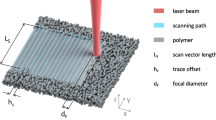
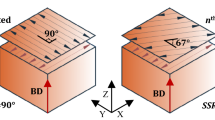
Abstract
One of the challenges regarding widespread use of parts created by the powder-bed fusion process is their high surface roughness, which necessitates some type of postbuild finishing process. Laser polishing (i.e., remelting), which uses surface-tension-driven flow to reduce the roughness of irradiated metallic surfaces, is one such potential finishing process. This work examines the effect that surface features on the as-built part have on the performance of continuous-wave laser remelting of Co-Cr-Mo alloy (Celsit 21-P, Stellite 21 equivalent) samples produced by powder-bed fusion manufacturing. This is accomplished by comparison of three-dimensional surface measurements before and after laser remelting using focus-variation microscopy. Engineering models used to simulate the surface profile as a result of laser remelting are also presented. The results from this work provide insight into the fundamental physics occurring during laser remelting on parts made by powder-bed fusion and will aid parameter selection for surface consolidation and smoothing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A.M. Tofail, E.P. Koumoulos, A. Bandyopadhyay, S. Bose, L. O’Donoghue, and C. Charitidis, Mater. Today 21, 22 (2018).
K.S. Chan, M. Koike, R.L. Mason, and T. Okabe, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 1010 (2013).
G. Strano, L. Hao, R.M. Everson, and K.E. Evans, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 213, 589 (2013).
A. Townsend, N. Senin, L. Blunt, R.K. Leach, and J.S. Taylor, Precis. Eng. 46, 34 (2016).
A. Thompson, N. Senin, C. Giusca, and R. Leach, CIRP Ann. 66, 543 (2017).
D.A. Hollander et al., Biomaterials 27, 955 (2006).
G. Pyka et al., Adv. Eng. Mater. 14, 363 (2017).
E. Łyczkowska, P. Szymczyk, B. Dybała, and E. Chlebus, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 14, 586 (2014).
A. Lamikiz, J.A. Sánchez, L. de Lacalle, L. Norberto, D. del Pozo, and J.M. Etayo, Mater. Sci. Forum 526, 217 (2006).
J.A. Ramos-Grez and D.L. Bourell, Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 21, 297 (2004).
A. Lamikiz, J.A. Sánchez, L.N. López de Lacalle, and J.L. Arana, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 47, 2040 (2007).
J.-P. Kruth, M. Badrossamay, E. Yasa, J. Deckers, L. Thijs, and J. Van Humbeeck, Part and material properties in selective laser melting of metals, in Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Electromachining, pp. 1–12 (2010).
B. Rosa, P. Mognol, and J. Hascoët, J. Laser Appl. 27, S29102 (2015).
B. Rosa, P. Mognol, and J.-Y. Hascoët, Rapid Prototyp. J. 22, 956 (2016).
J. Schanz, M. Hofele, L. Hitzler, M. Merkel, and H. Riegel, Mach. Join Modif. Adv. Mater. 34, 159 (2016).
W.S. Gora et al., Phys. Procedia 83, 258 (2016).
V. Alfieri, P. Argenio, F. Caiazzo, and V. Sergi, Materials 10, 30 (2016).
D. Bhaduri et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 405, 29 (2017).
J.A. Ramos, J. Murphy, K. Wood, D.L. Bourell, and J.J. Beaman, Surface roughness enhancement of indirect-SLS metal parts by laser surface polishing, in Solid Freeform Fabrication Proceedings, pp. 28–38 (2001).
J.A. Ramos, D.L. Bourell, and J.J. Beaman, Surface over-melt during laser polishing of indirect-SLS metal parts, in MRS Proceedings, vol. 758 (2002).
T.M. Shao, M. Hua, H.Y. Tam, and E.H.M. Cheung, Surf. Coat. Technol. 197, 77 (2005).
T.L. Perry, D. Werschmoeller, N.A. Duffie, X. Li, and F.E. Pfefferkorn, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 131, 0210021 (2009).
M. Vadali, C. Ma, N.A. Duffie, X. Li, and F.E. Pfefferkorn, J. Manuf. Process. 14, 307 (2012).
C. Ma, M. Vadali, N.A. Duffie, F.E. Pfefferkorn, and X. Li, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 135, 061023 (2013).
C. Ma, M. Vadali, X. Li, N.A. Duffie, and F.E. Pfefferkorn, J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 2, 021010 (2014).
Q. Wang, J.D. Morrow, C. Ma, N.A. Duffie, and F.E. Pfefferkorn, J. Manuf. Process. 20, 340 (2015).
P. Johnson and R. Christy, Phys. Rev. B 9, 5056 (1974).
Stellite 21 Alloy Technical Data, Deloro Stellite, http://exocor.com/downloads/product-datasheets/Stellite-21-Datasheet.pdf.
D.G. Farwick and R.N. Johnson, Thermophysical Properties of Selected Wear-Resistant Alloys (Richland: Hanford Engineering Development Lab, 1980).
Metal Powder and Continuous Casting Rods, Böhler Welding. http://www.bohlerwelding.ru/files/cat/metallpulver.pdf.
M.J. Assael, I.J. Armyra, J. Brillo, S.V. Stankus, J. Wu, and W.A. Wakeham, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 41, 033101 (2012).
E. Ukar, A. Lamikiz, L.N. López de Lacalle, D. del Pozo, and J.L. Arana, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 50, 115 (2010).
ISO 25178-1:2016(en), Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) Surface Texture: Areal: Part 1: Indication of Surface Texture.
J.M. Dowden, The Mathematics of Thermal Modeling: An Introduction to the Theory of Laser Material Processing (Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2001).
G.R.B.E. Römer and A.J. Huisint Veld, Phys. Procedia 5, 413 (2010).
T.L. Perry, D. Werschmoeller, X. Li, F.E. Pfefferkorn, and N.A. Duffie, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 131, 031002 (2009).
T.L. Perry, D. Werschmoeller, X. Li, F.E. Pfefferkorn, and N.A. Duffie, J. Manuf. Process. 11, 74 (2009).
F.E. Pfefferkorn, N.A. Duffie, X. Li, M. Vadali, and C. Ma, CIRP Ann. 62, 203 (2013).
M. Vadali, C. Ma, N.A. Duffie, X. Li, and F.E. Pfefferkorn, J. Micro Nano Manuf. 1, 011006 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) grant CMMI-1727366 and NSF-supported shared facilities at the University of Wisconsin, as well as by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation, 386371584).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, B., Blanke, N., Werner, C. et al. Effect of Initial Surface Features on Laser Polishing of Co-Cr-Mo Alloy Made by Powder-Bed Fusion. JOM 71, 912–919 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3216-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3216-2