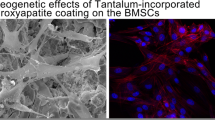
Abstract
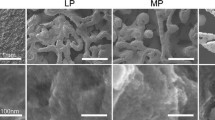
Tantalum is a promising orthopaedic implant coating material due to its robust mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and excellent biocompatibility. Previous studies have demonstrated improved biocompatibility and tissue integration of surface-treated tantalum coatings compared to untreated tantalum. Surface modification of tantalum coatings with biologically inspired microscale and nanoscale features may be used to evoke optimal tissue responses. The goal of this study was to evaluate commercial tantalum coatings with nanoscale, sub-microscale, and microscale surface topographies for orthopaedic and dental applications using human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs). Tantalum coatings with different microscale and nanoscale surface topographies were fabricated using a diffusion process or chemical vapor deposition. Biological evaluation of the tantalum coatings using hBMSCs showed that tantalum coatings promote cellular adhesion and growth. Furthermore, hBMSC adhesion to the tantalum coatings was dependent on surface feature characteristics, with enhanced cell adhesion on sub-micrometer- and micrometer-sized surface topographies compared to hybrid nano-/microstructures. Nanostructured and microstructured tantalum coatings should be further evaluated to optimize the surface coating features to promote osteogenesis and enhance osseointegration of tantalum-based orthopaedic implants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.D. Bermúdez, F.J. Carrión, G. Martínez-Nicolás, and R. López, Wear 258, 693 (2005).
M. Roy, V.K. Balla, S. Bose, and A. Bandyopadhyay, Adv. Eng. Mater. 12, B637 (2010).
K.J. Welldon, G.J. Atkins, D.W. Howie, and D.M. Findlay, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 84, 691 (2008).
D.M. Findlay, K. Welldon, G.J. Atkins, D.W. Howie, A.C. Zannettino, and D. Bobyn, Biomaterials 25, 2215 (2004).
B.R. Levine, S. Sporer, R.A. Poggie, C.J. Della, J. Valle, and J. Jacobs, Biomaterials 27, 4671 (2006).
H. Kato, T. Nakamura, S. Nishiguchi, Y. Matsusue, M. Kobayashi, T. Miyazaki, H.M. Kim, and T. Kokubo, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 53, 28 (2000).
V.K. Balla, S. Bodhak, S. Bose, and A. Bandyopadhyay, Acta Biomater. 6, 3349 (2010).
T. Sjöström, A.S. Brydone, R.D. Meek, M.J. Dalby, B. Su, and L.E. McNamara, Nanomedicine (Lond) 8, 89 (2013).
M. Ramazanoglu and Y. Oshida, in Implant Dentistry—A Rapidly Evolving Practice, ed. by I. Turkyilmaz (InTech, 2011). doi:10.5772/16936
M.J. Dalby, D. McCloy, M. Robertson, H. Agheli, and D. Sutherland, Biomaterials 27, 2980 (2006).
M.J. Dalby, D. McCloy, M. Robertson, C.D. Wilkinson, and R.O. Oreffo, Biomaterials 27, 1306 (2006).
S. Oh, K.S. Brammer, Y.J. Li, D. Teng, A.J. Engler, S. Chien, and S. Jin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 2130 (2009).
Y. Song, Y. Ju, G. Song, and Y. Morita, Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 2745 (2013).
G. Mendonça, D.B.S. Mendonça, L.G.P. Simões, A.L. Araújo, E.R. Leite, A.L. Golin, F.J. Aragão, and L.F. Cooper, Mater. Sci. Eng., C 31, 1809 (2011).
J. Park, S. Bauer, K. Von der Mark, and P. Schmuki, Nano Lett. 7, 1686 (2007).
J. Park, S. Bauer, K.A. Schlegel, F.W. Neukam, K. von der Mark, and P. Schmuki, Small 5, 666 (2009).
A.G. Hemmersam, M. Foss, J. Chevallier, and F. Besenbacher, Colloids Surf. B 43, 208 (2005).
C.P. Sharma and W. Paul, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 26, 1179–1184 (2004).
P. Zhang, S. Wang, S. Wang, and L. Jiang, Small 11, 1939–1946 (2015).
G.F. Muschler, C. Nakamoto, and L.G. Griffith, J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 86A, 1541 (2004).
M.J. Biggs, R.G. Richards, N. Gadegaard, R.J. McMurray, S. Affrossman, C.D. Wilkinson, R.O. Oreffo, and M.J. Dalby, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 91, 195 (2009).
M.J. Dalby, N. Gadegaard, R. Tare, A. Andar, M.O. Riehle, P. Herzyk, C.D. Wilkinson, and R.O. Oreffo, Nat. Mater. 6, 997 (2007).
D. Khang, J. Choi, Y.M. Im, Y.J. Kim, J.H. Jang, S.S. Kang, T.H. Nam, J. Song, and J.W. Park, Biomaterials 33, 5997 (2012).
K.K. Divine and P.L. Goering, Elements and their Compounds in the Environment, ed. E. Merian, M. Anke, M. Ihnat, and M. Stoeppler (Weinheim: Wiley, 2004), pp. 1087–1097.
J. Black, Clin. Mater. 16, 167 (1994).
A.C. Miller, A.F. Fuciarelli, W.E. Jackson, E.J. Ejnik, C. Emond, S. Strocko, J. Hogan, N. Page, and T. Pellmar, Mutagenesis 13, 643 (1998).
U. Dorn, D. Neumann, and M. Frank, J. Arthroplasty 29, 831 (2014).
H.A. Ching, D. Choudhury, M.J. Nine, and N.A. Abu Osman, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 15, 014402 (2014).
C. Balagna, M.G. Faga, and S. Spriano, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 8994 (2011).
Acknowledgements
Shelby Skoog was supported in part by NSF Award #1136330. The authors acknowledge the use of the Analytical Instrumentation Facility (AIF) at North Carolina State University, which is supported by the State of North Carolina and the National Science Foundation. The authors would like to acknowledge Chuck Mooney for assistance with SEM and EDS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The mention of commercial products, their sources, or their use in connection with material reported herein is not to be construed as either an actual or implied endorsement of such products by the Department of Health and Human Services. The statements in this article should not be construed as representing official agency policies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skoog, S.A., Kumar, G., Goering, P.L. et al. Biological Response of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Commercial Tantalum Coatings with Microscale and Nanoscale Surface Topographies. JOM 68, 1672–1678 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1934-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1934-x