Abstract
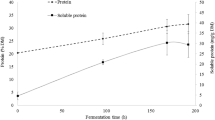
The effects of different microbes on fermenting feed for sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) were compared to select the optimal fermentation strain in this study. Saccharomgces cerevisae, Candida utilis, Bacillus subtilis and Geotrichum candidum were independently added into the experimental compound feed, while only saline was mixed with the control feed. The fermentation treatments were inoculated with 10% seed solution under the condition of 25°C and 70% water content, which lasted for 5 days to elucidate the optimal microbe strain for fermenting effect. Physicochemical indexes and sensorial characteristics were measured per day during the fermentation. The indexes included dry matter recovery (DMR), crude protein (CP), the percentage of amino acid nitrogen to total nitrogen (AA-N/tN), the percentage of ammonia nitrogen to total nitrogen (NH3-N/tN), and the ratio of fermentation strains and vibrios to the total microbes, color, smell and viscosity. The results showed that DMR, CP and AA-N/tN of the S. cerevisae group reached the highest level on day 3, but the ratio of fermentation strain was second to C. utilis group. In addition, its NH3-N/tN and the ratio of vibrios were maintained at low levels, and the sensory evaluation score including smell, color and viscosity was the highest in S. cerevisae group on day 3. Therefore, S. cerevisae could be the optimal strain for the feed fermentation for sea cucumber. This research developed a new production method of fermentation feed for sea cucumber.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andlid, T., Jufirez, R. V., and Gustafsson, L., 1995. Yeast colonizing the intestine of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) and turbot (Scophtalmus maximus). Microbial Ecology, 30: 321–334.
Battaglene, S. C., Seymour, E. J., and Ramofafia, C., 1999. Survival and growth of cultured juvenile sea cucumbers Holothuria scabra. Aquaculture, 178: 293–322.
Brooks, P. H., 2003. Liquid feeding as a means to promote pig health. In: London Swine Conference–Maintaining Your Competitive Edge 9-10 April 2003. London, Ontario, 83–103.
Chen, X., 2005. Study on the improvement of soybean meal ferment Process technology and development of function of fermented soybean meal. PhD thesis. Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, 1–51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chi, Z. M., and Gao, J., 1999. The research progress of alcohol resistance mechanism of yeast. Microbiology China, 26 (5): 373–376 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Choe, S., 1963. Study of Sea Cucumber: Morphology, Ecology and Propagation of Sea Cucumber. Kaibundo Publishing House, Tokyo, 219pp.
Conand, C., 2004. Present status of world sea cucumber resources and utilization: An international overview. In: Advances in Sea Cucumber Aquaculture and Management. FAO, Rome, 13–23.
Demecková, V., Kelly, D., Coutts, A. G. P., Brooks, P. H., and Campbell, A., 2002. The effect of fermented liquid feeding on the fecal microbiology and colostrum quality of farrowing sows. International Food Microbiology, 79 (1-2): 85–97.
Franklin, S. T., Newman, M. C., Newman, K. E., and Meek, K. I., 1993. Immune parameters of dry cows fed mannan oligosaccharide and subsequent transfer of immunity to calves. Journal of Dairy Science, 88 (2): 766–775.
Guo, C. H., Wei, R. L., Tao, W. Q., Chen, Z. H., and Tao, Z., 2009. Application of the protein feed processed by microbial fermentation to dairy cow. Journal of Southwest University for Nationalities Natural Science Edition, 35 (4): 759–763 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hamel, J. F., Conand, C., Pawson, D. L., and Mercier, A., 2001. The sea cucumber Holothuria scabra (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata): Its biology and exploitation as Beche-de-Mer. Advances in Marine Biology, 41: 131–202.
ICS 07.060 A45, 2007. The Specification for Marine Monitoring-Part 4: Seawater Analysis. Standards Press of China, Beijing, 111-113.
Ikenebomeh, M. J., 1989. The influence of salt and temperature on the natural fermentation of African locust bean. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 8: 133–139.
Jensen, B. B., and Mikkelsen, L. L., 1998. Feeding liquid diets to pigs. In: Recent Advances in Animal Nutrition. Nottingham University Press, Nottingham, 107–126.
