Abstract
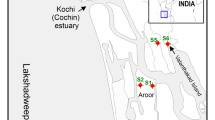
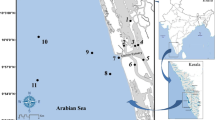
Oligochaetes play an important role in nutrient cycling and energy flow in benthic food webs as well as in mangrove wetlands. However, they have not been as extensively studied as other macrofaunal groups such as polychaetes, gastropods, bivalves, and crustaceans. Under the assumption that oligochaete density and biomass obey specific geographical distribution patterns in subtropical mangrove wetlands of China, we investigated these two parameters in the Luoyang Estuary of Quanzhou Bay, Zhangjiang Estuary and Gaoqiao mangrove wetlands. A geographical gradient in oligochaete density was present in Aegiceras corniculatum and Kandelia obovata habitats, whereby it decreased from lower latitudes to higher latitudes. Further, ANOVA tests on oligochaete distribution revealed that both oligochaete density and biomass were significantly influenced by region, season and region × season at the A. corniculatum and K. obovata habitats. The annual average oligochaete density and biomass at the A. corniculatum habitat were higher than that at the K. obovata habitat, in both the Luoyang and Zhangjiang estuaries. There were significant correlations between oligochaete density and biomass and sediment particle size parameters, confirming that sand, silt, and clay contents were the key environmental factors affecting oligochaete distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armendáriz, L., Ocón, C., and Capítulo, A. R., 2012. Potential responses of oligochaetes (Annelida, Clitellata) to global changes: Experimental fertilization in a lowland stream of Argentina (South America). Limnologica, 42: 118–126.
Aston, R. J., 1973. Field and experimental studies on the effects of a power station effluent on Tubificidae (Oligochaeta, Annelida). Hydrobiologia, 42 (2-3): 225–242.
Cai, L. Z., 2015. Zoobenthic Ecology in Shenzhen Bay. Xiamen University Press, 1–22 (in Chinese).
Cai, L. Z., Hwang, J. S., Dahms, H. U., Fu, S. J., Chen, X. W., and Wu, C., 2013. Does high organic matter content affect polychaete assemblages in a Shenzhen Bay mudflat, China? Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 21: 274–284.
Cai, L. Z., Lin, J. D., and Li, H. M., 2001. Macroinfauna communities in organic-rich mudflat at Shenzhen and Hong Kong, China. Bulletin of Marine Science, 69 (3): 1129–1138.
Cai, L. Z., Xu, P., Fu, S. J., Peng, X., Cao, J., Chen, X. W., Wu, C., and Liu, S., 2012. Secondary productivity of macrobenthos in mangrove and salt marsh in Gaoqiao of Zhanjiang. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23 (4): 965–971 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Carrol, H. J., and Dorris, T. T., 1972. The life history of Branchiura sowerbyi. American Midland Naturalist, 87: 413–422.
Chen, X. W., Cai, L. Z., Wu, C., Peng, X., Cao, J., Xu, P., Liu, S., and Fu, S. J., 2012. Polychaete community in mangrove and salt marsh in Zhangjiang River Estuary, Fujian. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23 (4): 931–938 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Erséus, C., 1984. The marine Tubificidae (Oligochaeta) of Hong Kong and southern China. Asian Marine Biology, 1: 135–175.
Erséus, C., 1990. Marine oligochaeta of Hong Kong. In: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China II. Morton, B., ed., Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, 259–335.
Erséus, C., 1992. Marine oligochaeta of Hong Kong: A supplement. In: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China III. Morton, B., ed., Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, 157–178.
Erséus, C., 1997. Additional notes on the taxonomy of the marine Oligochaeta of Hong Kong, with a description of a new species of Tubificidae. In: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China IV. Morton, B., ed., Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, 37–52.
Feng, J. X., Guo, J. M., Huang, Q., Jiang, J. X., Huang, G. M., Yang, Z. W., and Lin, G. H., 2014. Changes in the community structure and diet of benthic macrofauna in invasive Spartina alterniflora wetlands following restoration with native mangroves. Wetlands, 34: 673–683.
