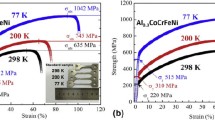
Abstract
Two definitions of high-entropy alloys (HEAs), based on composition and entropy, are reviewed. Four core effects, i.e., high entropy, sluggish diffusion, severe lattice distortion, and cocktail effects, are mentioned to show the uniqueness of HEAs. The current state of physical metallurgy is discussed. As the compositions of HEAs are entirely different from that of conventional alloys, physical metallurgy principles might need to be modified for HEAs. The thermodynamics, kinetics, structure, and properties of HEAs are briefly discussed relating with the four core effects of HEAs. Among these, a severe lattice distortion effect is particularly emphasized because it exerts direct and indirect influences on many aspects of microstructure and properties. Because a constituent phase in HEAs can be regarded as a whole-solute matrix, every lattice site in the matrix has atomic-scale lattice distortion. In such a distorted lattice, point defects, line defects, and planar defects are different from those in conventional matrices in terms of atomic configuration, defect energy, and dynamic behavior. As a result, mechanical and physical properties are significantly influenced by such a distortion. Suitable mechanisms and theories correlating composition, microstructure, and properties for HEAs are required to be built in the future. Only these understandings make it possible to complete the physical metallurgy of the alloy world.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Reed-Hill and R. Abbaschian, Physical Metallurgy Principles, 3rd ed. (Boston, MA: PWS Publishing Company, 1994), pp. xiii–xv.
R.W. Cahn and P, Haasen, eds., Physical Metallurgy, 3rd ed. (New York: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1983), pp. 1–35.
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299 (2004).
J.W. Yeh, JOM 65, 1759 (2013).
J.W. Yeh, Ann. Chim. Sci. Mater. 31, 633 (2006).
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Prog. Mater Sci. 61, 1 (2014).
L.J. Santodonato, Y. Zhang, M. Feygenson, C.M. Parish, M.C. Gao, R.J.K. Weber, J.C. Neuefeind, Z. Tang, and P.K. Liaw, Nat. Commun. 6, 5964 (2015).
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, and P.K. Liaw, Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 534 (2008).
Y. Zhang, Z.P. Lu, S.G. Ma, P.K. Liaw, Z. Tang, Y.Q. Cheng, and M.C. Gao, MRS Commun. 4, 57 (2014).
S. Guo, Q. Hu, C. Ng, and C.T. Liu, Intermetallics 41, 96 (2013).
S. Guo, J. Mater. Sci. Tech. 31, 1223 (2015).
K.Y. Tsai, M.H. Tsai, and J.W. Yeh, Acta Mater. 61, 4887 (2013).
C. Lee (Master’s thesis, National Tsing Hua University, 2013).
P.P. Bhattacharjee, G.D. Sathiaraj, M. Zaid, J.R. Gatti, C. Lee, C.W. Tsai, and J.W. Yeh, J. Alloy. Compd. 587, 544 (2014).
A.J. Zaddach, C. Niu, C.C. Kock, and D.L. Irving, JOM 65, 1780 (2013).
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, and R.O. Ritchie, Science 345, 1153 (2014).
M.C. Gao, J.W. Yeh, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang, High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications (Cham: Springer, 2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, JW. Physical Metallurgy of High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 67, 2254–2261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1583-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1583-5