Abstract
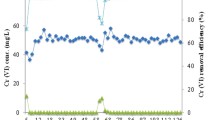
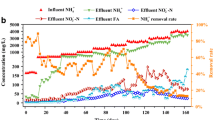
In this study, the effects of organic sulfur on anaerobic biological processes were investigated by operating two up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors with sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) as a representative of organic sulfur. The results indicated that the specific methanogenic activity (SMA) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency of R2 (with SDBS added) were higher than those of R1 (without SDBS) when the COD/SO42− ratio was above 5.0. However, when the COD/SO42− ratio was lower than 5.0, the sulfate reduction efficiency of R2 was higher than that of R1. These results and the observed SDBS transformation efficiency in anaerobic reactors indicate that low concentrations of SDBS accelerate methane production and the continuous accumulation of SDBS does not weaken the reduction of sulfate. Similarly, the calculated electron flux for a COD/SO42− ratio of 1.0 indicates that the utilization intensity of electrons by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in R2 was 36.48% higher than that of SRB in R1 and exceeded that of methane-producing archaea (MPA) under identical working conditions. Moreover, the addition of SDBS in R2 made sulfidogenesis the dominant reaction at low COD/SO42−, and Methanobacterium and Methanobrevibacter with H2/CO2 as the substrate and Desulfomicrobium were the dominant MPA and SRB, respectively. However, methanogenesis was still the dominant reaction in R1, and Methanosaeta with acetic acid as the substrate and Desulfovibrio were the dominant MPA and SRB, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Water Works Association/American Public Works Association/Water Environment Federation, 21st ed. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association
Carosia M F, Okada D Y, Sakamoto I K, Silva E L, Varesche M B A (2014). Microbial characterization and degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate in an anaerobic reactor treating wastewater containing soap powder. Bioresource Technology, 167: 316–323
Chen Y, He S, Zhou M, Pan T, Xu Y, Gao Y, Wang H (2018). Feasibility assessment of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket treatment of sulfamethoxazole pharmaceutical wastewater. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 12(5): 13
de Oliveira L L, Costa R B, Okada D Y, Vich D V, Duarte I C S, Silva E L, Varesche M B A (2010). Anaerobic degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) in fluidized bed reactor by microbial consortia in different support materials. Bioresource Technology, 101(14): 5112–5122
de Oliveira L L, Duarte I C S, Sakamoto I K, Varesche M B A (2009). Influence of support material on the immobilization of biomass for the degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate in anaerobic reactors. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(2): 1261–1268
Denger K, Cook A M (1999). Note: Linear alkylbenzenesulphonate (LAS) bioavailable to anaerobic bacteria as a source of sulphur. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 86(1): 165–168
Denger K, Kertesz M A, Vock E H, Schon R, Magli A, Cook A M (1996). Anaerobic desulfonation of 4-tolylsulfonate and 2-(4-sulfophenyl) butyrate by a Clostridium sp. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62(5): 1526–1530
Dojka M A, Hugenholtz P, Haack S K, Pace N R (1998). Microbial diversity in a hydrocarbon- and chlorinated-solvent-contaminated aquifer undergoing intrinsic bioremediation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64(10): 3869–3877
Garcia M T, Campos E, Dalmau M, Illan P, Sanchez-Leal J (2006). Inhibition of biogas production by alkyl benzene sulfonates (LAS) in a screening test for anaerobic biodegradability. Biodegradation, 17(1): 39–46
Hu Y, Jing Z, Sudo Y, Niu Q, Du J, Wu J, Li Y Y (2015). Effect of influent COD/SO42− ratios on UASB treatment of a synthetic sulfate-containing wastewater. Chemosphere, 130: 24–33
Jing Z Q, Hu Y, Niu Q G, Liu Y Y, Li Y Y, Wang X C C (2013). UASB performance and electron competition between methane-producing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria in treating sulfate-rich waste-water containing ethanol and acetate. Bioresource Technology, 137: 349–357
Khalil E F, Whitmore T N, Gamal-El-Din H, El-Bassel A, Lloyd D (1988). The effects of detergents on anaerobic digestion. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29(5): 517–522
Khalil E F, Whitmore T N, Gamel-El-Din H, El-Bassel A, Lloyd D (1989). The effect of detergent on methanogenesis by Methanosarcina barkeri. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 57(3): 313–316
Li W, Niu Q, Zhang H, Tian Z, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Li Y Y, Nishimura O, Yang M (2015). UASB treatment of chemical synthesis-based pharmaceutical wastewater containing rich organic sulfur compounds and sulfate and associated microbial characteristics. Chemical Engineering Journal, 260: 55–63
Lu X, Zhen G, Chen M, Kubota K, Li Y Y (2015). Biocatalysis conversion of methanol to methane in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor: Long-term performance and inherent deficiencies. Bioresource Technology, 198: 691–700
Lu X Q, Ni J L, Zhen G Y, Kubota K, Li Y Y (2018). Response of morphology and microbial community structure of granules to influent COD/SO42− ratios in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating starch wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 256: 456–465
