Abstract
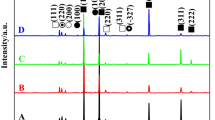
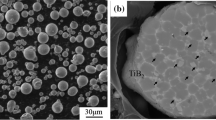
In this study, an in-situ 3 wt.% TiB2/Al-Cu-Mg-Ag composite was successfully fabricated by the salt-reaction method. The elevated temperature creep behaviour of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag matrix alloy and composite at 180–220°C under applied stresses of 150–275 MPa was investigated. The results showed that in-situ TiB2 particles greatly refined the grain size and improved the elevated temperature creep properties of composite. Compared with the matrix alloy, the steady creep rates of the composite were 45–320% lower than those of the matrix alloy, and the composite exhibited lower creep strain and longer creep life under the same creep conditions. The better creep behaviour of composite was attributed to the reinforcing effect of TiB2 particles and plenty of θ′ precipitates with small diameters in the composite. The true stress exponent of both the matrix alloy and composite is 5, indicating that their creep mechanism can be attributed to the dislocation climb mechanism.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this study are available from the authors on request.
References
Z. Ahmad, JOM-J. Minerals Metals & Mater. Soc. 55, 35–39 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-003-0224-6 (2003).
C. Yang, P. Zhang, D. Shao, R.H. Wang, L.F. Cao, J.Y. Zhang, G. Liu, B.A. Chen, and J. Sun, Acta Mater. 119, 68 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.013 (2016).
C. Wu, K. Ma, J. Wu, P. Fang, G. Luo, F. Chen, Q. Shen, L. Zhang, J.M. Schoenung, and E.J. Lavernia, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 675, 421 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.062 (2016).
I.J. Polmear, G. Pons, Y. Barbaux, H. Octor, C. Sanchez, A.J. Morton, W.E. Borbidge, and S. Rogers, Mater. Sci. Technol. 15, 861 https://doi.org/10.1179/026708399101506599 (1999).
M. Gazizov, and R. Kaibyshev, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 702, 29 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.06.110 (2017).
S.P. Ringer, T. Sakurai, and I.J. Polmear, Acta Mater. 45, 3731 https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6454(97)00039-6 (1997).
J.S. Robinson, R.L. Cudd, and J.T. Evans, Mater. Sci. Technol. 19, 143 https://doi.org/10.1179/026708303225009373 (2003).
Z. Huda, T. Zaharinie, J. Min Goh (2010) J. Aerospace Eng. 23: 124
F.M. Xu, L.C.M. Wu, G.W. Han, and Y. Tan, Chin. J. Aeronaut. 20, 115–119 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1000-9361(07)60016-8 (2007).
X.D. Hui, Y.S. Yang, Z.F. Wang, G.Q. Yuan, and X.C. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 282, 187–192 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00751-0 (2000).
D. Chen, M.L. Wang, Y.J. Zhang, X.F. Li, Z. Chen, N.H. Ma, and H.W. Wang, Mater. Res. Innovations 18, 514–518 https://doi.org/10.1179/1432891714Z.000000000731 (2014).
M. Emamy, M. Mahta, and J. Rasizadeh, Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 1063 (2006).
Y.W. Shen, X.F. Li, T.R. Hong, J.W. Geng, and H.W. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 655, 26. (2016)
B.W. Zhao, Q. Yang, L. Wu, X.F. Li, M.L. Wang, and H.W. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 742, 573–583 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.032 (2019).
A. Saxena, M. Indriyati, P. Rajveer, H.R.K. Biswas, and S. Das, Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 953–961 (2019).
S.L. Pramod, S.R. Bakshi, and B.S. Murty, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24, 2185–2207 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1424-2 (2015).
M. Mandal, and R. Mitra, JOM 68, 1902–1908 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1911-4 (2016).
X.Y. Liu, Q.L. Pan, X.L. Zhang, S.X. Liang, F. Gao, L.Y. Zheng, and M.X. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 599, 160. (2014)
M.H. Huang, H.W. Wang, X.F. Li, and H.Z. Yi, Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 34, 1394. (2005)
M.E. Van Dalen, D.C. Dunand, and D.N. Seidman, Acta Mater. 59, 5224. (2005)
W.J. Li, B. Cai, Y.C. Wang, Z.X. Liu, and S. Yang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 615, 148–152 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.07.071 (2014).
W.G. Zhao, J.G. Wang, H.L. Zhao, D.M. Yao, and Q.C. Jiang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 515, 10–13 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.03.080 (2009).
W.-S. Tian, Q.-L. Zhao, Q.-Q. Zhang, F. Qiu, and Q.-C. Jiang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 700, 42–48 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.05.101 (2017).
P. Zhang, Scripta Mater. 52, 277–282 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.10.017 (2005).
S. Latha, M.D. Mathew, P. Parameswaran, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, S.L. Mannan (2008) Int. J. Pressure Vessels and Piping, 85: 866
M. Vogelsang, R.J. Arsenault, R.M. Fisher, (1986) Metall. Trans. A, Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. (USA), 17A, 379
R.J. Arsenault, and N. Shi, Mater. Sci. Eng. (Switzerland) 81, 175. (1986)
S.P. Ringer, B.C. Muddle, and I.J. Polmear, MMTA 26, 1659. (1995)
M. Gazizov, and R. Kaibyshev, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 625, 119–130 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.11.094 (2015).
L. Jiang, J.K. Li, G. Liu, R.H. Wang, B.A. Chen, J.Y. Zhang, J. Sun, M.X. Yang, G. Yang, J. Yang, and X.Z. Cao, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 637, 139 (1986).
L. Fan, Q.T. Hao, and W.K. Han, Rare Met. 34, 308. (2015)
X.F. Xu, Y.G. Zhao, M. Zhang, Y.H. Ning, X.D. Wang (2018) J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit., 33: 710
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no.11974316).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, H., Li, M., Zhang, G. et al. Effect of In-Situ TiB2 Particles on the Creep Properties of 3 Wt.% TiB2/Al-Cu-Mg-Ag Composite. JOM 74, 4121–4128 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05251-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05251-x