Abstract
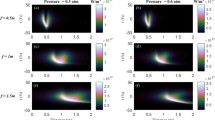
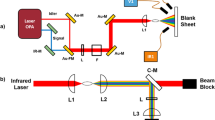
Transmission of intense femtosecond laser pulses in air is accompanied by energy depletion. By measuring the transmitted spectra of the focused femtosecond pulses in air, we study the influence of air pressure and initial pulse energy on the spectra around the central wavelength (800 nm) after the interaction of the focused femtosecond laser with air. On this basis, the energy transmittance of the central wavelength of the femtosecond pulses is obtained. It is found that as the air pressure is lower than 1 kPa, the transmitted spectra of focused femtosecond pulses change with the pressure, but there is almost no energy depletion, while as the air pressure is higher than 1 kPa, femtosecond filamentation occurs and the energy transmittance of the central wavelength of the femtosecond pulses decreases with the increase of air pressure and pulse energy. According to the different regimes (i.e., nonfilamentation, and filamentation regimes), we discuss the effect of energy conversion and transfer on the energy transmittance. This work can help to understand the energy depletion during the transmission of ultrashort intense laser pulses in air and provide a guidance for the practical applications of femtosecond filamentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
COUAIRON A, MYSYROWICZ A. Femtosecond filamentation in transparent media[J]. Physics reports, 2007, 441(2–4): 47–189.
DURAND M, HOUARD A, PRADE B, et al. Kilometer range filamentation[J]. Optics express, 2013, 21(22): 26836–26845.
RODRIGUEZ R, BOURAYOU R, MÉJEAN G, et al. Kilometric-range nonlinear propagation of femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Physical review E, 2004, 69(3): 036607.
DICAIRE I, JUKNA V, PRAZ C, et al. Spaceborne laser filamentation for atmospheric remote sensing[J]. Laser & photonics reviews, 2016, 10(3): 481–493.
XU H, CHENG Y, CHIN S L, et al. Femtosecond laser ionization and fragmentation of molecules for environmental sensing[J]. Laser & photonics reviews, 2015, 9(3): 275–293.
HOUARD A, WALCH P, PRODUIT T, et al. Laser-guided lighting[J]. Nature photonics, 2023: 1–5.
KOSAREVA O G, MOKROUSOVA D V, PANOV N A, et al. Remote triggering of air-gap discharge by a femtosecond laser filament and postfilament at distances up to 80 m[J]. Applied physics letters, 2021, 119(4): 041103.
ROHWETTER P, KASPARIAN J, STELMASZCZYK K, et al. Laser-induced water condensation in air[J]. Nature photonics, 2010, 4(7): 451–456.
RAN L, DENG Z Z, JU J J, et al. Femtosecond filamentation induced particles and their cloud condensation nuclei activity[J]. Atmospheric environment, 2019, 206: 271–279.
SU Y, WANG S, YAO D, et al. Stand-off fabrication of irregularly shaped, multi-functional hydrophobic and antireflective metal surfaces using femtosecond laser filaments in air[J]. Applied surface science, 2019, 494: 1007–1012.
LIAO K, WANG W, MEI X, et al. Fabrication of millimeter-scale deep microchannels in fused silica by femtosecond filamentation effect[J]. Optics and laser technology, 2021, 142: 107201.
QUINN M N, JUKNA V, EBISUZAKI T, et al. Space-based application of the CAN laser to LIDAR and orbital debris remediation[J]. The European physical journal special topics, 2015, 224(13): 2645–2655.
SCHELLER M, MILLS M S, MIRI M A, et al. Externally refuelled optical filaments[J]. Nature photonics, 2014, 8(4): 297–301.
FENG Z F, LAN J, LI W, et al. A long-distance two-color filament produced by three collinear femtosecond pulses in air[J]. Optics communications, 2020, 474: 126167.
