang, M. Bambach, J. Cao, J.R. Duflou, P. Groche, T. Kuboki, A. Sterzing, A.E. Tekkaya, C.W. Lee, and C.I.R.P. Ann-Manuf, Techn. 67, 743. (2018).
P.F. Gao, C. Yu, M.W. Fu, L. Xing, and J. Guo, Chinese. J. Aeronaut. 35, 320. (2022).
B. Kinsey, Z.H. Liu, and J. Cao, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 99, 145. (2000).
M. Merklein, M. Johannes, M. Lechner, and A. Kuppert, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 214, 151. (2014).
J. Liu, A.L. Wang, H.X. Gao, J. Gandra, K. Beamish, L.H. Zhan, and L.L. Wang, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 257, 33. (2018).
M. Abbasi, S.R. Hamzeloo, M. Ketabchi, M.A. Shafaat, and B. Bagheri, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 73, 999. (2014).
X.D. Ma, and Y.P. Guan, Met. Soc. China 26, 228. (2016).
M. Parente, R. Safdarian, A.D. Santos, A. Loureiro, P. Vilaca, and R.M.N. Jorge, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 83, 2129. (2015).
M.H. Wang, J. Zhou, C.F. He, M. Yang, and F. Xiang, J. Mech. Eng. 45(245), 234. ((in Chinese)) (2009).
J.H. Zhang, Z.X. Chen, L.Q. Xu, and J.H. Yu, Technology 38, 156. ((in Chinese)) (2013).
Z.H. Yin, K. Liu, J.X. Yu, Y. Tian, and M.Z. Hu, Technology 41, 39. ((in Chinese)) (2016).
S.L. Ma, M.Z. Li, G. Sun, X.J. Li, and Z.R. Qian, J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Technol. Edition). 38, 334. ((in Chinese)) (2008).
Z. Zimniak, and A. Piela, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 106, 254. (2000).
X.G. Qiu and W.L. Chen, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 187, 128. (2007).
Y.P. Guan, L.J. Wang, A.S. Lv, J. Zhao, and L.X. Ma, J. Plast. Eng. 17, 28. ((in Chinese)) (2010).
X.J. Liu, W.H. Zhou, B. Liu, Z. Wang, and C. Wang, Mater. Sci. Technol. 23, 114. ((in Chinese)) (2015).
J.M. Wang, Y. Zhao, and Y.F. Jiang, Forg. Stamp. Technol. 32, 28. ((in Chinese)) (2007).
H.R. Zhang, M. Zhan, Z.B. Zheng, R. Li, W. Lyu, and Y.D. Lei, Front. Mater. 8, 1. (2021).
H.R. Zhang, M. Zhan, Z.B. Zheng, R. Li, F. Ma, X.L. Cui, S.W. Chen, and Y.D. Lei, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 120, 3113. (2022).
G.F. Xiao, Q.X. Xia, and J.C. Long, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 97, 2979. (2018).
T. Sakthivel, G.S. Sengar, and J. Mukhopadhyay, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 43, 468. (2009).
Z. Yan, X. Liu, and H. Fang, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 91, 3025. (2017).
J. Zhang, M. Zhan, H. Yang, Z.Q. Jiang, and D. Han, Comp. Mater. Sci. 53, 303. (2012).
K. Essa and P. Hartley, Int. J. Mater. Form. 2, 271. (2009).
M. Zhan, X.X. Wang, and H. Long, Mater. Des. 108, 207. (2016).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the funding support from the National Key R&D Program of China (Project 2020YFA0711100), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Project 51625505), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 52105399, Project U1937203 and Project U1910213) and the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Project 2020JQ-166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhan, M., Zheng, Z. et al. Manufacture of Thin-Walled Axisymmetric Components by Friction Stir Welding and Spinning of Al-Li Alloy. JOM 74, 3248–3260 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05394-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05394-x