Guo, T., Cai, L. Z., Zhuo, Y., Rao, Y. Y., Li, X., Chen, X. W., Fu, S. J., and Ji, J. F., 2014. Comparison of benthic macrofaunal communities in two mangrove habitats of Luoyangjiang Estuary in Quanzhou Bay. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 33 (2): 204–211 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Kanaya, G., and Kikuchi, E., 2008. Spatial changes in a macrozoobenthic community along environmental gradients in a shallow brackish lagoon facing Sendai Bay, Japan. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 78: 674–684.
Kristensen, E., Bouillon, S., Dittmar, T., and Marchand, C., 2008. Organic carbon dynamics in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Aquatic Botany, 89: 201–219.
Lee, S. Y., 1993. Invertebrate species new to science recorded from the Mai Po Marshes, Hong Kong. The marine biology of the South China Sea. Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Marine Biology of Hong Kong and the South China Sea. Morton, B., ed., Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, 199–209.
Lee, S. Y., 2008. Mangrove macrobenthos: Assemblages, services, and linkages. Journal of Sea Research, 59: 16–29.
Li, R. X., 2001. Studies on the growth and reproduction of Tubifex tubifex Müller. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 25 (1): 14–20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, R. X., 2003. Effects of water temperature on reproduction of Tubifex tubifex Müller. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 27 (4): 443–444 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang, P., Huang, X., Qian, Y., and Ding, G. J., 2004. Influence of environmental factors on the growth of Aeolosoma hemprichi. China Environmental Science, 24 (5): 610–613 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Prantoni, A. L., and Domênico, M. D., 2014. A taxonomic overview of marine and estuarine oligochaetes from Brazil. Marine Biodiversity, 44: 275–278.
Wang, H. Z., and Erséus, C., 2001. Marine Phallodrilinae (Oligochaeta, Tubificidae) of Hainan Island in southern China. Hydrobiologia, 462: 199–204.
Wang, H. Z., and Erséus, C., 2003. Marine species of Ainudrilus and Heterodrilus (Oligochaeta: Tubificidae: Rhyacodrilinae) from Hainan Island in southern China. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 37: 205–217.
Wang, H. Z., and Erséus, C., 2004. New species of Doliodrilus and other Limnodriloidinae (Oligochaeta, Tubificidae) from Hainan and other parts of the north-west Pacific Ocean. Journal of Natural History, 38: 269–299.
Wang, M., Gao, X. Q., and Wang, W. Q., 2014. Differences in burrow morphology of crabs between Spartina alterniflora marsh and mangrove habitats. Ecological Engineering, 69: 213–219.
Wu, Z. B., He, F., Fu, G. P., Kuang, Q. J., and Lei, Z. H., 2002. Investigation of plankton and benthos in Shenzhen Bay. Marine Sciences, 26 (8): 58–64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ysebaert, T., Meire, P., Coosen, J., and Essink, K., 1998. Zonation of intertidal macrobenthos in the estuaries of Schelde and Ems. Aquatic Ecology, 32: 53–71.
Zhou, H., and Erséus, C., 2003. Marine oligochaete assemblages in a Hong Kong mangrove and adjacent foreshore sandflat, with description of a new species. In: Perspectives on Marine Environmental Changes in Hong Kong and Southern China. Hong Kong Workshops Reunion Conference (1977-2001). Morton, B., ed., Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, 121–135.
Zhou, X. P., Cai, L. Z., Fu, S. J., and Wang, W., 2010. Comparative study of the macrobenthic community in intertidal mangrove and non-mangrove habitats in Tong’an Bay, Fujian Province. Biodiversity Science, 18 (1): 60–66.
Zhu, H., Wei, Y. S., and Liu, J. X., 2008. Growth of Tubificidae in activated sludge. Environmental Science, 29 (5): 1342–1347 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41376113) and Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Oceans (No. 201505004). The authors are grateful to Prof. Jiang-Shiou HWANG and Hans-Uwe DAHMS for their professional advices, to Ms. Su-Jing FU, Sha LIU, Xin PENG, Jing CAO, Yi ZHUO, Xiang LI, Mr. Peng XU, Chen WU, Tao GUO and Lu-Lu YAN for their assistance with sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Cai, L., Zhou, X. et al. Geographical variation in oligochaete density and biomass in subtropical mangrove wetlands of China. J. Ocean Univ. China 16, 925–931 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3191-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3191-1