Abstract
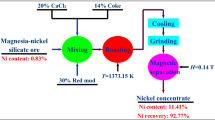
Process mineralogy of low-grade laterite nickel ore in Indonesia was systematically characterized and the beneficiation process of mineral components such as limonite, serpentine and chromite was studied on the basis of process mineralogy. The results show that the low-grade laterite nickel ore is a typical weathering sedimentary metamorphic oxidized ore, with the main valuable elements of Ni, Co and Cr and the main mineral components of limonite, serpentine, chromite, etc. There is no independent carrier mineral of Ni and Co in the raw ore, and the occurrence states of Ni and Co are relatively dispersed. For the limonite in laterite nickel mine, the nickel bearing magnetite concentrate with nickel grade of 1.98% and recovery rate of 88.42% can be obtained by reduction roasting magnetic separation process. For the serpentine in laterite nickel mine, the cobalt bearing concentrate with Co grade of 0.17% and recovery rate of 23.17% can be obtained by positive and reverse flotation process. A chromium concentrate containing 35.17% Cr2O3 and a recovery of 33.42% can be obtained by using the combined process of coarse and fine classification and gravity and magnetic.
摘要
对印尼低品位红土镍矿进行了系统的工艺矿物学表征, 并在工艺矿物学表征的基础上对褐铁 矿、蛇纹石和铬铁矿等矿物组分进行可选性研究. 结果表明, 该低品位红土镍矿属于典型的风化沉积 变质型氧化矿, 主要有价成分为Ni、Co 和Cr, 主要矿物组成为褐铁矿、蛇纹石、铬铁矿等, 未见有 Ni 和Co的独立载体矿物. Ni 和Co赋存状态较为分散, 通过选矿方法来富集Ni 和Co难度较大; Cr 则 主要赋存于铬铁矿中, 可以通过选矿方法来富集Cr; 高温可以促进褐铁矿向磁铁矿的转变. 针对红土 镍矿中的褐铁矿采用还原焙烧磁选工艺可以获得含镍品位1.98%, 回收率88.42%的含镍磁选精矿; 针 对红土镍矿中的蛇纹石采用先正后反的浮选工艺可获得含钴品位0.17%, 回收率为23.17%的含钴精 矿; 针对红土镍矿中的铬铁矿采用粗细分级-重磁联合工艺可获得含Cr2O3品位为35.17%、回收率为 33.42%的铬精矿.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SRINIVASAN S, KALE C, HORNBUCKLE B C, DARLING K A, PERALTA P, SOLANKI K N. Thermomechanical response of an ultrafine-grained nickel-yttrium alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2020, 187: 434–438. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.06.068.
YUAN S D, YANG C X, JIANG G D, XIONG J, AI Q, HUANG R Z. Research progress in nickel-rich ternary materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2019, 47(10): 1–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.001301.
GUSEV V Y, BAIGACHEVA E V, GOGOLISHVILI V O. Azo derivatives of pyrocatechol, resorcinol, and salicylic acid as collectors for sulfide ore flotation [J]. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2019, 92(12): 1734–1744. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427219120150.
MUDD G M. Global trends and environmental issues in nickel mining: sulfides versus laterites [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2010, 38(1, 2): 9–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.05.003.
KIRJAVAINEN V, HEISKANEN K. Some factors that affect beneficiation of sulphide nickel - copper ores [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(7): 629–633. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2007.01.001.
CIFTCI H, ATIK S, GURBUZ F. Biocatalytic and chemical leaching of a low-grade nickel laterite ore [J]. Metallurgical Research & amp; Technology, 2018, 115(3): 305. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2018006.
ALKHIRBASH S A. Mineralogical characterization of low-grade nickel laterites from the North Oman Mountains: Using mineral liberation analyses - scanning electron microscopy-based automated quantitative mineralogy [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103429. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103429.
ZHANG H, NGUYEN H, BUI X N, TRUNG N T, BUI T T, NGUYEN N, VU D A, MAHESH V, MOAYEDI H. Developing a novel artificial intelligence model to estimate the capital cost of mining projects using deep neural network-based ant colony optimization algorithm [J]. Resource Policy, 2020, 66: 101604. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101604.
ZHANG Y Y, QIE J M, WANG X F, CUI K K, FU T, WANG J, QI Y H. Mineralogical characteristics of the nickel laterite, southeast Ophiolite belt, Sulawesi island, Indonesia [J]. Mining Metallurgy & amp; Exploration, 2020, 37(1): 79–91. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-019-00147-y.
