Abstract
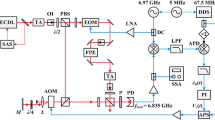
Microwave-to-optical phase synchronization techniques have attracted growing research interests in recent years. Here, we demonstrate tight, real-time phase synchronization of an optical frequency comb to a rubidium atomic clock. A detailed mathematical model of the phase locking system is developed to optimize its built-in parameters. Based on the model, we fabricate a phase locking circuit with high integration. Once synchronized, the fractional frequency instability of the repetition rate agrees to 6.35×10−12 at 1 s and the standard deviation is 1.5 mHz, which indicates the phase synchronization system can implement high-precision stabilization. This integrated stable laser comb should enable a wide range of applications beyond the laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trocha P, Karpov M, Ganin D, Pfeiffer MHP, Kordts A, Wolf S, Krockenberger J, Marin-Palomo P, Weimann C, Randel S, Freude W, Kippenberg TJ and Koos C, Science 359, 887 (2018).
Wang Guo-chao, Tan Li-long and Yan Shu-hua, Sensors 18, 500 (2018).
Coddington I, Swann W C, Nenadovic L and Newbury N R, Nature Photonics 3, 351 (2009).
Oliver Kliebisch, Dirk C. Heinecke, Stefano Barbieri, Giorgio Santarelli, Hua Li, Carlo Sirtori and Thomas Dekorsy, Optica 5, 1431 (2018).
Chen Xing, Shang Jian-ming, Wang Dong-xing, Ci Cheng, Zhang Wan-peng, Liu Bo, Wu Hong, Yu Song and Zhang Zhi-gang, CLEO: Applications and Technology, Optical Society of America, JW2A.152 (2018).
Kwangyun Jung, Junho Shin, Jinho Kang, Stephan Hunziker, Chang-Ki Min and Jungwon Kim, Optics Letters 39, 1577 (2014).
CI Cheng, Wu Hong, Tang Ran, Liu Bo, Chen Xing, Zhang Xue-song, Zhang Yu and Zhao Ying-xin, Optoelectronics Letters 14, 109 (2018).
Ronald Holzwarth, Rafael A. Probst, Tilo Steinmetz, Yuanje Wu, Thomas Udem and Theodor W. Hänsch, CLEO: Science and Innovations, Optical Society of America, STh4H.3 (2016).
E. Obrzud, M. Rainer, A. Harutyunyan, M.H. Anderson, J. Liu, M. Geiselmann, B. Chazelas, S. Kundermann, S. Lecomte, M. Cecconi and A. Ghedina, 2018 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), IEEE (2018).
Cundiff, Steven T. and Jun Ye, Journal of Modern Optics 52, 201 (2005).
Micalizio S, Godone A, Calosso C, Levi F, Affolderbach C and Gruet F, IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics & Frequency Control 59, 457 (2012).
Brian R. Washburn, Scott A. Diddams, Nathan R. Newbury, Jeffrey W. Nicholson, Man F. Yan and Carsten G. Jørgensen, Optics Letters 29, 250 (2004).
Hou Dong, Ning Bo, Li Peng, Zhang Zhi-gang and Zhao Jian-ye, IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 47, 891 (2011).
Hou Dong, Wu Jiu-tao, Ren Quan-sheng and Zhao Jian-ye, IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 48, 839 (2012).
Kwangyun Jung, Junho Shin and Jungwon Kim, IEEE Photonics Journal 5, 5500906 (2013).
Hanumolu P. K., Brownlee M., Mayaram K. and Moon, IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems I Regular Papers 51, 1665 (2004).
R. E. Best, McGraw-Hill Education, 2007.
X. Shan and D. M. Spirit, Electronics Letters 29, 979 (1993).
Richard G. Wiley, IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 26, 38 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.61571244 and 61871239), and the Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (No.18YFZCGX00480).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Wp., Wu, H., Zhou, Wf. et al. Study on ultra-precision phase synchronization technique employing phase-locked loop. Optoelectron. Lett. 17, 134–139 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-021-0036-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-021-0036-3