Abstract
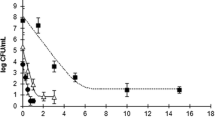
The effects of high pressure (HP) treatment on spoilage characteristic and shelf life extension of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) during refrigerated storage were studied. Results showed that HP treatment of 275 MPa for 3 min or 300 MPa for 2 min could achieve 100% full release of oyster adductor muscle, pressures higher than 350 MPa caused excessive release as the shells of oysters were broken, thus use of higher pressures should be cautious in oyster processing industry because of its adverse impact on the appearance of shells. HP treatment (300 MPa, 2 min) was proper for the shucking of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) in China. This treatment caused no organoleptic disadvantage. Moreover, HP treatment resulted in obvious differences in biochemical spoilage indicators (pH, TVB-N and TBARS) changes and volatile compounds profile determined by electronic nose during storage. HP treatment (300 MPa, 2 min) also led to a reduction of aerobic bacterial count (APC) by 1.27 log cycles. Furthermore, the APC values of oysters treated by HP were always lower than those of the control samples during storage. Based on the organoleptic, biochemical and microbiological indicators, shelf life of 6−8 d for control and 12 d for HP-treated oysters could be expected. HP treatment showed great potential in oyster processing and preservation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, H., Saeed, S. H., and Engg, C., 2012. Electronic nose in food and health applications: A Review. International Journal of Computing and Corporate Research, 2 (6): 1–17.
Ashie, I. N. A., Smith, J. P., and Simpson, B. K., 1996. Spoilage and shelf life extension of fresh fish and shellfish. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 36: 87–121.
Bruner, D. M., Huch, W. L., McEvoy, D. M., and Morgan, O. A., 2014. Consumer valuation of food safety: The case of postharvest processed oysters. Agricultural and Resource Economics Review, 43 (2): 300.
Cao, R., Liu, Q., Yin, B. Z., and Zhu, L. L., 2010. Combined effect of ozonated water and chitosan on the shelf-life of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 11 (1): 108–112.
Cheng, J. H., Sun, D. W., Zeng, X. A., and Pu, H. B., 2014. Non-destructive and rapid determination of TVB-N content for freshness evaluation of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) by hyperspectral imaging. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 21: 179–187.
Cruz-Romero, M., Smiddy, M., Hill, C., Kerry, J. P., and Kelly, A. L., 2004. Effects of high pressure treatment on physicochemical characteristics of fresh oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 5 (2): 161–169.
Cruz-Romero, M., Kelly, A. L., and Kerry, J. P., 2007. Effects of high-pressure and heat treatments on physical and biochemical characteristics of oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 8 (1): 30–38.
Ginson, J., Kamalakanth, C. K., Bindu, J., Venkateswarlu, R., Das, S., Chauhan, O. P., and Gopal, T. S., 2013. Changes in K value, microbiological and sensory acceptability of high pressure processed Indian white prawn (Fenneropenaeus indicus). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6 (5): 1175–1180.
Harpaz, S., Glatman, L., Drabkin, V., and Gelman, A., 2003. Effects of herbal essential oils used to extend the shelf-life of fresh water reared Asian sea bass fish (Lates calcarifer). Journal of Food Protection, 66: 410–417.
He, H., Adams, R. M., Farkas, D. F., and Morrissey, M. T., 2002. Use of high-pressure processing for oyster shucking and shelf-life extension. Journal of Food Science, 67 (2): 640–645.
Hsu, K. C., Hwang, J. S., Chi, H. Y., and Lai, K. M., 2010. Effect of different high pressure treatments on shucking, biochemical, physical and sensory characteristics of oysters to elaborate a traditional Taiwanese oyster omelette. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 90 (3): 530–535.
Kim, Y. M., Paik, H. D., and Lee, D. S., 2002. Shelf-life characteristics of fresh oysters and ground beef as affected by bacteriocin-coated plastic packaging film. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 82 (9): 998–1002.
Khan, M. Z. A., 2015. Protection of foods from microbes: A review on food preservation. International Journal of Pharmacy & Biomedical Research, 2 (1): 13–18.
Lai, K. M., Chi, H. Y., and Hsu, K. C., 2010. High-pressure treatment for shelf-life extension and quality improvement of oysters cooked in a traditional Taiwanese oyster omelet. Journal of Food Protection, 73 (1): 53–61.
Li, T., Li, J., and Hu, W., 2013. Changes in microbiological, physicochemical and muscle proteins of post mortem large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Control, 34 (2): 514–520.
Murchie, L. W., Cruz-Romero, M., Kerry, J. P., Linton, M., Patterson, M. F., Smiddy, M., and Kelly, A. L., 2005. High pressure processing of shellfish: A review of microbiological and other quality aspects. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 6 (3): 257–270.
Ortigosa, M., Garay, E., and Pujalte, M. J., 1994. Numerical taxonomy of aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria associated with oysters and surrounding seawater of the Mediterranean coast. Systematic & Applied Microbiology, 17 (4): 589–600.
Reyes, J. E., Tabilo-Munizaga, G., Pérez-Won, M., Maluenda, D., and Roco, T., 2015. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) treatments on microbiological shelf-life of chilled Chilean jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi). Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 29: 107–112.
Sasaki, K., Iwanaga, C., and Hamaoka, T., 1994. Freshness judgement of raw oyster by fuzzy reasoning. Journal of Japan Society for Fuzzy Theory & Systems, 6: 14–23.
Scott, S. M., James, D., and Ali, Z., 2006. Data analysis for electronic nose systems. Microchimica Acta, 156 (3-4): 183–207.
Yordanov, D. G., and Angelova, G. V., 2010. High pressure processing for foods preserving. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 24 (3): 1940–1945.
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31301587) is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, R., Zhao, L. & Liu, Q. High pressure treatment changes spoilage characteristics and shelf life of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) during refrigerated storage. J. Ocean Univ. China 16, 351–355 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3087-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3087-0