Abstract
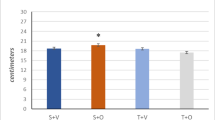
Dietary supplementation with sea cucumber saponins (SCS) and exercise have been confirmed to be effective in preventing the development of obesity and its related diseases. However, the combined effectiveness of these interventions has not been explored. Here, we studied whether the beneficial influences of exercise could be further enhanced by dietary supplementation with SCS in high-fat diet-fed KM (Kunming) mice. Mice were randomly divided into four groups, including the high-fat diet group (HF), the SCS group (HF-S), the exercise group (HF-E), and the combination of dietary SCS and exercise group (HF-S + E). There were eight mice in every group. The results demonstrated that the combination of dietary SCS and exercise could synergistically reduce fat accumulation. In particular, white adipose tissue decreased by 63% in the HF-S + E group compared with that in the HF group. SCS supplementation with exercise also improved peripheral markers, such as serum parameters and hepatic TG levels. Further mechanical testing indicated that the combined effects of dietary SCS and exercise on inhibiting fat accumulation might be attributed to the inhibition of lipid synthesis in the liver and the activation of lipolysis in white adipose tissue to increase energy consumption.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC1 :
-
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate 1
- ACOX1 :
-
acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1
- ATGL :
-
adipose triglyceride lipase
- ACAA1 :
-
acetyl-coenzyme A acyltransferase 1
- CPT1a :
-
carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1a
- CPT2 :
-
carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2
- EA:
-
echinoside A
- FAS :
-
fatty acid synthase
- FABP4 :
-
fatty acid binding protein 4
- FFA:
-
free fatty acid
- G6PDH :
-
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- HA:
-
holothurin A
- HDL-C:
-
density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HF:
-
high-fat diet group
- HF-S:
-
sea cucumber saponins group
- HF-E:
-
exercise group
- HF-S + E:
-
sea cucumber saponins and exercise group
- HSL :
-
hormone-sensitive lipase
- LPL :
-
lipoprotein lipase
- LDL-C:
-
low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
- ME :
-
malic enzyme
- PPARα :
-
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha
- PPARγ :
-
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- SCS:
-
sea cucumber saponins
- SCD1 :
-
stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1
- SREBP-1c :
-
sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1
- TC:
-
cholesterol
- TG:
-
triacylglycerol
References
Adegboye, A. R. A., and Linne, Y. M., 2013. Diet or exercise, or both, for weight reduction in women after childbirth. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 7: CD005627.
Bhattacharya, A., Rahman, M. M., Sun, D., Lawrence, R., Mejia, W., McCarter, R., O’shea, M., and Fernandes, G., 2005. The combination of dietary conjugated linoleic acid and treadmill exercise lowers gain in body fat mass and enhances lean body mass in high fat-fed male balb/c mice. The Journal of Nutrition, 135(5): 1124–1130.
Brunani, A., Caumo, A., Graci, S., Castagna, G., Viberti, G., and Liuzzi, A., 2008. Rosiglitazone is more effective than metformin in improving fasting indexes of glucose metabolism in severely obese, non-diabetic patients. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 10(6): 460–467.
Carlson, C., and Winder, W., 1999. Liver AMP-activated protein kinase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase during and after exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology, 86(2): 669–674.
Chen, G., Liang, G., Ou, J., Goldstein, J. L., and Brown, M. S., 2004. Central role for liver X receptor in insulin-mediated activation of Srebp-1c transcription and stimulation of fatty acid synthesis in liver. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101(31): 11245–11250.
Cho, A. S., Jeon, S. M., Kim, M. J., Yeo, J., Seo, K. I., Choi, M. S., and Lee, M. K., 2010. Chlorogenic acid exhibits anti-obesity property and improves lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced-obese mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48(3): 937–943.
Davitt, P. M., Arent, S. M., Tuazon, M. A., Golem, D. L., and Henderson, G. C., 2013. Postprandial triglyceride and free fatty acid metabolism in obese women after either endurance or resistance exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology, 114(12): 1743–1754.
Dyck, D. J., and Bonen, A., 1998. Muscle contraction increases palmitate esterification and oxidation and triacylglycerol oxidation. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 275(5): E888–E896.
Eaton, S., 2002. Control of mitochondrial β-oxidation flux. Progress in Lipid Research, 41(3): 197–239.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Stanley, G. S., 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 226(1): 497–509.
Galani, C., and Schneider, H., 2007. Prevention and treatment of obesity with lifestyle interventions: Review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Public Health, 52(6): 348–359.
Guo, L., Gao, Z., Zhang, L., Guo, F., Chen, Y., Li, Y., and Huang, C., 2016. Saponin-enriched sea cucumber extracts exhibit an antiobesity effect through inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity and upregulation of LXR-β signaling. Pharmaceutical Biology, 54(8): 1312–1325.
Hu, X. Q., Wang, Y. M., Wang, J. F., Xue, Y., Li, Z. J., Nagao, K., Yanagita, T., and Xue, C. H., 2010. Dietary saponins of sea cucumber alleviate orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats via PPARα and SREBP-1c signaling. Lipids in Health and Disease, 9(1): 25.
Karbowska, J., and Kochan, Z., 2012. Fat-reducing effects of dehydroepiandrosterone involve upregulation of ATGL and HSL expression, and stimulation of lipolysis in adipose tissue. Steroids, 77(13): 1359–1365.
Kushner, R. F., 2014. Weight loss strategies for treatment of obesity. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 56(4): 465–472.
Lavoie, J. M., and Gauthier, M. S., 2006. Regulation of fat metabolism in the liver: Link to non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and impact of physical exercise. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS, 63(12): 1393–1409.