LI S, SUI L, LI S, et al. Filamentation induced by collinear femtosecond double pulses with different wavelengths in air[J]. Physics of plasmas, 2015, 22(9): 093113.
BODROV S, ALEKSANDROV N, TSAREV M, et al. Effect of an electric field on air filament decay at the trail of an intense femtosecond laser pulse[J]. Physical review E, 2013, 87(5): 053101.
SHUMAKOVA V, ALIŠAUSKAS S, MALEVICH P, et al. Chirp-controlled filamentation and formation of light bullets in the mid-IR[J]. Optics letters, 2019, 44(9): 2173–2176.
ZHANG H, ZHANG Y, LIN S, et al. Influence of pressure on spectral broadening of femtosecond laser pulses in air[J]. Physics of plasmas, 2021, 28(4): 043302.
MÉCHAIN G, OLIVIER T, FRANCO M, et al. Femtosecond filamentation in air at low pressures. Part II: laboratory experiments[J]. Optics communications, 2006, 261(2): 322–326.
ZHOKHOV P A, ZHELTIKOV A M. Scaling laws for laser-induced filamentation[J]. Physical review A, 2014, 89(4): 043816.
LIN S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Femtosecond laser-induced nitrogen fluorescence emission at different air pressures[J]. Physics of plasmas, 2021, 28(7): 073302.
LI S Y, GUO F M, SONG Y, et al. Influence of group-velocity-dispersion effects on the propagation of femtosecond laser pulses in air at different pressures[J]. Physical review A, 2014, 89(2): 023809.
TALEBPOUR A, ABDEL-FATTAH M, BANDRAUK A D, et al. Spectroscopy of the gases interacting with intense femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Laser physics, 2001, 11(1): 68–76.
MITRYUKOVSKIY S, LIU Y, DING P, et al. Plasma luminescence from femtosecond filaments in air: evidence for impact excitation with circularly polarized light pulses[J]. Physical review letters, 2015, 114(6): 063003.
POPMINTCHEV T, CHEN M C, POPMINTCHEV D, et al. Bright coherent ultrahigh harmonics in the keV X-ray regime from mid-infrared femtosecond lasers[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6086): 1287–1291.
AHMMED K M T, GRAMBOW C, KIETZIG A M. Fabrication of micro/nano structures on metals by femtosecond laser micromachining[J]. Micromachines, 2014, 5(4): 1219–1253.
SOLLAPUR R, KARTASHOV D, ZÜRCH M, et al. Resonance-enhanced multi-octave supercontinuum generation in antiresonant hollow-core fibers[J]. Light-science & applications, 2017, 6(12): e17124.
HEYL C M, COUDERT-ALTEIRAC H, MIRANDA M, et al. Scale-invariant nonlinear optics in gases[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(1): 75–81.
KOSAREVA O G, LIU W, PANOV N A, et al. Can we reach very high intensity in air with femtosecond pW laser pulses?[J]. Laser physics, 19: 1776–1792.
TALEBPOUR A, YANG J, CHIN S L. Semi-empirical model for the rate of tunnel ionization of N2 and O2 molecule in an intense Ti: sapphire laser pulse[J]. Optics communications, 1999, 163(1–3): 29–32.
ARNOLD B R, ROBERSON S D, PELLEGRINO P M. Excited state dynamics of nitrogen reactive intermediates at the threshold of laser induced filamentation[J]. Chemical physics, 2012, 405: 9–15.
XU H L, AZARM A, BERNHARDT J, et al. The mechanism of nitrogen fluorescence inside a femtosecond laser filament in air[J]. Chemical physics, 2009, 360(1–3): 171–175.
KELDYSH L V. Ionization in the field of a strong electromagnetic wave[J]. Soviet physics JETP, 1965, 20(5): 1307–1314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.11704145 and 11974138).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Yu, M., Cai, X. et al. Energy transmittance of focused femtosecond pulses at different air pressures. Optoelectron. Lett. 19, 605–613 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-023-3037-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-023-3037-6