Abstract
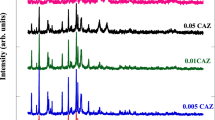
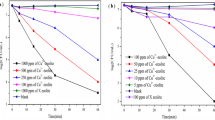
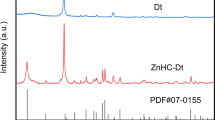
Copper oxide-loaded zeolite 4A nanocomposites (CuO-zeolite NCs) were successfully prepared by modifying zeolite 4A with CuSO4 aqueous solution as the copper source. Zeolite 4A showed an important role in hosting copper oxide, and CuO-zeolite NCs exhibited a controlled release of copper ions. XRD patterns confirmed the appearance of new diffraction peaks of copper oxide at 35.83° and 38.83°. CuO nanosheets formed on the surface of zeolite 4A were about 30–40nm thick over a width of 200–300nm. CuO-zeolite NCs were primarily composed of Cu, Si, Al and O, as measured by XPS. Cu 2p3/2 and Cu 2p1/2 peaks were fitted into two main peaks centered at 934.7eV and 954.6eV, which were attributed to Cu (II). Zeolite 4A and CuO-zeolite NC displayed reversible Langmuir isotherm (type-I) characteristics and showed maximum adsorption quantities of almost 200 cm3 g−1 at a relative pressure of 1.0 by CO2 adsorption-desorption experiments. The antibacterial efficiencies of the CuO-zeolite NC were 99.4%, 96.7%, and 96.8% against Pseudoalteromonas tetraodonis (P. tetraodonis), Micrococcus luteus (M. luteus), and Shewanella putrefaciens (S. putrefaciens), respectively. These values showed that nano CuO-loaded zeolite 4A acted as a strong bactericide against marine bacteria. CuO-zeolite NCs can be further applied to marine antifouling coating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, I., Islam, M., Habis, N. A., and Parvez, S., 2020. Hot-pressed graphene nanoplatelets or/and zirconia reinforced hybrid alumina nanocomposites with improved toughness and mechanical characteristics. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 40: 135–145.
Akintelu, S. A., Folorunso, A. S., Folorunso, F. A., and Oyebamiji, A. K., 2020. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application and environmental remediation. Heliyon, 6(7): e04508.
Alswat, A. A., Ahmad, M. B., and Saleh, T. A., 2017. Preparation and characterization of zeolitezinc oxide-copper oxide nanocomposite: Antibacterial activities. Colloid and Interface Science Communications, 16: 19–24.
Ananth, A., Dharaneedharan, S., Heo, M. S., and Mok, Y. S., 2015. Copper oxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, characterization and structure-specific antibacterial performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 262: 179–188.
Araki, S., Li, T., Li, K., and Yamamoto, H., 2019. Preparation of zeolite hollow fibers for high-efficiency cadmium removal from waste water. Separation and Purification Technology, 221: 393–398.
Brazlauskas, M., and Kitrys, S., 2008. Synthesis and properties of CuO/zeolite sandwich type adsorbent-catalysts. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 29(1): 25–30.
Cheng, M., Wang, Y., Wang, W. H., Wang, G. W., Zhu, X. L., and Li, C. Y., 2021. Promoting effect of copper oxide on CsX zeolite catalyst for side-chain alkylation of toluene with methanol. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 311: 110732.
Dong, J. P., Tian, T. L., Ren, L. X., Zhang, Y., Xu, J. Q., and Cheng, X. W., 2015. CuO nanoparticles incorporated in hierarchical MFI zeolite as highly active electrocatalyst for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 125: 206–212.
El-Shafai, N. M., Abdelfatah, M., El-Mehasseb, I. M., Ramadan, M. S., Ibrahim, M. M., El-Shaer, A., et al., 2021. Enhancement of electrochemical properties and photocurrent of copper oxide by heterojunction process as a novel hybrid nano-composite for photocatalytic anti-fouling and solar cell applications. Separation and Purification Technology, 267: 118631.
Karuppannan, S. K., Ramalingam, R., Khalith, M. S. B., Musthafa, S. A., Dowlath, M. J. H., Ramanujam, G. M., et al., 2021. Copper oxide nanoparticles infused electrospun polycaprolactone/gelatin scaffold as an antibacterial wound dressing. Materials Letters, 294: 129787.
Lv, Y. Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Z. Y., Zhang, W. H., Wang, A. Y., Tian, F., et al., 2021. Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles-loaded ZnO nanowires arrays with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 267: 124703.
Majumdar, D., and Ghosh, S., 2020. Recent advancements of copper oxide based nanomaterials for supercapacitor applications. Journal of Energy Storage, 34: 101995.
Mekatel, E. H., Amokrane, S., Aid, A., Nibou, D., and Trari, M., 2015. Adsorption of methyl orange on nanoparticles of a synthetic zeolite NaA/CuO. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 18(3): 336–344.