Jia, X. F., Li, A. K., Yao, J. H., Zhang, X. L., Zhou, N. J., Hao, S. H., and Pan, L., 2009. Effect of solid-state fermentation on gossypol detoxification and protein degradation in cottonseed meal. Journal of Northwest A&F University, 37 (3): 49–54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y. G., Xue, T. S., Zou, A. G., Liao, M. J., Zhang, Z., Zhu, J. X., Chen, G. P., Mai, K. S., and Zhang, W. B., 2012. The production and feeding experiment of fermented feed in pond cultuer system of sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 33 (1): 66–71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Kim, J. H., Heo, K. N., Odle, J., Han, K., and Harrell, R. J., 2001. Liquid diets accelerate the growth of early-weaned pigs and the effects are maintained to market weight. Journal of Animal Science, 79 (2): 427–434.
Kobashi, Y., Ohmori, H., Tajima, K., Kawashima, T., and Uchiyama, H., 2008. Reduction of chlortetracycline-resistant Escherichia coli in weaned piglets fed fermented liquid feed. Anaerobe, 14 (4): 201–204.
Li, W. J., Ni, Y. Z., Huang, H. K., Wang, X. M., Zhang, B. Z., and Niu, X. S., 2003. A preliminary studies of micro-ecological agents on ecological livestock husbandry. Journal of China Agricultural University, 8 (Supp.): 85–92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J., Zhang, H., Wang, L., and Guo, X. N., 2010. Screening of producing high protein feedstuff strains by solid state fermentation of peanut meal. China Oils and Fats, 35 (6): 16–18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, T. X., Liu, Y. Q., and Ma, J. L., 2009. Study on fermentation of corn straw powder with multi-strains in feed production of proteins. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 30 (9): 36–38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Li, Z., Han, M. M., Xu, Q. F., Han, J. G., Yu, Z., and Bai, C. S., 2011. Effects of moisture content and additives on the quality of Agropyron elongatum silage. Acta Prataculture Sinica, 20 (6): 203–207 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, Y., Dong, S. L., Tian, X. L., Wang, F., and Gao, Q. F., 2010. The effect of different macroalgae on the growth of sea cucumbers (Apostichopus japonicus Selenka). Aquaculture Research, 41: e881–e885.
Lu, B. S., Li, X. S., Wang, F. Y., and Li, L. L., 2007. Production of feed protein by Candida mycoderma on Daqu waste lees. China Brewing, 4 (169): 35–37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo, Y. Q., Zhang, H., Xu, Y., Huang, Z. B., and Chu, J. S., 2011. Improvement of fiber palatability of bean curd residue mixed with apple marc by solid state fermentation. Transactions of the CSAE, 27 (Supp.1): 407–412 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo, Z., Liu, Y. J., Mai, K. S., Tian, L. X., Liu, D. H., and Tan, X. Y., 2004. Partial replacement of fish meal by soybean protein in diets for grouper Epinephelus coioides juveniles. Journal of Fisheries of China, 28 (2): 175–181.
Lv, W. L., Diao, Q. Y., and Yan, G. L., 2011. Effect of Lactobacillus buchneri on the quality and aerobic stability of green corn-stalk silages. Acta Prataculture Sinica, 20 (3): 143–148 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mo, C. W., and Huang, G., 2007. Production of fermented soybean meal by solid state fermentation. China Oils and Fats, 32 (7): 38–40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
MOAC (Ministry of Agriculture, China), 2012. China Fisheries Yearbook. China agriculture Publisher, Bejing, 29-56.
Moriarty, D. J. W., 1982. Feeding of Holothuria atra and Sticopus chloronotus on bacteria, organic carbon and organic nitrogen in sediments of the Great Barrier Reef. Australian Journal of Marine & Freshwater Research, 33 (2): 255–263.
Okorie, O. E., Ko, S. H., Go, S., Lee, S., Bea, J. Y., Han, K., and Bal, S. C., 2008. Preliminary study of the optimum dietary ascorbic acid level in sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicas (Selenka). Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 39: 758–765.
Öner, M. D., Tekin, A. R., and Erdem, T., 1993. The use of soybean in the traditional fermented food–Tarhana. Food Science and Technology (Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und-Technologie), 26 (4): 371–372.
Omafuvbe, B. O., Abiose, S. H., and Shonukan, O. O., 2002. Fermentation of soybean (Glycine max) for soy-daddawa production by starter cultures of Bacillus. Food Microbiology, 19: 561–566.
Seo, J. Y., Shin, I. S., and Lee, S. M., 2011. Effect of dietary inclusion of various plant ingredients as an alternative for Sargassum thunbergii on growth and body composition of juvenile sea cucumber Aspostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture Nutrition, 17 (5): 549–556, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2095.2010.00849.x.
