Abstract
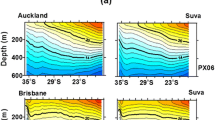
The Subantarctic Mode Water (SAMW) forms in the deep mixed layer north of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current and spreads northward into the subtropical gyre. The subtropical South Indian Countercurrent (SICC) flows eastward on the north flank of the thick SAMW layer within 22° – 32°S from south of Madagascar at around 25°S, 50°E toward western Australia. The dynamical relation of the SAMW and the southern branch of the SICC (30° – 32°S) is investigated in this work based on the monthly mean Argo data from 2004 to 2019. The physical properties of the SAMW and its pathway from the formation region are described. Most of the SAMW in the Indian Ocean sector originates from the deep mixed layers of the southeastern Indian Ocean (about 40°S, 85° – 105°E) and moves along the subtropical gyre. It takes around ten years to arrive east of Madagascar Island preserving its low potential vorticity characteristics. As a thick layer with homogeneous vertical properties, the SAMW forces the upper pycnocline to shoal, and the associated eastward shear results in the surface-intensified SICC. The SAMW forms a tongue-shaped thickness pattern, which influences the southern branch of the SICC above the northern flank of the thickest SAMW layer between 24°S and 32°S. The seasonal, interannual, and decade variations of the southern branch of the SICC are closely related to the meridional gradient of the underlying SAMW thickness. The SAMW thickened and strengthened from 2005 to 2015, thereby anchoring a strengthened SICC. The interannual covariability of the SAMW and SICC further supports the SAMW’s role in driving SICC variability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, S., Hariyama, M., Mitsudera, H., Sasaki, H., and Sasai, Y., 2007. Formation regions of Subantarctic Mode Water detected by OFES and Argo profiling floats. Geophysical Research Letters, 34 (10): L10606, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL029828.
Aoki, Y., Suga, T., and Hanawa, K., 2002. Subsurface subtropical fronts of the North Pacific as inherent boundaries in the ventilated thermocline. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 32: 2299–2311.
Cerovečki, I., Talley, L. D., Mazloff, M. R., and Maze, G., 2013. Subantarctic mode water formation, destruction, and export in the eddy-permitting Southern Ocean state estimate. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 43 (7): 1485–1511, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/JPO-D-12-0121.1.
Dong, S., Sprintall, J., Gille, S. T., and Talley, L., 2008. Southern Ocean mixed-layer depth from Argo float profiles. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 113 (C6): C06013, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JC004051.
Fofonoff, N. P., and Millard Jr., R. C., 1983. Algorithms for the computation of fundamental properties of seawater. UNESCO Technical Papers in Marine Science, UNESCO.
Gao, L., Rintoul, S. R., and Yu, W., 2018. Recent wind-driven change in Subantarctic Mode Water and its impact on ocean heat storage. Nature Climate Change, 8 (1): 58–63, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0022-8.
Hanawa, K., and Talley, L. D., 2001. Mode waters. International Geophysics Series, 77: 373–386.
Holte, J. W., and Talley, L. D., 2009. A new algorithm for finding mixed layer depths with applications to Argo data and Sub-antarctic Mode Water formation. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 26 (9): 1920–1939, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JTECHO543.1.
Holte, J. W., Talley, L. D., Chereskin, T. K., and Sloyan, B. M., 2012. The role of air-sea fluxes in Subantarctic Mode Water formation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117 (C3): C03040, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JC007798.
Jones, D. C., Meijers, A. J., Shuckburgh, E., Sallée, J. B., Haynes, P., McAufield, E. K., et al., 2016. How does Subantarctic Mode Water ventilate the Southern Hemisphere subtropics? Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121 (9): 6558–6582, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JC011680.
Kobashi, F., and Kubokawa, A., 2012. Review on North Pacific Subtropical Countercurrents and subtropical fronts: Role of mode waters in ocean circulation and climate. Journal of Oceanography, 68 (1): 21–43, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-011-0083-7.
Kobashi, F., Mitsudera, H., and Xie, S. P., 2006. Three subtropical fronts in the North Pacific: Observational evidence for mode water-induced subsurface frontogenesis. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978–2012), 111 (C9): C09033, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JC003479.
Kubokawa, A., 1997. A two-level model of subtropical gyre and subtropical countercurrent. Journal of Oceanography, 53: 231–244.
Kubokawa, A., 1999. Ventilated thermocline strongly affected by a deep mixed layer: A theory for subtropical countercurrent. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 29 (6): 1314–1333, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1999)029<1314:VTSABA>2.0.CO;2.
Kubokawa, A., and Inui, T., 1999. Subtropical countercurrent in an idealized ocean GCM. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 29 (6): 1303–1313, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1999)029<1303:SCIAIO>2.0.CO;2.
Liu, L. L., and Huang, R. X., 2012: The global subduction/obduction rates: Their interannual and decadal variability. Journal of Climate, 25 (4): 1096–1115, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4228.1.