Lu X Q, Zhen G Y, Ni J L, Hojo T, Kubota K, Li Y Y (2016). Effect of influent COD/SO42− ratios on biodegradation behaviors of starch wastewater in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Bioresource Technology, 214: 175–183
Lu X Q, Zhen G Y, Ni J L, Kubota K, Li Y Y (2017). Sulfidogenesis process to strengthen re-granulation for biodegradation of methanolic wastewater and microorganisms evolution in an UASB reactor. Water Research, 108: 137–150
MacLeod F A, Guiot S R, Costerton J W (1990). Layered structure of bacterial aggregates produced in an upflow anaerobic sludge bed and filter reactor. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56(6): 1598–1607
Mayer A S, Zhong L, Pope G A (1999). Measurement of mass-transfer rates for surfactant-enhanced solubilization of nonaqueous phase liquids. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(17): 2965–2972
McEvoy J, Giger W J N (1985). Accumulation of linear alkylbenzene-sulphonate surfactants in sewage sludges. Naturwissenschaften, 72(8): 429–431
Mogensen A S, Haagensen F, Ahring B K (2003). Anaerobic degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(4): 706–711
O’Flaherty V, Mahony T, O’Kennedy R, Colleran E (1998). Effect of pH on growth kinetics and sulphide toxicity thresholds of a range of methanogenic, syntrophic and sulphate-reducing bacteria. Process Biochemistry, 33(5): 555–569
Pan X, Sun J, Zhang Y, Zhu G (2020). Effect of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) on the performance of anaerobic co-digestion with sewage sludge, food waste, and green waste. Chemical Engineering Communications, 207(2): 242–252
Paulo P L, Vallero M V G, Trevino R H M, Lettinga G, Lens P N L (2004). Thermophilic (55°C) conversion of methanol in methanogenic-UASB reactors: Influence of sulphate on methanol degradation and competition. Journal of Biotechnology, 111(1): 79–88
Perez-Armendariz B, Moreno Y M, Monroy-Hermosillo O, Guyot J P, Gonzalez R O (2010). Anaerobic biodegradability and inhibitory effects of some anionic and cationic surfactants. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 85(3): 269–273
Rezende Silva A F, Magalhaes N C, Martinelli Cunha P V, Santos Amaral M C, Koch K (2020). Influence of COD/SO42− ratio on vinasse treatment performance by two-stage anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Journal of Environmental Management, 259:110034
Sanz J L, Culubret E, Ferrer J D, Moreno A, Berna J L (2003). Anaerobic biodegradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Biodegradation, 14(1): 57–64
Schmidt J E, Ahring B K (1993). Effects of hydrogen and formate on the degradation of propionate and butyrate in thermophilic granules from an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59(8): 2546–2551
Smith K S, Ingram-Smith C (2007). Methanosaeta, the forgotten methanogen? Trends in Microbiology, 15(4): 150–155
Tanimoto Y, Tasaki M, Okamura K, Yamaguchi M, Minami K (1989). Screening growth inhibitors of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their effects on methane fermentation. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 68(5): 353–359
Van Leerdam R C, de Bok F A M, Bonilla-Salinas M, Van Doesburg W, Lomans B P, Lens P N L, Stams A J M, Janssen A J H (2008). Methanethiol degradation in anaerobic bioreactors at elevated pH (⩾8): Reactor performance and microbial community analysis. Bioresource Technology, 99(18): 8967–8973
Vilela R S, Damianovic M H R Z, Foresti E (2014). Removing organic matter from sulfate-rich wastewater via sulfidogenic and methanogenic pathways. Water Science and Technology, 69(8): 1669–1675
Yang W, He S, Han M, Wang B, Niu Q, Xu Y, Chen Y, Wang H (2018). Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure in the start-up and substrate inhibition stages of an anammox reactor. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 126(1): 88–95
Zhang L, Ban Q, Li J, Jha A K (2016). Response of syntrophic propionate degradation to pH decrease and microbial community shifts in an UASB reactor. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26(8): 1409–1419
Zhang P, Chen Y, Huang T Y, Zhou Q (2009). Waste activated sludge hydrolysis and short-chain fatty acids accumulation in the presence of SDBS in semi-continuous flow reactors: effect of solids retention time and temperature. Chemical Engineering Journal, 148(2–3): 348–353
Zhang P, Chen Y, Zhou Q (2010). Effect of surfactant on hydrolysis products accumulation and short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) production during mesophilic and thermophilic fermentation of waste activated sludge: Kinetic studies. Bioresource Technology, 101(18): 6902–6909
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019XKQYMS78) for the support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• UASB reactor can work efficiently with high COD/SO42− ratios when SDBS exists.
• Outcome of the competition between SRB and MPA was affected by SDBS.
• Presence of SDBS makes methanogens with H2/CO2 as a substrate dominant.
• Microbial diversity decreases in the presence of SDBS.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Zhou, M., He, S. et al. Deciphering the effect of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate on up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket treatment of synthetic sulfate-containing wastewater. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 15, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1385-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1385-z