Menazea, A. A., and Ahmed, M. K., 2020. Nanosecond laser ablation assisted the enhancement of antibacterial activity of copper oxide nano particles embedded though Polyethylene Oxide/Polyvinyl pyrrolidone blend matrix. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 174: 108911.
Meng, T., Ren, N., and Ma, Z., 2015. Silicalite-1@Cu-ZSM-5 core-shell catalyst for N2O decomposition. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 404–405: 233–239.
Murugappan, G., and Sreeram, K. J., 2021. Nano-biocatalyst: Bi-functionalization of protease and amylase on copper oxide nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 197: 111386.
Nayan, N., Sahdan, M. Z., Wei, L. J., Ahmad, M. K., Lias, J., Fhong, S. C., et al., 2016. Correlation between microstructure of copper oxide thin films and its gas sensing performance at room temperature. Procedia Chemistry, 20: 45–51.
Ninan, N., Muthiah, M., Yahaya, N. A. B., Park, I. K., Elain, A., Wong, T. W., et al., 2014. Antibacterial and wound healing analysis of gelatin/zeolite scaffolds. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 115: 244–252.
Noroozi, R., Musawi, T. J. A., Kazemian, H., Kalhori, E. M., and Zarrabi, M., 2018. Removal of cyanide using surface-modified Linde type — A zeolite nanoparticles as an efficient and eco-friendly material. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 21: 44–51.
Panda, A. P., Jha, U., and Swain, S. K., 2020. Synthesis of nanostructured copper oxide loaded boehmite (CuO_Boehmite) for adsorptive removal of As(III/V) from aqueous solution. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 37: 101506.
Pandiyarajan, T., Udayabhaskar, R., Vignesh, S., James, R. A., and Karthikeyan, B., 2013. Synthesis and concentration dependent antibacterial activities of CuO nanoflakes. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 33(4): 2020–2024.
Perla, V. K., Ghosh, S. K., and Mallick, K., 2020. Bipolar resistive switching behavior of carbon nitride supported copper oxide nanoparticles. Chemical Physics Letters, 754: 137650.
Rezaie, A. B., Montazer, M., and Rad, M. M., 2018. Environmentally friendly low cost approach for nano copper oxide functionalization of cotton designed for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Journal of Cleaner Production, 204: 425–436.
Rutkowska, I. A., Wadas, A., Szaniawska, E., Chmielnicka, A., Zlotorowicz, A., and Kulesza, P. J., 2020. Elucidation of activity of copper and copper oxide nanomaterials for electrocatalytic and photoelectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 23: 131–138.
Show, B., Ahmed, S. F., Mondal, A., and Mukherjee, N., 2020. Hierarchical copper oxide as efficient enzymeless amperometric biosensor and promising photocatalyst. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2): 104748.
Soori, F., and Ejhieh, A. N., 2018. Synergistic effects of copper oxide-zeolite nanoparticles composite on photocatalytic degradation of 2,6-dimethylphenol aqueous solution. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 255: 250–256.
Sorekine, G., Anduwan, G., Waimbo, M. N., Osora, H., Velusamy, S., Kim, S., et al., 2021. Photocatalytic studies of copper oxide nanostructures for the degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1248: 131487.
Stohs, S. J., and Bagchi, D., 1995. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 18(2): 321–336.
Sultana, S., Rafiuddin, K. M. Z., Umar, K., and Muneer, M., 2013. Electrical, thermal, photocatalytic and antibacterial studies of metallic oxide nanocomposite doped polyaniline. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 29(9): 795–800.
Thangamani, J. G., and Pasha, S. K. K., 2021. Hydrothermal synthesis of copper (II) oxide-nanoparticles with highly enhanced BTEX gas sensing performance using chemiresistive sensor. Chemosphere, 277: 130237.
Vajda, M., Ursu, D., Duteanu, N., and Miclau, M., 2020. Low lying valence band edge materials based on copper oxide for tandem dye-sensitized solar cells. Materials Letters, 275: 128151.
Wang, H., Luo, Y. Y., Liu, B., Gao, L., and Duan, G. T., 2021. CuO nanoparticle loaded ZnO hierarchical heterostructure to boost H2S sensing with fast recovery. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 338: 129806.
Yadav, M. S., Sinha, A. K., Singh, M. N., and Kumar, A., 2021. Electrochemical study of copper oxide and activated charcoal based nanocomposite electrode for supercapacitor. Materials Today: Proceedings, 46: 5722–5729.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support of the National Key Research and the Development Project (No. 2019YFC0312 103), and the Open Fund of Shandong Key Laboratory of Corrosion Science (No. KLCS201905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Ye, Y. Design of Copper Oxide Nanosheets-Loaded Zeolite with Efficient Inhibition of Marine Bacteria. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 1237–1243 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-5240-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-5240-7