Marshall, J., and Speer, K., 2012. Closure of the meridional overturning circulation through Southern Ocean upwelling. Nature Geoscience, 5: 171–180, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1391.
McCartney, M. S., 1977. Subantarctic mode water. A Voyage of Discovery, Deep Sea Research, 24: 103–119.
McCartney, M. S., 1982. The subtropical recirculation of mode waters. Journal of Marine Research, 40: 427–464.
Menezes, V. V., Phillips, H. E., Schiller, A., Bindoff, N. L., Domingues, C. M., and Vianna, M. L., 2014. South Indian Counter-current and associated fronts. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119 (10): 6763–6791, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JC010076.
Menezes, V. V., Phillips, H. E., Vianna, M. L., and Bindoff, N. L., 2016. Interannual variability of the South Indian Countercurrent. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121: 3465–3487, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JC011417.
Orsi, A. H., Whitworth, T., and Nowlin, W. D., 1995. On the meridional extent and fronts of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Deep Sea Research I, 42: 641–673.
Palastanga, V., Van Leeuwen, P. J., Schouten, M. W., and de Ruijter, W. P. M., 2007. Flow structure and variability in the subtropical Indian Ocean: Instability of the South Indian Ocean Countercurrent. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978-2012), 112 (C1): C01001, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JC003395.
Qu, T., Gao, S., and Fine, R. A., 2020. Variability of the sub-Antarctic mode water subduction rate during the Argo period. Geophysical Research Letters, 47: e2020GL088248, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL088248.
Roemmich, D., and Gilson, J., 2009. The 2004–2008 mean and annual cycle of temperature, salinity, and steric height in the global ocean from the Argo program. Progress in Oceanography, 82 (2): 81–100, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2009.03.004.
Sabine, C. L., Feely, R. A., Gruber, N., Key, R. M., Lee, K., Bullister, J. L., et al., 2004. The oceanic sink for anthropogenic CO2. Science, 305 (5682): 367–371, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097403.
Sallée, J. B., Matear, R. J., Rintoul, S. R., and Lenton, A., 2012. Localized subduction of anthropogenic carbon dioxide in the Southern Hemisphere oceans. Nature Geoscience, 5: 579–584, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1523.
Sallée, J. B., Speer, K. G., and Rintoul, S. R., 2010. Zonally asymmetric response of the Southern Ocean mixed-layer depth to the Southern Annular Mode. Nature Geoscience, 3 (4): 273–279, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo812.
Sallée, J. B., Wienders, N., Speer, K., and Morrow, R., 2006. Formation of subantarctic mode water in the southeastern Indian Ocean. Ocean Dynamics, 56 (5–6): 525–542, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-005-0054-x.
Schott, F. A., Xie, S. P., and McCreary Jr., J. P., 2009. Indian Ocean circulation and climate variability. Reviews of Geophysics, 47 (1): RG1002, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007RG000245.
Siedler, G., Rouault, M., and Lutjeharms, J. R., 2006. Structure and origin of the subtropical South Indian Ocean Countercurrent. Geophysical Research Letters, 33 (24): L24609, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL027399.
Talley, L. D., 2013. Closure of the global overturning circulation through the Indian, Pacific, and Southern Oceans: Schematics and transports. Oceanography, 26 (1): 80–97, DOI: https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2013.07.
Xie, S. P., Xu, L., Liu, Q., and Kobashi, F., 2011. Dynamical role of mode water ventilation in decadal variability in the central subtropical gyre of the North Pacific. Journal of Climate, 24 (4): 1212–1225, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3896.1.
Xu, L., Li, P., Xie, S. P., Liu, Q., Liu, C., and Gao, W., 2016. Observing mesoscale eddy effects on mode-water subduction and transport in the North Pacific. Nature Communications, 7: 10505, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10505.
Xu, L., Xie, S. P., and Liu, Q., 2012. Mode water ventilation and subtropical countercurrent over the North Pacific in CMIP5 simulations and future projections. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978-2012), 117 (C12): C12009, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JC008377.
Yamanaka, G., Ishizaki, H., Hirabara, M., and Ishikawa, I., 2008. Decadal variability of the subtropical front of the western North Pacific in an eddy-resolving ocean general circulation model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 113 (C12): C12027, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JC005002.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2018YFA0605700, 2016YFA0601800) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41876006). The Roemmich-Gilson Gridded Monthly Argo Data are available at http://sio-argo.ucsd.edu/RG_Climatology.html. The Argo data are collected and made freely available by the International Argo Program and the national programs that contribute to it. The Argo Program is part of the Global Ocean Observing System. The ECMWF ERA-Interim monthly mean data is freely downloaded from https://doi.org/10.5065/D68050NT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Liu, Q. & Xie, SP. Covariability of Subantarctic Mode Water and the Southern Branch of the Subtropical Indian Ocean Countercurrent in Argo Observations. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 1316–1324 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4677-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4677-4