Sun, H. L., Liang, M. Q., Yan, J. P., and Chen, B. J., 2004. Nutrient requirements and growth of the sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. In: Advances in Sea Cucumber Aquaculture and Management. FAO, Rome, 327–331.
Tamang, J. P., and Nikkuni, S., 1996. Selection of starter cultures for the production of kinema a fermented soybean food of the Himalaya. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 12: 629–635.
Uthicke, S., 2004. Overfishing of holothurians: Lessons from the Great Barrier Reef. In: Advances in Sea Cucumber Aquaculture and Management. FAO, Rome, 163–171.
Wang, C. S., and Lin, J. Y., 1998. A nutritional fermented feed by using waste yeast from beer brewery. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 17 (supp.): 79–83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, P. Y., Wang, H. Y., Duan, W. J., Lu, X. F., and Cui, S. N., 2011. The study and application of Saccharomyces cerevisiae source feed additives. Feed Industry Magazine, 32 (2): 30–35.
Wang, X. X., Yi, Z. H., Ji, C., Ma, Q. G., and Chen, X. D., 2006. Effects of fructo-oligosaccharide and Bacillus subtilis on intestinal microflora, fecal emission of ammonia and sulfureted hydrogen and nutrient availability in broilers. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 37 (4): 337–341 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, Y. G., Fang, B., Zhang, C. Y., and Rong, X. J., 2006. Etiology of skin ulcer syndrome in cultured juveniles of Apostichopus japonicus and analysis of reservoir of the pathogens. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 13 (4): 610–616 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, Y. G., Rong, X. J., Zhang, C. Y., and Sun, S. F., 2005. Main diseases of cultured Apostichopus japonicus: Prevention and treatment. Marine Sciences, 29 (3): 1–7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, N., Wang, W., Lin, S. C., Chen, X. P., and Zhang, W. J., 1992. The research of amino acid fermentation by yeast. Amino Acid Magazine, 4:10–16.
Yang, X., Xue, Y. L., and Li, L., 2011. Improvement of nutritional value of bran fermented by multi-strains in solid-state fermentation. China Brewing, 3: 113–115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yingst, J. Y., 1976. The utilization of organic matter in shallow marine sediments by an epibenthic deposit-feeding holothurian. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 23 (1): 55–69.
Yuan, C. Y., 2005. Current status and development of feed in sea cucumber. Fisheries Science, 24 (12): 54–56 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan, X. T., Yang, H. S., Zhou, Y., Mao, Y., Zhang, T., and Liu, Y., 2006. The influence of diets containing dried bivalve feces and/or powdered algae on growth and energy distribution in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Aquaculture, 256: 457–467.
Yun, J. M., Liu, L. S., An, Z. G., Su, Y. S., and Guo, B., 2010. Technology of single cell protein feed production from raw potato starch residue by multi-strains solid fermentation. Transactions of the CSAE, 26 (Supp.2): 399–404 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, B. L., Sun, D. Y., and Wu, Y. Q., 1995. Preliminary analysis on the feeding habit of Apostichopus japonicus in the rocky coast waters off Lingshan Island. Marine Sciences, 3: 11–13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, H., and Chu, X. N., 1996. The study of transformation ability of nonprotein nitrogen by solid fermented forage yeast. Feed Industry Magazine, 17 (2): 17–19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, J., Feng, X. Y., Liu, X. B., Xie, G., Fang, Q., and Luo, H., 2011. Process optimization of brewers’grains fermentation using photosynthetic bacteria to make fish feed. Transactions of the CSAE, 27 (8): 387–392 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, S. Z., Zhou, Z. M., and Meng, Q. X., 2007. Effects of different biology additives on the fermentation quality and digestibility of whole corn silage in vitro. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 43 (1): 53–56 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou, F. Z., Xie, B. E., Jia, Y. L., and Wang, H. Y., 2007. Analysis of ferment bean meal using probiotics and its produce. Feed Industry, 28 (6): 35–37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu, J., Liu, H., Leng, K., Wang, S., Xue, Z., and Sun, Y., 2007. Studies on the effects of some common diets on the growth of Apostichopus japonicus. Marine Fisheries Research, 25: 48–53 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang, Y. F, Zhang, W. C., Chen, X. Z., Luo, T. Y., and Lin, B. F., 2006. Effect on the quality of fermented fungus chaff feed supplied by green ferment juice and cellulose. Journal of Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities, 21 (6): 653–655 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y., Mai, K. et al. Effects of different microbes on fermenting feed for sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus). J. Ocean Univ. China 14, 873–880 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2591-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2591-3