Liu, R., Zheng, Y., Cai, Z., and Xu, B., 2017. Saponins and flavonoids from adzuki bean (Vigna angularis L.) ameliorate high-fat diet-induced obesity in ICR mice. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 8: 687.
Liu, X., Cui, J., Leng, K., Xue, C., Li, Z., Xue, Y., and Wang, Y., 2016. Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids exhibit superior effects on obesity-related metabolic disorders to egg yolk phospholipids and soybean phospholipids in mice. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 118(11): 1712–1721.
Liu, X., Cui, J., Li, Z., Xu, J., Wang, J., Xue, C., and Wang, Y., 2014. Comparative study of DHA-enriched phospholipids and EPA-enriched phospholipids on metabolic disorders in diet-induced-obese C57BL/6J mice. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 116(3): 255–265.
Marques, C., Motta, V., Torres, T., Aguila, M., and Mandarimde-Lacerda, C., 2010. Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 43(5): 467–475.
Meng, J., Hu, X., Zhang, T., Dong, P., Li, Z., Xue, C., Chang, Y., and Wang, Y., 2018. Saponin from sea cucumber exhibited more significant effects than ginsenoside on ameliorating high fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. MedChemComm, 9(4): 725–734.
Ohyama, K., Nogusa, Y., Suzuki, K., Shinoda, K., Kajimura, S., and Bannai, M., 2014. A combination of exercise and capsinoid supplementation additively suppresses diet-induced obesity by increasing energy expenditure in mice. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 308(4): E315–E323.
Oktay, A. A., Lavie, C. J., Kokkinos, P. F., Parto, P., Pandey, A., and Ventura, H. O., 2017. The interaction of cardiorespiratory fitness with obesity and the obesity paradox in cardiovascular disease. Progress in Vardiovascular Diseases, 60(1): 30–44.
Pillitteri, J. L., Shiffman, S., Rohay, J. M., Harkins, A. M., Burton, S. L., and Wadden, T. A., 2008. Use of dietary supplements for weight loss in the United States: Results of a national survey. Obesity, 16(4): 790–796.
Schweiger, M., Schreiber, R., Haemmerle, G., Lass, A., Fledelius, C., Jacobsen, P., Tornqvist, H., Zechner, R., and Zimmermann, R., 2006. Adipose triglyceride lipase and hormonesensitive lipase are the major enzymes in adipose tissue triacylglycerol catabolism. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(52): 40236–40241.
Sjögren, P., Sierra-Johnson, J., Gertow, K., Rosell, M., Vessby, B., De Faire, U., Hamsten, A., Hellenius, M. L., and Fisher, R., 2008. Fatty acid desaturases in human adipose tissue: Relationships between gene expression, desaturation indexes and insulin resistance. Diabetologia, 51(2): 328–335.
Sullivan, D. R., Kruijswijk, Z., West, C. E., Kohlmeier, M., and Katan, M. B., 1985. Determination of serum triglycerides by an accurate enzymatic method not affected by free glycero. Clinical Chemistry, 31(7): 1227–1228.
Swift, D. L., McGee, J. E., Earnest, C. P., Carlisle, E., Nygard, M., and Johannsen, N. M., 2018. The effects of exercise and physical activity on weight loss and maintenance. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 61(2): 206–213.
Sylow, L., Kleinert, M., Richter, E. A., and Jensen, T. E., 2017. Exercise-stimulated glucose uptake-regulation and implications for glycaemic control. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 13(3): 133–148.
Takeuchi, Y., Yahagi, N., Izumida, Y., Nishi, M., Kubota, M., Teraoka, Y., Yamamoto, T., Matsuzaka, T., Nakagawa, Y., and Sekiya, M., 2010. Polyunsaturated fatty acids selectively suppress sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 through proteolytic processing and autoloop regulatory circuit. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(15): 11681–11691.
Uemura, T., Goto, T., Kang, M. S., Mizoguchi, N., Hirai, S., Lee, J. Y., Nakano, Y., Shono, J., Hoshino, S., and Taketani, K., 2011. Diosgenin, the main aglycon of fenugreek, inhibits LXRα activity in HepG2 cells and decreases plasma and hepatic triglycerides in obese diabetic mice. The Journal of Nutrition, 141(1): 17–23.
Wang, T., Xue, C., Zhang, T., and Wang, Y., 2018. The improvements of functional ingredients from marine foods in lipid metabolism. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 81: 74–89.
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Yanagita, R. C., Liu, C., Hu, X., Dong, P., Xue, C., and Xue, Y., 2014. Effects of two sulfated triterpene saponins echinoside A and holothurin A on the inhibition of dietary fat absorption and obesity reduction. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 78(1): 139–146.
Wu, T., Qi, X., Liu, Y., Guo, J., Zhu, R., Chen, W., Zheng, X., and Yu, T., 2013. Dietary supplementation with purified mulberry (Morus australis Poir) anthocyanins suppresses body weight gain in high-fat diet fed C57BL/6 mice. Food Chemistry, 141(1): 482–487.
Ye, S. Y., and Liu, J., 2016. Chinese adults’ physical exercise, static behaviors, trends and influencing factors. Journal of Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, 28: 365–369.
Zhang, J., Zhao, Y., Xu, C., Hong, Y., Lu, H., Wu, J., and Chen, Y., 2014. Association between serum free fatty acid levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. Scientific Reports, 4: 5832.
Zhao, Y. C., Xue, C. H., Zhang, T. T., and Wang, Y. M., 2018. Saponins from sea cucumber and their biological activities. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66(28): 7222–7237.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFD0901103) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31901688 and 31571771).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Meng, J., Shi, H. et al. Dietary Supplementation with Sea Cucumber Saponins and Exercise Can Significantly Suppress Adipose Accumulation in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 629–640 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4577-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4577-7