Abstract
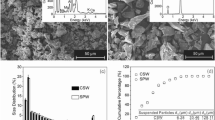
In coastal areas, excessive exploitation of groundwater causes seawater intrusion. In artificial recharge of aquifer remediation process, the replacement of saltwater and freshwater with each other causes colloid release, and permeability also decreases. In this paper, the aquifer samples containing minimal clay mineral (mainly illite) in Dagu River aquifer were used. Adopting horizontal column experiments, we studied the influences of seepage velocity and ionic strength on particle release, as well as the relationship between them. In the column experiments, the Critical Salt Concentration (CSC) of the Dagu River aquifer was determined as 0.05 mol L−1 approximately. This result was basically consistent with the DLVO theoretical calculation. For the constant seepage velocity, the salinity descending rate and partical release were slower, and the peak of particle concentration was lower. However, the total amount of released particles was almost constant at different salinity descending rate. For constant salinity descending rates, the peak of particle concentration decreased as seepage velocity increased, but the total amount of released particles rose up. The experiments also indicated the existence of a critical seepage velocity, which dropped with the decrease of salt concentration. When the concentration of NaCl solution decreased from 0.17 mol L−1 to 0.06 mol L−1, the critical seepage velocity decreased from 3 cm min−1 to 2.5 cm min−1, which is consistent to the results predicted by DLVO theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arulanadan, K., Gillogley E., and Tulley, R., 1980. Development of quantitative methods to predict critical shear and rate of erosion of natural undisturbed cohesive soils. Technical Report GL-80-5, USCOE Waterways, Vickshurg, 2pp.
Blume, T., Weisbrod, N., and Selker, J. S., 2005. On the critical salt concentration for particle detachment in homogeneous sand and heterogeneous Hanford sediments. Geoderma, 214: 121–132.
Goldenberg, L. C., and Magaritz, M., 1983. Experimental investigation on irreversible changes of hydraulic conductivity on the seawater-freshwater interface in coastal aquifer. Water Resources Research, 19 (1): 77–85.
Gregory, J., 1975. Interaction of unequal double layers at constant charge. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 51: 44–51.
Gregory, J., 1981. Approximate expressions for retarded van der Walls interaction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 83: 138–145.
Gruesbeck, C., and Collins, R. E., 1982. Entrainment and deposition of fine particles in porous media. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 22: 847–856.
Huang, X. Q., Lin, J. Q., Gan, H. Y., Xia, Z., Zheng, Z. C., and Pan, Y., 2013. Characteristics of groundwater chemical elements variation and seawater intrusion in east coast of Leizhou peninsula. Ground Water, 35 (3): 38–48.
Khilar, K. C., Fogler, H. S., and Ahluwalia, J. S., 1983. Sandstone water sensitivity: Existence of a critical rate of salinity decrease for particle capture. Chemical Engineering Science, 5: 789–800.
Khublaryan, M. G., Frolov, A. P., and Yushmanov, I. O., 2008. Seawater intrusion into coastal aquifers. Water Resources, 35: 274–286.
Lin, G. G., Wang, F., Ding, J. D., and Zheng, X. L., 2012. Experimental study of permeability mutation on salt-fresh water transition zone mutations with permeability. Chinese Environmental Science Society Symposium, 3: 1944–1947.
Shammas, M. I., 2008. The effectiveness of artificial recharge in combating seawater intrusion in Salalah coastal aquifer, Oman. Environmental Geology, 55: 191–204.
Shang, J., Flury, M., Chen, G., and Zhuang, J., 2008. Impact of flow rate, water content, and capillary forces on in situ colloid mobilization during infiltration in unsaturated sediments. Water Resources Research, 44: W06411, DOI: 10.1029/2007WR006516.
Sun, J. M., Li, J. J., and Gao, Z. J., 2012. Study on the status quo and prevention-control measures of seawater intrusion in Qingdao city. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 40 (33): 16330–16332.
Wang, Y., Han, Z. Y., Chen, J. H., and Li, M., 2009. Influence of hydro-chemical action on particle release. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 35 (4): 57–60.
Wang, X., Han, G., and Qiao, Y. Q., 2012. Discussion on seawater intrusion and ecological restoration of southern Liaodong Peninsula. Shanxi Architecture, 38 (9): 60–61.
Yang, J. L., Han, D. M., Su, X. S., Xiao G. Q., Zhao, C. R., Song, Q. C., and Wang, N., 2012. Environmental tracers (d2 H-d18 O, d34 S, d13 C) as indicators of seawater intrusion processes in the coastal karst area. Advances in Earch Science, 27 (12): 1344–1352.
Zhang, L., and Li, W. M., 2012. Monitoring the seawater intrusion at the Lingjiang coast in eastern Zhejiang. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 23 (3): 43–46.
Zhou, J., Zheng, X. L., Flury, M., and Lin, G. Q., 2009. Permeability changes during remediation of an aquifer affected by sea-water intrusion: A laboratory column study. Journal of Hydrology, 376: 557–566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Lin, G., Liu, J. et al. A laboratory column study on particles release in remediation of seawater intrusion region. J. Ocean Univ. China 14, 1013–1018 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2850-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2850-3