FARROKHPAY S, FILIPPOV L. Challenges in processing nickel laterite ores by flotation [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 151: 29–67. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2016.04.007.
BRODSKAYA R L, MARIN Y B. Ontogenic analysis of mineral individuals at micro and nanolevel for the restoration of ore-forming conditions and assessment of minerals processing properties [J]. Journal of Mining Institute, 2016, 219: 369–376. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18454/PMJ.2010.3.369.
ZHU D Q, CUI Y, HAPUGODA S, VINING K, PAN J. Mineralogy and crystal chemistry of a low grade nickel laterite ore [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 907–916. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61264-8.
RUBISOV D H, KROWINKEL J M, PAPANGELAKIS V G. Sulphuric acid pressure leaching of laterites-universal kinetics of nickel dissolution for limonites and limonitic/saprolitic blends [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 58(1): 1–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00094-3.
WANG B Q, GUO Q, WEI G Y, ZHANG P Y, QU J K, QI T. Characterization and atmospheric hydrochloric acid leaching of a limonitic laterite from Indonesia [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 129: 7–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.06.017.
XU C L, ZHONG C B, LYU R L, RUAN Y Y, ZHANG Z Y, CHI R A. Process mineralogy of Weishan rare earth ore by MLA [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 37(3): 334–338. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.06.008.
FAN R, GERSON A R. Mineralogical characterisation of Indonesian laterites prior to and post atmospheric leaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 134: 102–109. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.02.004.
BASILE A, HUGHES J, MCFARLANE A J, BHARGAVA S K. Development of a model for serpentine quantification in nickel laterite minerals by infrared spectroscopy [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2009, 23(5): 407–412. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2009.11.018.
MURTHY Y R, TRIPATHY S K, KUMAR C R. Chrome ore beneficiation challenges & amp; opportunities—A review [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(5): 375–380. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2010.12.001.
KHASSEN B, BALTYNOVA N, DAKHNO L. Investigation of dephosphorization of brown iron ore concentrates by sintering and magnetic beneficiation [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014, 126: 136–140. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2013.11.013.
LI G H, SHI T M, RAO M J J, JIANG T, ZHANG Y B. Beneficiation of nickeliferous laterite by reduction roasting in the presence of sodium sulfate [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 32: 19–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.03.012.
FARROKHPAY S, FILIPPOV L, FORNASIERO D. Preconcentration of nickel in laterite ores using physical separation methods [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 141: 105892. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.105892.
LIU D Z, ZHANG G F, HUANG G H, GAO Y W, WANG M T. The flotation separation of pyrite from serpentine using lemon yellow as selective depressant [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2019, 581: 123823. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123823.
GALLIOS G P, DEHYANNI E A, PELEKA E N, MATIS K A. Flotation of chromite and serpentine [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2007, 55(2): 232–237. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.12.015.
ZHAO W J, LIU D W, FENG Q C. Enhancement of salicylhydroxamic acid adsorption by Pb(II) modified hemimorphite surfaces and its effect on floatability [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 152: 106373. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106373.
HAN G, WEN S M, WANG H, FENG Q C. Selective adsorption mechanism of salicylic acid on pyrite surfaces and its application in flotation separation of chalcopyrite from pyrite [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 240: 116650. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116650.
GULSOY O Y, GULCAN E. A new method for gravity separation: Vibrating table gravity concentrator [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 211: 124–134. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.09.074.
TRIPATHY S K, MURTHY Y R, SINGH V, SURESH N. Processing of ferruginous chromite ore by dry high-intensity magnetic separation [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2016, 37(3): 196–210. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2016.1168418.
TRIPATHY S K, MURTHY Y R, SINGH V. Characterisation and separation studies of Indian chromite beneficiation plant tailing [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 122: 47–53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2013.04.008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Project(2019M653082) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project(BGRIMM-KJSKL-2020-02) supported by the Found of State Key Laboratory of Mineral Processing, China
Contributors
The overarching research goals were developed by XU Peng-yun, GUO Xue-yi and LI Chuang. XU Peng-yun, LI Chuang and FANG Hao provided experimental data and analyzed the experimental data. SU Jian-fang and WANG Qiang provided project administration. XU Peng-yun, LI Chuang, YU Qi and FANG Hao edited the draft of manuscript. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Conflict of interest
XU Peng-yun, WANG Qiang, LI Chuang, YU Qi, FANG Hao, SU Jian-fang and GUO Xue-yi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Py., Wang, Q., Li, C. et al. Relationship between process mineralogical characterization and beneficiability of low-grade laterite nickel ore. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 3061–3073 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4794-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4794-7